Mechanical Properties of Solids | Physics Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
Till now we have learned that solids have fixed shapes and dimensions i.e. they are rigid. You must have observed that if a weight is hung from the end of a vertically hung steel spring, it gets stretched. When the weight is removed, it goes back to its original shape and size. This shows that steel spring has some elastic behavior!
 Stretching of Springs
Stretching of Springs
In this document, we will be studying the Elasticity of solids in detail.
Behaviour Under Deforming Forces
When a solid experiences a force that changes its shape or size, several outcomes can occur:
- If you gently pull the ends of a helical spring, its length increases slightly. When you let go, it returns to its original size and shape.
- Conversely, if you apply force to a lump of putty or mud, they do not tend to regain their previous shape and become permanently deformed. Such materials are termed plastic, and this property is known as plasticity. Putty and mud are examples of nearly ideal plastics.
Elastic Behaviour of Solids
The property of the body to regain its original configuration (length, volume, or shape) when the deforming forces are removed, is called elasticity.
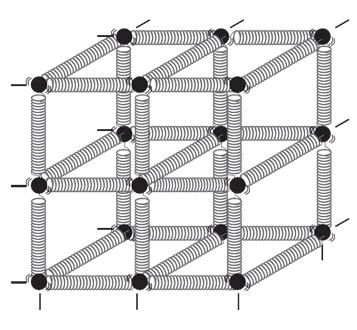 Spring-ball model for the illustration of elastic behavior of solids
Spring-ball model for the illustration of elastic behavior of solids
- In a solid, atoms and molecules are arranged in such a way that each molecule is acted upon by the forces due to the neighboring molecules. These forces are known as intermolecular forces. For instance, assume the atoms or molecules of solid as the balls in the image below and the springs represent the interatomic or intermolecular forces. This is called the spring-ball model of solids.
- In this system, if any ball is displaced from its equilibrium position, the ball attached to it will be stretched or compressed. Due to this, restoring forces will come into play and force the ball to come back to its original position. This leads to elastic behavior in solids.
- The change in the shape or size of a body when external forces act on it is determined by the forces between its atoms or molecules. These short-range atomic forces are called elastic forces.
Terms Related to Elasticity
 1. Deforming force
1. Deforming force
A deforming force is one that changes the usual position of molecules, leading to a change in the shape of a body.
2. Elastic body
A body that regains its original configuration immediately and completely after the removal of deforming force from it is called a perfectly elastic body. Quartz and phosphorus bronze are examples of nearly perfectly elastic bodies.
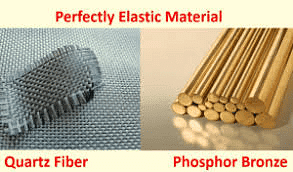 Elastic Materials
Elastic Materials
3. Plastic body
The inability of a body to return to its original size and shape even on removal of the deforming force is called plasticity and such a body is called a plastic body.
 Plastic Materials
Plastic Materials
Stress
Stress is defined as the ratio of the internal force F, produced when the substance is deformed, to the area A over which this force acts.
In equilibrium, this force is equal in magnitude to the externally applied force. In other words,
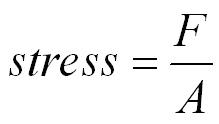 The SI Unit of stress is newton per square meter (Nm-2).In CGS units, stress is measured in dyne cm-2. The dimensional formula of stress is ML-1T-2
The SI Unit of stress is newton per square meter (Nm-2).In CGS units, stress is measured in dyne cm-2. The dimensional formula of stress is ML-1T-2
Stress is of two types:
1. Normal stress: It is defined as the restoring force per unit area perpendicular to the surface of the body. Normal stress is of two types, tensile stress and compressive stress.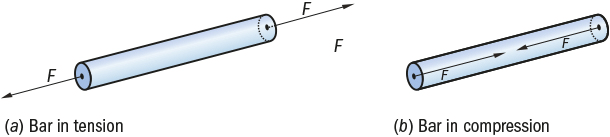 Tensile and compressive stress
Tensile and compressive stress
2. Tangential stress: When the elastic restoring force or deforming force acts parallel to the surface area, the stress is called tangential stress or shear stress.
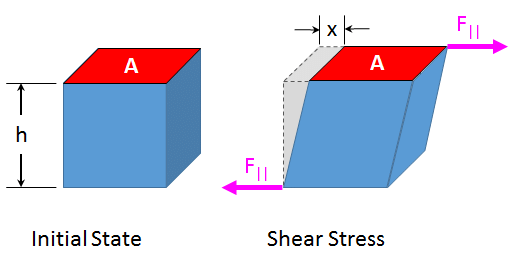 Tangential Stress
Tangential Stress
Strain
It is defined as the ratio of the change in size or shape to the original size or shape. It has no dimensions, it is just a number.
Strain is of three types:
1. Longitudinal strain: If the deforming force produces a change in length alone, the strain produced in the body is called longitudinal strain or tensile strain.
It is given as:
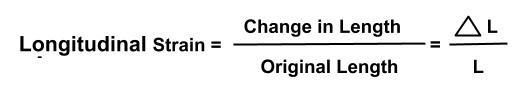
Longitudinal strain
2. Volumetric strain: If the deforming force produces a change in volume alone, the strain produced in the body is called volumetric strain. It is given as:
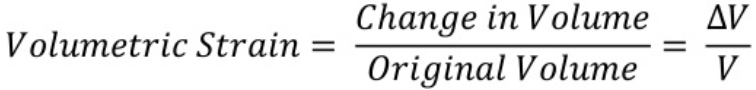
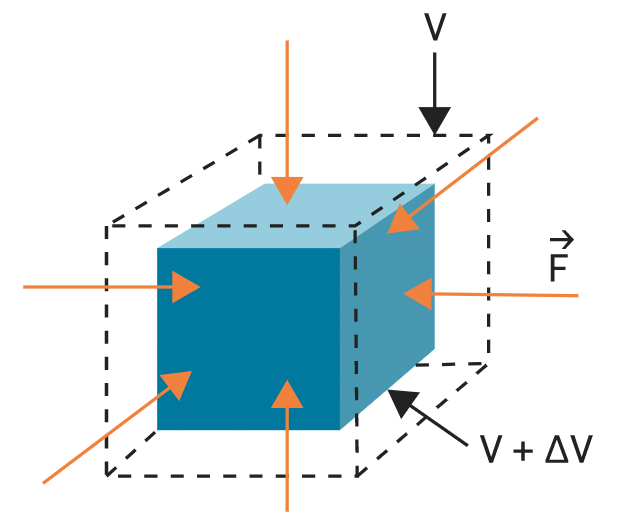 Volumetric strain3. Shear strain: The angle tilt caused in the body due to tangential stress expressed is called shear strain. It is given as:
Volumetric strain3. Shear strain: The angle tilt caused in the body due to tangential stress expressed is called shear strain. It is given as:
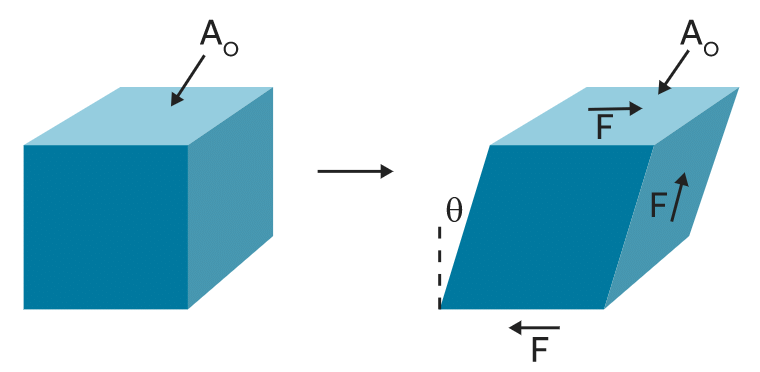 Shear strain
Shear strain
The maximum stress to which the body can regain its original status on the removal of the deforming force is called the elastic limit.
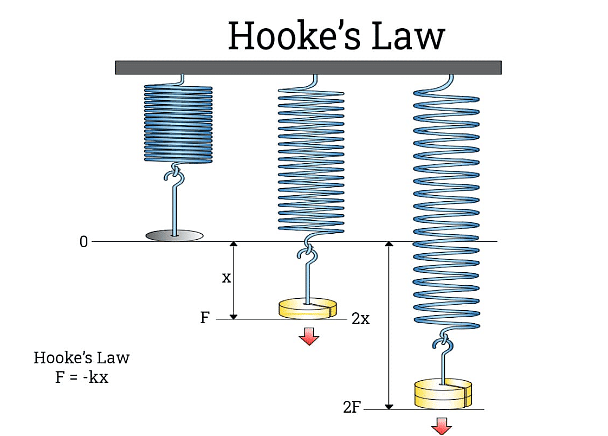
Hooke’s Law
Hooke’s law states that, within elastic limits, the ratio of stress to the corresponding strain produced is a constant.
This constant is called the modulus of elasticity. Thus,
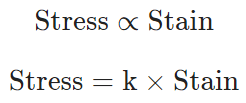
Stress-Strain Curve
Stress-strain curves are useful to understand the tensile strength of a given material. The given figure shows a stress-strain curve of a given metal.
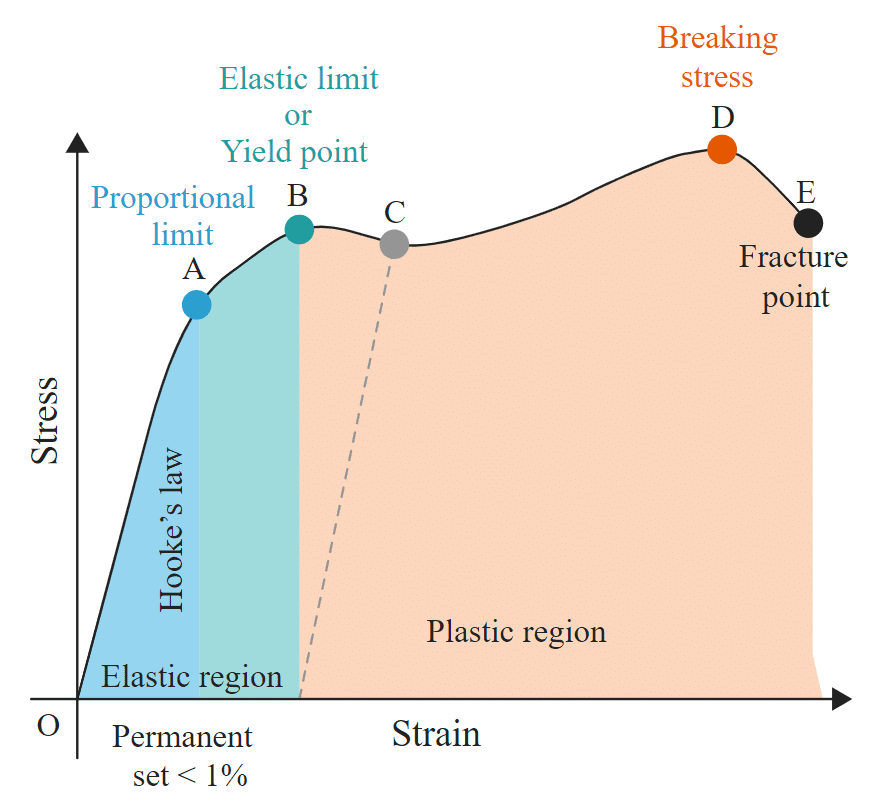 Stress-strain curve
Stress-strain curve
- The curve from O to A is linear. In this region, Hooke’s Proportional limit law is obeyed.
- In the region from A to B stress and strain are not proportional. Still, the body regains its original dimension, once the load is removed.
- Point B in the curve is the yield point or elastic limit and the corresponding stress is known as yield strength of the material.
- The curve beyond B shows the region of plastic deformation.
- The point D on the curve shows the tensile strength of the material. Beyond this point, additional strain leads to fracture, in the given material.
Depending upon three types of strain, namely, longitudinal, volumetric, and shearing strain, there are three types of Modulus of Elasticity.
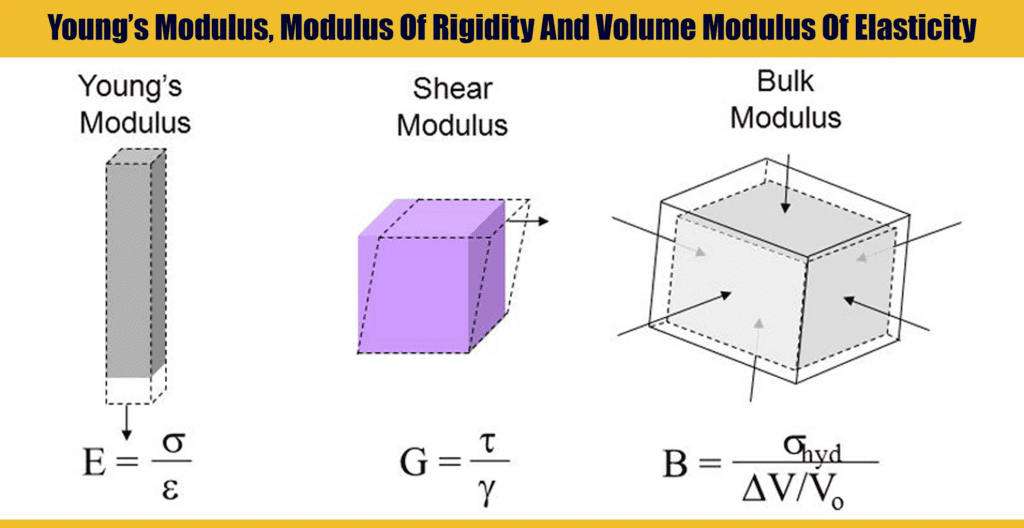 Types of Modulus of Elasticity
Types of Modulus of Elasticity
Young's Modulus of Elasticity (Y)
Young's modulus (Y) quantifies the elasticity of a material in terms of its ability to withstand changes in length under longitudinal stress. It is defined as the ratio of longitudinal stress to longitudinal strain within the elastic limit, which is the range where the material returns to its original shape after the deforming force is removed.
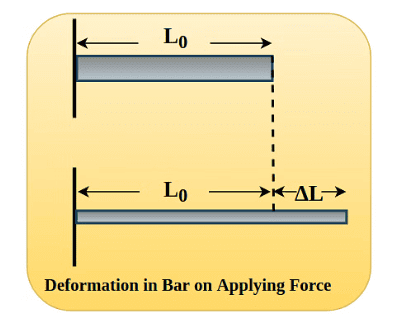 Young's Modulus
Young's Modulus

Where:
- F is the force applied,
- A is the cross-sectional area,
- ΔL is the change in length,
- L is the original length.
Unit: As strain has no units, Young's modulus shares the same unit as stress, which is N/m² or Pascal (Pa).
Dimensions:
Bulk Modulus of Elasticity (K or B)
The bulk modulus (K or B) measures a material's resistance to uniform compression. It is the ratio of volume stress to volume strain, applicable when the deforming force is applied equally from all directions, causing a change in volume.
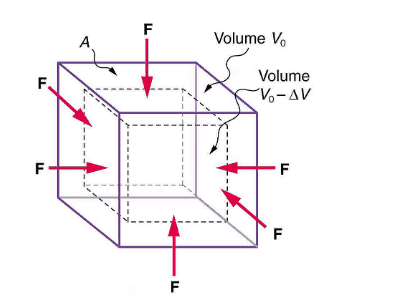 Bulk Modulus
Bulk Modulus

The negative sign indicates that an increase in pressure results in a decrease in volume.
Unit: Newton per square meter (N/m2)
Process-Dependence for Ideal Gases:
- Isothermal process:
- Adiabatic process: (where is the adiabatic index)
- Polytropic process: (where is the polytropic index)
Compressibility: The reciprocal of the bulk modulus
Modulus of Rigidity (η) or Shear Modulus
The modulus of rigidity (η), also known as the shear modulus, measures a material's resistance to shear deformation. It is defined as the ratio of shearing stress to shearing strain within the elastic limit.
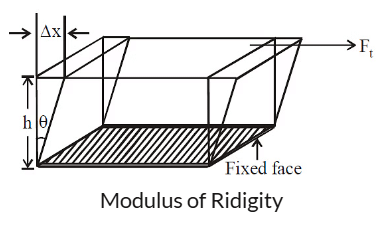

Where:
- Ftangential is the tangential force,
- A is the area,
- ϕ is the shear angle.
Poisson's Ratio (σ)
Poisson's ratio (σ) is a measure of the transverse strain (contraction or expansion) relative to the longitudinal strain when a material is stretched or compressed.

Where:
- is the change in diameter,
- is the original diameter,
- is the change in length,
- is the original length.
Relations between Elastic Moduli
For isotropic materials (i.e., materials having the same properties in all directions), only two of the three elastic constants are independent. For example, Young’s modulus can be expressed in terms of the bulk and shear moduli.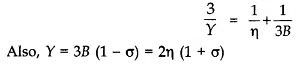
Q1: As shown in the figure, in an experiment to determine Young's modulus of a wire, the extension-load curve is plotted. The curve is a straight line passing through the origin and makes an angle of 45º with the load axis. The length of wire is 62.8 cm and its diameter is 4 mm. The Young's modulus is found to be x * 104 Nm-2.
The value of x is .
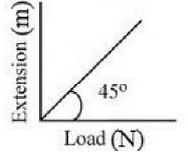
Ans: 5
Sol:
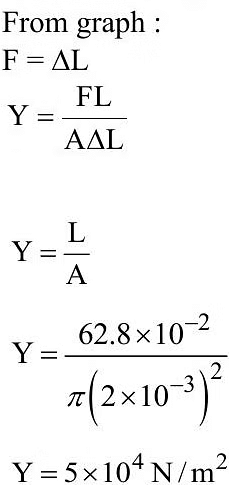
Q2: Choose the correct relationship between Poisson ratio (σ), bulk modulus (K) and modulus of rigidity (η) of a given solid object:
(a) 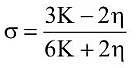 (b)
(b) 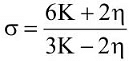 (c)
(c) 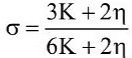 (d)
(d) 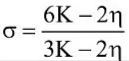
Ans: (a)
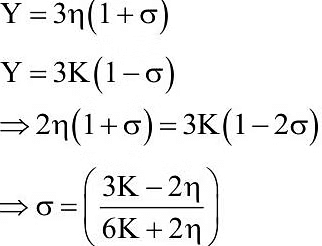
Q3: A force is applied to a steel wire ‘A’, rigidly clamped at one end. As a result elongation in the wire is 0.2 mm. If same force is applied to another steel wire ‘B’ of double the length and a diameter 2.4 times that of the wire ‘A’, the elongation in the wire ‘B’ will be (wires having uniform circular cross sections)
(a) 6.06 x 10-2 mm
(b) 2.77 x 10-2 mm
(c) 3.0 x 10-2 mm
(d) 6.9 x 10-2 mm
Ans: 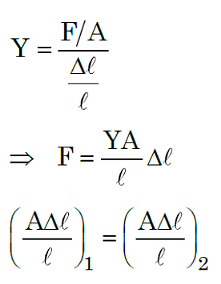
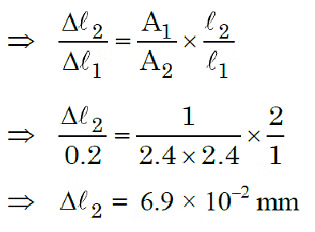
Q4: A thin rod having a length of 1 m and area of cross-section 3 x l0-6m2 is suspended vertically from one end. The rod is cooled from 210°C to 160°C. After cooling, a mass M is attached at the lower end of the rod such that the length of rod again becomes 1 m. Young's modulus and coefficient of linear expansion of the rod are 2 x l011Nm-2 and 2 x lO-5K-1, respectively. The value of M is ______ kg. (Take g = 10 ms-2)
Ans: 60
Sol: If Δl is decrease in length of rod due to decrease in temperature

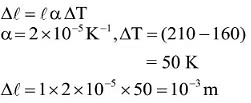
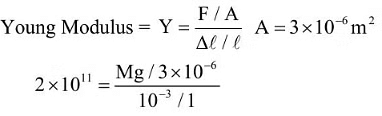
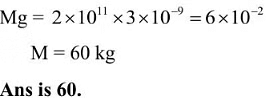
Q5: The Young's modulus of a steel wire of length 6 m and cross-sectional area 3 mm2, is 2 x 1111N/m2. The wire is suspended from its support on a given planet. A block of mass 4 kg is attached to the free end of the wire. The acceleration due to gravity on the planet is 1/4 of its value on the earth. The elongation of wire is (Take g on the earth = 10 m/s2):
(a) 1 cm
(b) 1 mm
(c) 0.1 mm
(d) 0.1 cm
Ans: (c)
Sol: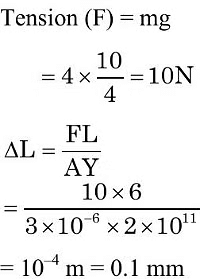
Elastic Potential Energy in a Stretched Wire
The ultimate tensile strength of a material is the stress required to break a wire or a rod by pulling on it. The breaking stress of the material is the maximum stress that a material can withstand. Beyond this point, breakage occurs.
When a wire of original length L is stretched by a length 1 by the applied I inn of force F at one end, then
Work done to stretch wire 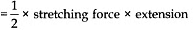
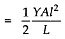
Work done per unit volume of wire is given as:

According to the formula given by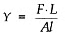
Where F is the force needed to stretch the wire of length L and area of cross-section A, is the increase in the length of the wire.
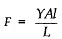
The work done by this force in stretching the wire is stored in the wire as potential energy.
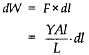
Integrating both sides, we get
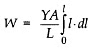
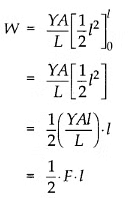
which equals the elastic potential energy U. 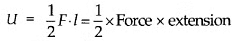
Now the potential energy per unit volume is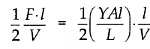
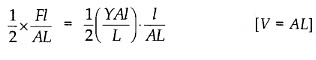
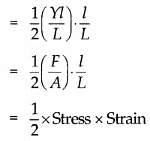
Hence, the elastic potential energy of a wire (energy density) is equal to half the product of its stress and strain.
Effect of Temperature on Elasticity
- The impact of temperature on elasticity differs across materials.
- Understanding the elastic behaviour of materials is crucial in engineering design.
- For instance, when designing a building, knowing the elastic properties of materials like steel and concrete is vital.
- A material with a high Young's modulus needs a significant force to cause small changes in length.
- Some materials keep their elastic properties stable across various temperatures, making them ideal for uses that require dimensional stability.
Effect of Impurity on Elasticity
- Impurities can change the elastic properties of a material.
- The effect varies based on the material and the type of impurity.
- Adding impurities often strengthens the intermolecular forces, making materials more resistant to deformation when force is applied.
- The ratio of stress to strain, known as the modulus of elasticity, is a key characteristic of the material.
- A force applied in one direction can also cause strains in other directions.
Applications of Elastic Behaviour of Materials
A slingshot deforms when you stretch it. However, it regains its original shape when you stop applying a force. But let us say that you take a thin steel rod and try to bend. You manage to bend it a little and then stop applying force. Does the rod regain its original shape? No, it doesn’t. This difference in the behaviour of the material is based on their elastic and plastic nature.
Why does this happen?
- The rubber strip of the slingshot has high elasticity.
- Elasticity is the ability of a body to resist any permanent change to it when stress is applied.
- When stress application ceases, the body regains its original shape and size.
- Different materials show different elastic behaviour.
- The study of the elastic behaviour of a material is of much importance.
- Almost every engineering design requires knowledge of the elastic behaviour of materials.
Applications of this Concept
- In the construction of various structures like bridges, columns, pillars, beams, etc., knowledge of the strength of the materials used in the construction is of prime importance.
- For example: While constructing a bridge, a load of traffic that it can withstand should be adequately measured beforehand.
- Or while constructing a crane used to lift loads, it is kept in mind that the extension of the rope does not exceed the elastic limit of rope.
- To overcome the problem of bending under force, the elastic behaviour of the material used must be considered primarily.
- To study the elastic behaviour of materials let us consider a beam of length l, breadth b and depth d supported at the ends and loaded at the centre by load W.
- In this case, it is given as; δ = Wl3/4bd3Y, where δ is the sag or the measure of bending, Y is Young’s modulus of elasticity.
- Study of beams is very useful in civil engineering and other such avenues.
- Using the above equation we can easily say that to reduce the amount of bending for a certain load, Young’s modulus of elasticity of the material used must be large.
- Also, the depth d must be considered since sag is inversely proportional to the cube of depth.
- But the problem faced on increasing the depth is that bending increases and this is known as buckling.
- Therefore, a compromise is made between the different cross-sectional shapes.
Solved Example
Q: Why is steel used in the construction of bridges?
Ans:
- Among all materials used in bridge construction, steel is known for having the highest and most favorable strength qualities.
- This makes steel suitable for building ambitious bridges that span long distances.
- Regular building steel has compressive and tensile strengths of 370 N/sq mm.
- This strength is approximately ten times greater than the compressive strength of medium concrete.
- Additionally, it is about one hundred times stronger in tensile strength compared to medium concrete.
- One of the notable advantages of steel is its ductility.
- This means that steel can stretch and change shape significantly before it breaks, as it starts to yield when it is subjected to a certain level of stress.
|
96 videos|367 docs|98 tests
|
FAQs on Mechanical Properties of Solids - Physics Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is stress in the context of elasticity? |  |
| 2. How is strain different from stress? |  |
| 3. What does Hooke's Law state about elastic materials? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of Young's Modulus of Elasticity? |  |
| 5. How does Poisson's Ratio relate to the deformation of materials? |  |

















