Linkage | Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Associated Terms |

|
| Characteristic of Linked Genes |

|
| Chromosome Theory of Linkage |

|
| Types of Linkage |

|
| Incomplete Linkage |

|
| Significance of Linkage |

|
Associated Terms
- The occurrence of different genes on the same chromosome. They show non- random assortment at meiosis.
- Linkage group. All of the genes located physically on a given chromosome.
- Linkage map. A chromosome map; an abstract map of chromosomal loci, based on recombinant frequencies.
Characteristic of Linked Genes
Genes on different chromosomes assort independently giving a 1: 1: 1: 1 test cross ratio. Linked genes do not assort independently but tend to stay together in the same combination as they were in the parents.
Chromosome Theory of Linkage
Morgan along with Castle formulated the chromosome theory of linkage which is as follows:
- The genes which show the phenomenon of linkage are situated in the same chromosomes and these linked genes usually remain bounded by the chromosomal material so that they cannot be separated during the process of inheritance.
- The distance between the linked genes determines the strength of linkage. The closely located genes show strong linkage than the widely located genes which show the weak linkage.
- The genes are arranged in linear fashion in the chromosomes.
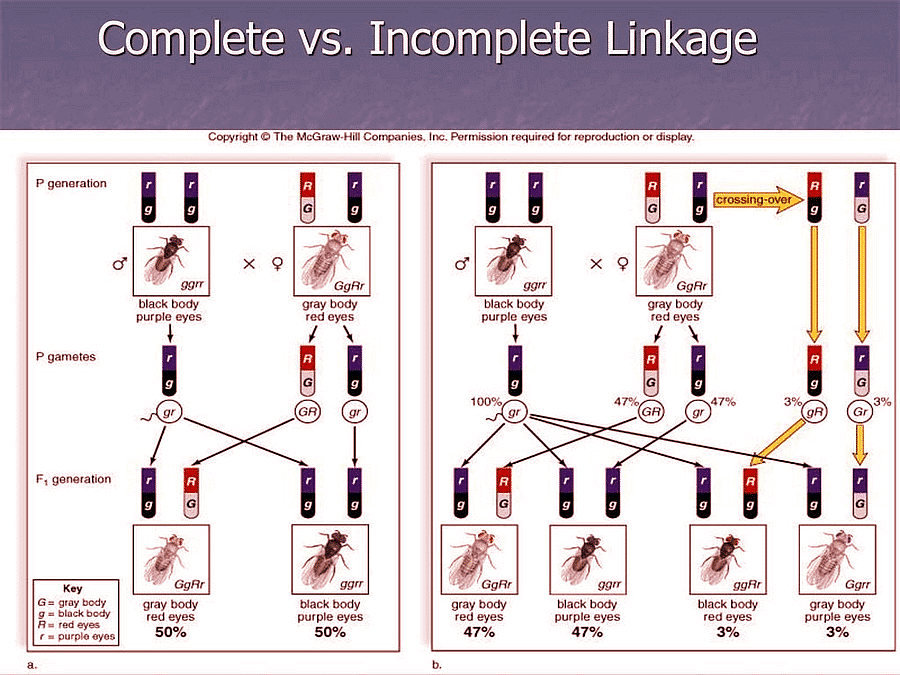
Types of Linkage
Morgan and his co-workers by their investigation on the Drosophila found two types of linkage –
- Complete linkage and
- Incomplete linkage.
Complete Linkage
- The complete linkage is the phenomenon in which parental combinations of characters appear together for two or more generations in a continuous and regular fashion.
- In this type of linkage genes are closely associated and tend to transmit together.
Example. The genes for bent wings (bt) and shaven bristles (svn) of the fourth chromosome mutant of Drosophila melanogaster exhibit complete linkage.
In 1919, T.H. Morgan mated gray bodied and vestigial winged (b+vg/b+vg) fruit flies with flies having black bodies and normal wings (bvg+/bvg+). F1 progeny had gray bodies and normal long wings (b+vg/bvg+), indicating thereby that these characters are dominant.When F1 males (b+vg/bvg+), were backcrossed (i.e., test crossed) to double recessive females (bvg/bvg or black vestigial), only two types of progeny (one with gray bodies and vestigial wings, b+vg/bvg and the other with black bodies and normal wings, to bvg+/bvg instead of four types of phenotypes were obtained.
Incomplete Linkage
- The linked genes which are widely located in chromosomes and have chances of separation by crossing over are called incompletely linked genes and the phenomenon of their inheritance is called incomplete linkage.
- The linked genes do not always stay together because homologous non-sister chromatids may exchange segments of varying length with one another during meiotic prophase. This sort of exchange of chromosomal segments in between homologous chromosomes is known as crossing over.
Example. The incomplete linkage has been reported in female Drosophila and various other organisms such as tomato, maize, pea, mice, poultry and man, etc.
Incomplete Linkage in maize. In Zea mays (maize) a case of incomplete linkage between the
alleles for colour and shape of the seed has been observed by Hutchison. When a maize plant with seeds having coloured and full endosperm (CS/CS) is crossed with another plant having recessive alleles for colourless, shrunken seeds (cs/cs), the F1 heterozygotes are found with the phenotype of coloured full and genotype of CS/cs. When F1 hybrid is test crossed with double recessive parent (cs/cs) four classes of descendants are obtained instead of two. The test cross results are clearly showing that parental combination of alleles (e.g., CS/cs and cs/ cs) are those expected from complete linkage and appear in 96% cases, the other two are new combinations (e.g., Cs/cs and cS/cs) and appear in 4% cases. Thus, in 4% cases crossing over has occurred between linked genes.
Significance of Linkage
The phenomenon of linkage has one of the great significance for the living organisms in that it reduces the possibility of variability in gametes unless crossing over occurs.
|
198 videos|351 docs
|
FAQs on Linkage - Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is the significance of linkage in genetics? |  |
| 2. What is the chromosome theory of linkage? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of linkage? |  |
| 4. What is incomplete linkage? |  |
| 5. What are the characteristics of linked genes? |  |