Legal General Knowledge | Legal Reasoning for CLAT PDF Download
Introduction
Following are some of the Important Legal terms, Judgments, Constitutional, Legal Provisions & GK which are useful to lawyers and students appearing for different Law entrance tests like CLAT, LSAT, Delhi University L.LB Entrance Test, AILET etc
1. What are the Writs that can be issued by High Court and Supreme Court?
Mandamus, Habeas Corpus, Certiorari, Quo Warranto

2. Legal Advisor to the Government of a State in India
The Advocate General
3. Issues D.K. Basu v. State of West Bengal deal with
Safeguards for arrested persons
4. The age of retirement of a Judge of a High Court in India
62 Years
5. In law, the term 'neighbour' means
People who might be affected by your actions
6. Supreme Court directed the compulsory registration of all marriages in India in
Seema vs Ashwini Kumar
7. Principle applicable for the purpose of reducing multiplicity of proceedings in court
Res judicata
8. Legal phrase amicus curiae means
Friend of the Court
9. Appellate Jurisdiction: Interpretation of the constitution falls under Appellate jurisdiction.
10. Bye-Laws: Laws made by executives for administrative convenience are called Bye-Laws.
11. Supreme Court for the first time lay down that Fundamental Rights have primacy over the Directive Principles of State Policy:
Minerva Mills vs Union of India
12. Writs can be used against a person believed to be holding a public office he is not entitled to hold:
Quo Warranto
13. Statutory duty of laying down the standards of professional conduct and etiquette for advocates in India is entrusted with:
Bar Council of India
14. A person has designed a new type of automatic motor pump. Under which act can he seek protection of his invention
The Patents Act
15. Speaker can ask a member of a house to stop speaking & let another member speak: Yielding the floor.
16. Laws deal with intellectual property protection for horticultural products:
Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmers Rights Act
17. What is the limitation period (maximum time limit) for filing of a complaint before the consumer disputes redressal forum from the date when the cause of action arises?
Two years
18. Under which law a minor is incapable of entering into contract
Indian Contract Act, 1872
19. Which writ is said to be a guarantor of personal freedom?
Habeas Corpus
20. Which is the oldest High Court in India ?
High Court of Calcutta
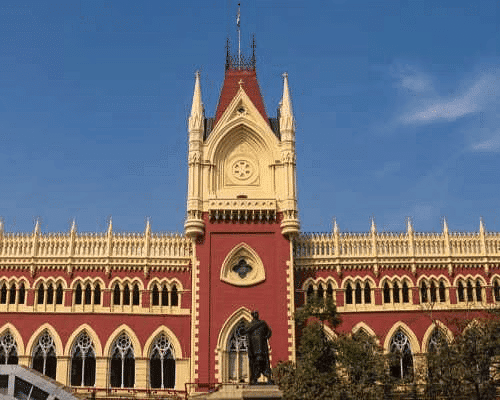 Oldest High Court in India: Calcutta 21. The power to issue writs has been envisaged under the provisions of which fundamental rights
Oldest High Court in India: Calcutta 21. The power to issue writs has been envisaged under the provisions of which fundamental rights
Right to Constitutional Remedies
22. Rule of Law means
All persons are equal in the eyes of law
23. The writ to force a public authority to perform a public or statutory duty
Mandamus
24. In which landmark judgment did the Supreme Court of India lay down guidelines against sexual harassment of women at workplace: Vishakha vs. State of Rajasthan
25. The marriage of a 15 year old girl with a 45 year old man is voidable at the option of the girl.
26. Legal Term Caveat Emptor refer to: Let the buyer beware
27: First woman judge appointed to the Supreme Court of India: Justice Smt M. Fathima Beevi
25. State which has the highest number of seats reserved for ST in Lok Sabha: Madhya Pradesh.
26. Five Year plan Concept borrowed from: USSR.
27. The act that provided for the first time for separate representation of Muslim community – Indian council act (Morley Minto Reforms) 1909.
28. Minerva Mills V. UOI – Struck down principles over Fundamental Rights
29. BCI – Statutory body of laying down the standards of professional conduct & etiquette for advocates in India.
30. MCI – Statutory body of laying down the standards of professional conduct & etiquette for Doctors in India.
31. Max. time for filing of a complaint before consumer disputes redressal forum from the date when Cause of action arises – 2 Years.
32. First English legal charter relating to Fundamental Rights of the citizens – Magna Carta.
34. 1st Woman Supreme court Judge – J. Fatima Beevi.
35. 1st Woman High court judge – J. Leela Seth.
 J. Leela Seth36. Aruna Shaunbaug V. UOI Passive euthanasia under exceptional circumstances allowed.
J. Leela Seth36. Aruna Shaunbaug V. UOI Passive euthanasia under exceptional circumstances allowed.
37. Andaman & Nicobar islands come under the jurisdiction of Calcutta High court.
38. Lakshadweep islands come under the jurisdiction of the Kerala High court.
39. Finance Secretary – Not a constitutional post.
40. CEC, CAG, Vice president of India – Constitutional posts.
41. Constitutional bench – 5 Judges.
42. Full bench – All judges in a court or Specified No. of judges fixed by Chief justice.
43. Division bench – 2 Judges.
44. Right to vote – Legal/Constitutional Right.
45. Right to Property – Legal/Statutory right.
46. 1 st Law Minister of India – Dr. B.R. Ambedkar.
47. 1 st committee on Backward classes – Kelkar commission.
48. Babri Masjid demolition case – Liberhan commission.
49. Reservation of seats for Backward classes – Mandal commission.
50. Center-states relations – Sarkaria commission (First) M.M. Punchhi Commission (Second)
51. Advocates act – 1961.
52. 1st Indian state to be formed on a Linguistic basis – Andhra Pradesh
53. First General elections took place – 1951
54. Setting a Supreme court was in Calcutta is a part of Regulating act, 1773
55. NJAC has been set up – 99th Amendment act (Collegium system restored)
56. Exchange of territories b/w India and Bangladesh – 100th amendment (w.e.f. May 2015 )
57. Anti Defection law is provided under – 10th Schedule.
58. Constituent assembly which framed the constitution for independent India was set up in 1946.
59. Original members in Constituent assembly – 389 Members.
60. Defamation – Both Tort & Crime
61. The First hour of every sitting of Parliament is known as Question Hour.
62. 1st Speaker of Lok Sabha – G.V. Mavlankar
63. 1st India Governor-General of Free India – C. Rajgopalachari
64. 1st Governor-General of India – Lord Mountbatten
65. 1st Amendment came in 1951
66. Primary education was added to 93rd Amendment.
67. Child marriage Restraint Act, 2006 is applicable to all, irrespective of religions
68. Manager of Wakf is known as – Mutawalli.
69. A witness who is unable to speak gives his evidence by writing in open court – Oral evidence.
70. 1st Chairman of NHRC – J. Ranganath Mishra.
71. Ossification test is done to determine the age.
72. Sedition is the crime of arousing hatred or contempt against GOI 60. An act done under the threat or fear is done under Duress.
73. In law, a man is presumed to be dead if he is not heard of as alive for 7 Years.
74. Chairman of First law Commission of India – M.C. Setalvad (1955).
75. Lex Loci – Law of Place.
76. In the year 2002, the competition act was enacted replacing MRTP Act 1969.
77. The disobedience of any judgment, order of a court amounts to Contempt of court.
78. Lok Adalat camps were started at Junagarh District in Gujarat in 1982 and First Lok Adalat was held at Chennai in 1986.
79. Father of Jurisprudence – John Locke.
80. Vishaka V. State of Raj. – Supreme court issued guidelines on Sexual harassment of women at workplaces.
81. Goa comes under the jurisdiction of the Mumbai High Court.
82. In an election, electioneering has to be stopped 48 Hrs. before starting the polling.
83. Power to decide an election petition vests with High Courts.
84. The examination of a witness by the adverse party is called Cross-Examination.
85. 1st Attorney general of India – M.C. Setalvad
86. 1 st Solicitor general of India – C.K. Daphtary
87. After independence, the Supreme court of India came into existence in the year 1950.
88. J. P.N. Bhagwati-Responsible for the introduction of PIL in India.
89. A post-dated cheque bears a Future date.
90. SLP can be filed before the Supreme Court
91. Oldest code of law in India is Manusmriti.
92. 1st CIC – Wajahat Habibullah.
93. The constitutional (117th amendment) bill 2012 deals with Reservation in promotions.
94. E-Court project was launched on 9th July 2007 by the President of India at Vigyan Bhawan, New Delhi.
95. Estonia Country – Recently introduced a law which allows to cast vote through mobile phones.
96. Calcutta High Court – Established first green bench in the country. Dishonour of a cheque – Compoundable offence.
97. Simultaneous civil & criminal proceedings are maintainable but the result of one proceeding is not binding on another.
98. Cognizable offence – Arrest without warrant.
99. Supreme court or High court – authority to designate an advocate as Senior Advocate.
100. First chairman of BCI – M.C. Setalvad.
101.First National Legal Services Day celebrated in India – 9th November 1995.
102. Members of CVC are appointed for the term of 4 Yrs or 65 Yrs. of age whichever is earlier.
103.Supreme Court case establishing environmental protection as part of Fundamental Rights – MC Mehta v. Union of India (1987), emphasizing the right to a healthy environment under Article 21.
104. An Indian citizen with a wife & 2 Children marries a British girl in the UK – He can be tried in India for bigamy on his return to India.
105. No-fault liability – Absolute liability even without any negligence or fault
106. NHRC – Statutory body
107. Copyright subsists for 60 Yrs.
108. The first model E-Court of the country was launched at Ahmedabad by Gujarat High Court (Providing tamper-proof authentic audio-video recording of proceedings with multi-point video conferencing facilities linking the courtroom, central jail, the police commissioner office and the forensic science laboratory)
109. Inquest – Inquiry into the apparent cause of death.
110. The concept of PIL was originated in the USA.
111. Legal Services day – 9th Nov.
112. ICJ was established in 1946.
113. ICJ judges are elected for 9 Yrs.
114. Registration of immovable property is required if the value of the property is more than 100/-
115. An offence punishable with imprisonment for a term exceeding 2 Yrs. is a Warrant Case.
116. FIR can be quashed only by High Court.
117. A foreigner committing an offence in India will be amenable to the Indian Law
118. Demand draft, cheque, pay orders & Bankers cheque are valid for 3 Months (w.e.f 01/04/2012)
119. In India, UCC is applicable in the state of Goa (Single code governs all Goans, irrespective of religion, ethnicity or linguistic affiliation)
120. The duration of CAG of India – 6 Yrs or 65 Yrs. of age whichever is earlier
125. First woman CM of state – Mrs. Sucheta Kriplani (U.P.)
126. First woman Governor of state – Mrs. Sarojini Naidu (U.P)
127. The first woman to climb Mount Everest – Bachhendri Pal
128. 1st woman advocate – Cornelia Sorabjee
129. 1st British Governor-General – Warren Hastings
130. 1st Viceroy of India – Lord Canning
131. 1st judge to face impeachment proceedings in Lok Sabha – J. V. Ramaswamy
132. Guardian of the public purse – CAG
133. B.N. Rau – Constitutional advisor to the constituent assembly.
134. Zonal Councils (Advisory or statutory bodies) – Five
135. 1st amendment – Added 9th Schedule to give legislation (Land reforms)
136. 42nd amendment 1976 – Mini Constitution
137. 1st Commercial courts were set up in Delhi (Mar. 25, 2016)
138. The first two states established Panchayati Raj – Rajasthan & Andhra Pradesh in 1956.
139. Five Yr. Plan in India is finally approved by NDC (National Development Council).
140. The Supreme court was set up by Regulating Act 1773.
141. 1st Indian state to go for internet voting – Gujarat (Apr. 2011).
142. Longest-serving PM – Pt. Jawaharlal Nehru.
143. A fiduciary relationship is based on Trust (Eg. Doctor-Patient)
144. CBI was established in 1963
145. Ernest Barker – Preamble is the keystone to the Constitution
146. Gram Panchayat is the lowest stage of Local govt.
147. Japan Parliament is known as Diet
148. The Chairman of the PAC of Parliament is appointed by President.
149. A person who is not an MP can be appointed as a minister by the president for a maximum period of 6 Months.
150. Judges and magistrates of civil courts are appointed by Governor.
151. In case the office of President of India falls vacant the same must be filed within 6 Months.
152. The senior-most member of Lok Sabha – Presides over the Lok Sabha if neither the speaker nor the deputy speaker is available.
153. Distribution of powers b/w union and state have been borrowed from Canada.
154. Longest-serving CM in India – Pawan Chamling (Sikkim – 5th consecutive term).
155. Public holidays are declared under the Negotiable instruments act, 1881.
156. Indian Constitution as quasi-federal said by – K.C. Wheare.
157. Ashok Mehta committee – Panchayati Raj Institutions
158. Balwant rai Mehta committee – 3 Tier system
159. Leaving the opposition party to join the ruling party or vice versa – Crossing the floor
160. A bill referred to as the joint sitting of parliament is to be passed by a Simple majority.
161. The members of the State public service commission can be removed by the President on a report by the Supreme Court.
162. The members of Rajya Sabha are elected by elected members of the Legislative assembly.
163. J. LN Reddy's committee was made to look into the anomalies that may arise in the implementation of OROP.
164. 101 st constitutional amendment 2016 – GST (Introduced Art. 264A, 269A, 279A)
List of Committees and Commissions in India
➤ Committees in India
- Butler Committee – Relation between Indian states & paramount power.
- Hartog Committee – Growth of British India education-its effects.
- Muddiman Committee – Working of Diarchy as in Montague Chelmsford reforms.
- Malhotra Committee – Insurance Reforms.
- Janaki Ram Committee – Security Scam.
- Ajay Vikram Singh Committee – Faster promotions in Army.
- Rajinder Sachar Committee 1 – Companies and MRPT Act.
- Rajindar Sachar Committee 2 – Report on the social, economic and educational status of the Muslims of India.
- Jyoti Basu Committee – Report on Octroi abolition.
- Balwant Rai Mehta Committee – Recommendations on decentralization system.
- Sawant Committee – Enquiry on corruption, charges against ministers & Anna Hazare.
- Chelliah Committee – Eradicating black money.
- Wanchoo Committee – Tax enquiry.
- Bhanu Pratap Singh Committee – Agriculture.
- Agarwal Committee – Nepotism in granting petrol pump, LPG connections.
- Rangarajan Committee – Reforms in the private sector.
- Naresh Chandra Committee – Corporate governance.
- Chakravarti Committee – Banking sector reforms.
- Rekhi Committee – Structure of indirect taxation.
- G.V.Ramakrishna Committee – Disinvestment in PSU shares.
- Kelkar Committee 1 – First committee on backward castes.
- P.C.Hotha Committee – Restructuring of civil services.
- Justice B.N.Kirpal Committee – 1st chairman National Forest Commission.
- Godbole Committee – Enron Power Project.
- J.C.Kumarappa Committee – Congress Agrarian Reforms Committee.
- Swaminathan Committee – Population policy.
- Rangaraju Committee – Statistics.
- Wardha Committee – Inquiry on the murder of Graham Staines.
- Vohra Committee – Criminalization of politics.
- Kelkar Committee 2 – Direct-Indirect Taxes.
- Alagh Committee – Civil Service Examinations
- Abid Hussain Committee – Recommendations on Small scale industries.
- Narasimham Committee – Banking sector reforms.
- Chelliah Committee – Tax reforms.
- Mashelkar Committee – National Auto Fuel Policy.
- Boothalingam Committee – Recommendations on integrated wages, income and price policy.
- Omkar Goswami Committee Industrial sickness.
- Yashpal Committee – Review of School Education system.
- Ram Nandan Prasad Committee – Constitution of creamy layers among Backward Castes.
- Kelkar Committee 3 – Enquiry on Kargil defence deals.
- Saharya Committee – Tehelka tapes.
- J. Narasimha committee – OROP (One rank one pension)
➤ List of Commissions
- U.C.Benerjee Commission – Enquiry into Godhra carnage (Railways).
- Nanavati-Shah Commission- Post Godhra riots.
- Palekar Tribunal – Journalist pays reforms.
- Hunter Commission – Jallianwala Bagh massacre.
- Nanavati Commission – 1984 Sikh riots.
- Mukherjee Commission – Death/Disappearance of Subhash Chandra Bose.
- Librehan Commission – Babri Masjid demolition case.
- Sarkaria Commission – Centre-State relations.
- Sri Krishna Commission – 1992 Bombay riots.
- Thakkar Commission – Indira Gandhi assassination case.
- Phukhan Commission – Tehelka tapes.
- Malimath Commission – Criminal Justice.
- Upendra Commission – Inquiry on rape and murder Thangjam Manorama Devi.
- G.C.Garg Commission – Train accident near Khanna, Punjab.
- Mandal Commission – Reservation of seats for Backward castes.
- Kothari Commission – Educational reforms.
Important Judgments for 2024-2025
Imran Pratapgadhi v. State of Gujarat (2025)
- This case involves a Supreme Court ruling on the misuse of criminal provisions.
- The Court held that posting a poem promoting sacrifice and non-violence does not constitute offences under Sections 196, 197, 299, 302, or 57 of the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS).
- The Court deemed the registration of an FIR in such a case as an abuse of law, emphasizing the need to protect free expression and prevent frivolous legal actions.
Aniruddha Kumar v. Chief Election Commissioner (2024)
- The Supreme Court addressed the issue of electoral transparency in this case, ruling that the disclosure of candidates’ assets and liabilities is integral to ensuring free and fair elections under Article 324 of the Constitution.
- The Court clarified that voters have a right to access such information to make informed choices, reinforcing the principles of democratic governance.
X Corp v. Union of India (2024)
- This case pertains to the regulation of social media platforms under the Information Technology Act, 2000.
- The Supreme Court ruled that intermediaries must comply with government orders to remove content deemed unlawful but emphasized that such orders must be specific and proportionate to avoid infringing on freedom of expression under Article 19(1)(a).
Sita Soren v. Union of India (2024)
- In this landmark Constitutional Law case, the Supreme Court revisited the issue of parliamentary privileges under Article 105.
- The Court held that legislators cannot claim immunity from prosecution for accepting bribes to influence their votes or speeches in the legislature.
- This ruling overturned a 1998 judgment and strengthened anti-corruption measures in legislative processes.
Re: Article 370 (2024)
- The Supreme Court upheld the abrogation of Article 370, which granted special status to Jammu and Kashmir.
- The Court ruled that the President’s power to issue a Constitutional Order under Article 370(3) was valid and that the reorganization of Jammu and Kashmir into Union Territories was constitutionally permissible.
Priya Gupta v. State of Uttar Pradesh (2025)
- The Allahabad High Court addressed the issue of dowry harassment under Section 498A of the Indian Penal Code (now replaced by the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita).
- The Court emphasized the need for prima facie evidence before registering an FIR to prevent misuse of dowry laws.
- It laid down guidelines to ensure fair investigation, protecting both the complainant and the accused.
Association for Democratic Reforms v. Union of India (2024)
- The Supreme Court struck down the Electoral Bonds Scheme, ruling that it violated the right to information under Article 19(1)(a) by allowing anonymous political donations.
- The Court mandated transparency in political funding to ensure accountability and curb corruption.
Rajesh Kumar v. State of Bihar (2025)
- The Patna High Court, in this case, clarified the scope of anticipatory bail under Section 438 of the Code of Criminal Procedure (now under the Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita).
- The Court held that anticipatory bail can be granted in cases of economic offences only under exceptional circumstances, emphasizing the need to balance individual liberty with societal interests.
|
63 videos|175 docs|37 tests
|
FAQs on Legal General Knowledge - Legal Reasoning for CLAT
| 1. What are the main committees and commissions formed in India for legal and judicial reforms? |  |
| 2. What significant legal judgments have shaped the Indian judicial landscape recently? |  |
| 3. How can one prepare for legal general knowledge sections in competitive exams like CLAT? |  |
| 4. What role do committees and commissions play in legislative processes in India? |  |
| 5. What are some of the key factors to consider when analyzing important legal judgments? |  |






















