Long Questions: The Living Organisms - Characteristics & Habitats | NCERT Summary: UPSC PDF Download
Q1: How do you characterize a living thing?
Ans: Anything that has life is called living things.
The following are some of the characteristics that distinguish a living thing:
- All living creatures require food and nutrients to survive.
- To receive energy from food, all living creatures breathe.
- All living things are in the process of growing.
- Stimuli affect all living things.
- All living things discharge waste from their bodies.
- All living things reproduce to generate offspring.
- All living things have substance mobility in their bodies.
Q2: Compare the adaptations of animals in grasslands to those in mountains.
Ans: Differences between adaptation of grassland and mountain animals are as follows: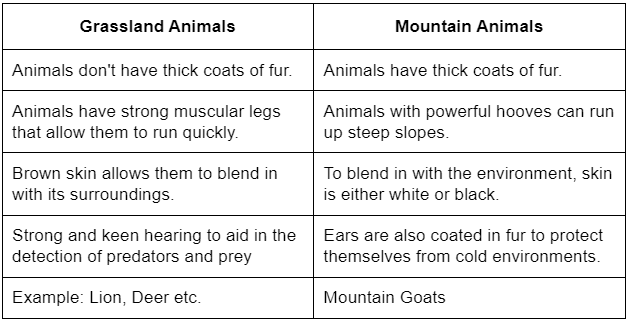
Q3: Compare the adaptations of a desert plant with a mountain plant?
Ans: Differences between desert and mountain plants are as follows: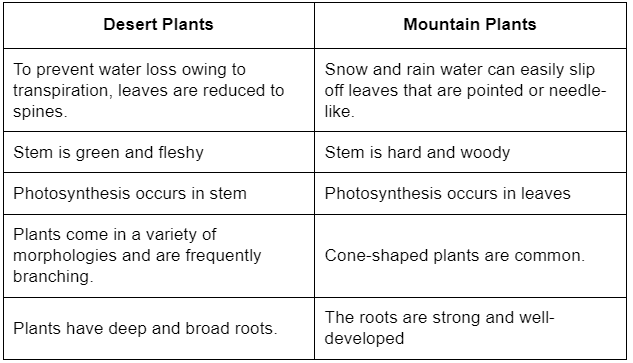
Q4: Explain the characteristics of living organisms. How are these characteristics different from non-living things? Provide examples to support your answer.
Ans: Living organisms possess several characteristics that differentiate them from non-living things:
- Cellular Organization: All living things are composed of cells, which are the basic units of life. For example, humans are made up of trillions of cells.
- Growth and Development: Living organisms grow in size and undergo changes as they mature. Seeds sprouting into plants and infants growing into adults are examples.
- Reproduction: Living things can produce offspring similar to themselves. Plants produce seeds, animals give birth, and bacteria reproduce through cell division.
- Response to Stimuli: Living organisms can sense and respond to changes in their environment. For instance, plants grow towards light, and animals move away from danger.
- Metabolism: Living things carry out various chemical reactions to obtain energy and build molecules. Plants use photosynthesis, while animals perform digestion.
These characteristics are absent in non-living things like rocks or water. Non-living things do not grow, reproduce, respond to stimuli, or have cells.
Q5: Describe the concept of habitat and explain why different living organisms are found in different habitats. Provide examples to illustrate your answer.
Ans: A habitat is a specific place where a living organism lives and obtains all its requirements for survival.
Different living organisms are found in different habitats due to their adaptations:
- Adaptations to Environment: Organisms develop specific characteristics that help them survive in a particular habitat. For instance, polar bears are adapted to cold environments with thick fur and blubber.
- Food and Resources: Each habitat offers distinct sources of food, water, and shelter. Desert plants like cacti store water, while rainforest animals have adaptations to access abundant water.
- Temperature and Climate: Organisms are adapted to the temperature and climate of their habitat. Camel's humps store water for desert conditions, while penguins have insulating feathers for cold environments.
- Interactions with Other Organisms: Organisms in a habitat interact with one another. Some animals are predators, while others are prey. For example, lions are predators in grassland habitats.
Due to these adaptations, different living organisms are uniquely suited to their specific habitats, ensuring their survival and successful reproduction.
Q6: Explain the classification of living organisms into plants and animals. Describe the key characteristics of each group and provide examples to illustrate these characteristics.
Ans: Living organisms are classified into two main groups: plants and animals.
Plants:
- Cell Wall: Plants have cell walls made of cellulose, providing structure.
- Photosynthesis: They use chlorophyll to make food through photosynthesis.
- Stationary: Most plants are stationary and cannot move.
- Reproduction: Reproduce through seeds or spores.
- Examples: Mango tree, rose plant, grass.
Animals:
- No Cell Wall: Animals lack cell walls.
- Heterotrophic Nutrition: They cannot make their own food and rely on consuming other organisms.
- Movement: Most animals can move from place to place.
- Reproduction: Animals reproduce through eggs or live birth.
- Examples: Lion, cat, fish.
These characteristics differentiate plants and animals. While plants produce their own food and are stationary, animals are mobile and consume other organisms for energy.
Q7: Discuss the importance of adaptation in the survival of living organisms. Provide examples of specific adaptations observed in plants and animals in different habitats.
Ans: Adaptation is crucial for the survival of living organisms as it helps them adjust to their environment and meet their needs:
- Survival: Adaptations enable organisms to find food, water, shelter, and reproduce successfully.
- Reproduction: Adaptations enhance an organism's ability to find mates and reproduce.
- Protection: Adaptations protect organisms from predators, harsh climates, and other challenges.
Examples of Adaptations:
- Camouflage: Chameleons change color to blend into their surroundings, avoiding predators.
- Mimicry: Non-poisonous butterflies mimic the appearance of poisonous ones to deter predators.
- Cactus Adaptations: Cacti store water in their stems and have modified leaves to reduce water loss.
- Polar Bear Adaptations: Thick fur and blubber help polar bears survive cold Arctic environments.
Adaptations improve an organism's chances of survival in its specific habitat, enabling it to compete, reproduce, and thrive.
Q8: Explain the concept of life cycle in living organisms. Describe the stages of a typical life cycle and how it ensures the continuation of species. Provide an example to illustrate the concept.
Ans: A life cycle is the sequence of changes an organism goes through from birth to reproduction and eventual death.
It ensures the continuation of a species:
Stages of a Typical Life Cycle:
- Birth or Germination: The beginning of life from a seed or birth of an animal.
- Growth and Development: The organism matures, gaining size and abilities.
- Reproduction: Organisms produce offspring, continuing the species.
- Aging and Senescence: Organisms become older and eventually die.
Example: Consider the life cycle of a butterfly:
- Egg: The butterfly lays eggs on a leaf.
- Larva (Caterpillar): The egg hatches into a caterpillar that eats and grows.
- Pupa (Chrysalis): The caterpillar forms a chrysalis and undergoes metamorphosis.
- Adult Butterfly: The chrysalis opens, and an adult butterfly emerges, ready to reproduce.
This life cycle ensures the survival and continuation of the butterfly species.
Q9: Describe the concept of adaptation and its significance in the survival of aquatic organisms. Explain how aquatic organisms are adapted to their underwater habitats, providing examples of adaptations in both plants and animals.
Ans: Adaptation is the process by which organisms develop traits that help them survive and thrive in their environments.
Aquatic organisms, those living in water, have unique adaptations to their underwater habitats:
- Gills: Many aquatic animals have gills to extract oxygen dissolved in water. Fish, for example, use gills to extract oxygen from water as it flows over their gill membranes.
- Buoyancy: Aquatic organisms often have structures like swim bladders or air sacs to help them control their buoyancy. This adaptation allows them to float or sink as needed.
- Streamlined Bodies: Aquatic animals, including fish and dolphins, have streamlined bodies that reduce water resistance, allowing them to move efficiently through water.
- Webbed Feet: Many aquatic birds, like ducks, have webbed feet that help them swim effectively through water while propelling themselves.
- Waterproof Coatings: Aquatic plants, like water lilies, have leaves with waterproof coatings that prevent excessive water absorption.
- Camouflage: Underwater creatures like seahorses and certain fish have coloration and patterns that help them blend into their surroundings, protecting them from predators.
These adaptations ensure that aquatic organisms can obtain oxygen, move, and find food efficiently, ultimately aiding their survival in watery environments.
Q10: Discuss the concept of hibernation and migration as adaptations in animals. Explain how these behaviors contribute to the survival of animals in different seasons and environments. Provide examples of animals that exhibit each behavior.
Ans: Hibernation: Hibernation is a state of deep sleep that some animals enter during the winter months. It's an adaptation to cope with extreme cold and scarcity of food. During hibernation, an animal's body temperature drops, and its metabolism slows down significantly, conserving energy.
Examples:
- Bears: Bears hibernate in their dens during winter, conserving energy when food is scarce.
- Hedgehogs: Hedgehogs hibernate to survive colder months when insects, their primary food, are scarce.
Migration:
- Migration is the seasonal movement of animals from one region to another in search of food, better climate, or breeding grounds. It's an adaptation to changing environmental conditions.
Examples:
- Birds: Birds like swallows migrate over long distances to escape harsh winters and find abundant food.
- Monarch Butterflies: Monarch butterflies migrate thousands of miles to warmer climates for breeding.
Both hibernation and migration are essential strategies for animals to survive changing seasons and challenging environments. Hibernation conserves energy during extreme conditions, while migration allows animals to find more favorable conditions for survival, reproduction, and access to resources.
|
666 docs
|















