UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > History for UPSC CSE > Mind Map: Buddhism and Jainism
Mind Map: Buddhism and Jainism | History for UPSC CSE PDF Download
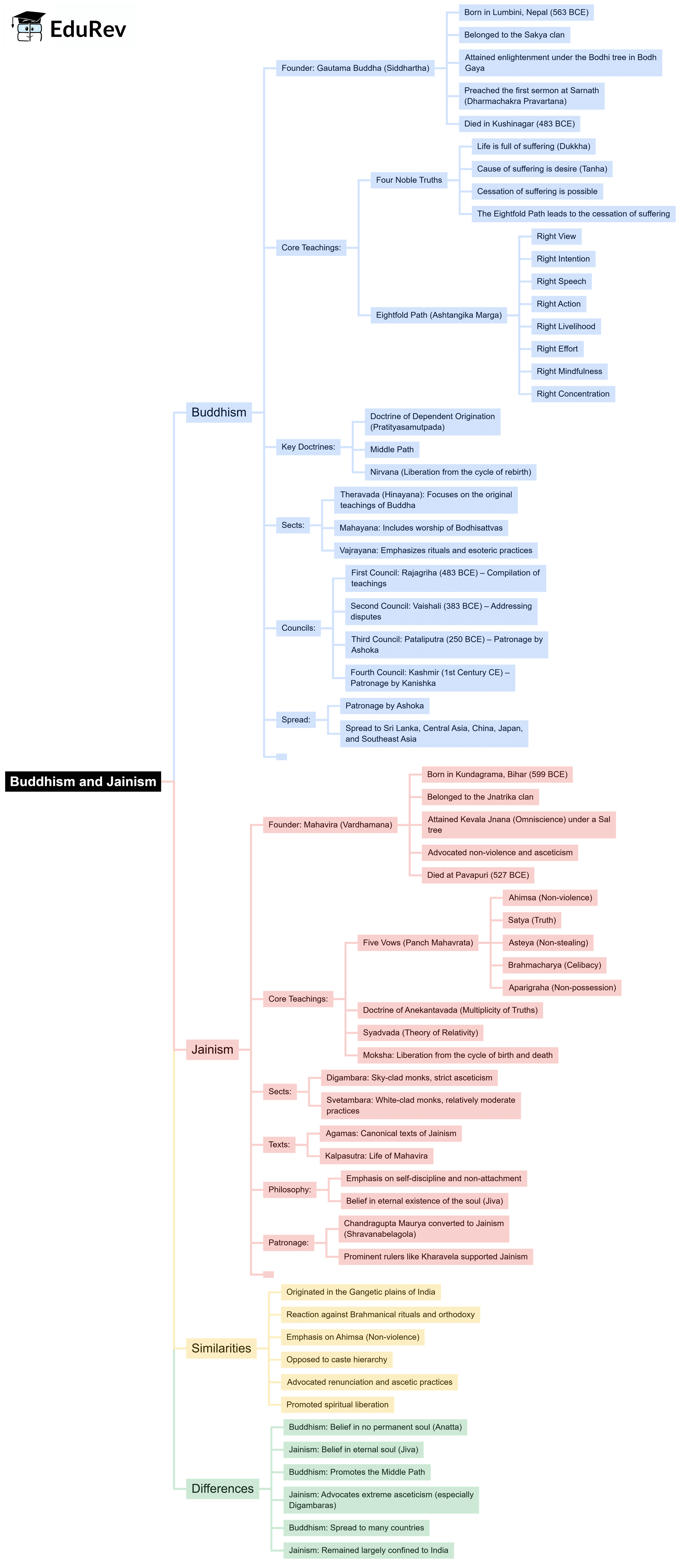
The document Mind Map: Buddhism and Jainism | History for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course History for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
210 videos|848 docs|219 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Buddhism and Jainism - History for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the main differences between Buddhism and Jainism? |  |
Ans. Buddhism and Jainism, while both originating in India and sharing some philosophical concepts, differ significantly in their beliefs and practices. Buddhism, founded by Siddhartha Gautama (the Buddha), emphasizes the Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold Path as a means to attain enlightenment and liberation from suffering. In contrast, Jainism, founded by Mahavira, places a strong emphasis on non-violence (ahimsa), truthfulness, and asceticism, advocating for the liberation of the soul from the cycle of birth and rebirth through strict ethical conduct and self-discipline.
| 2. How do Buddhism and Jainism view the concept of karma? |  |
Ans. Both Buddhism and Jainism believe in the concept of karma, which refers to the actions of individuals and their consequences. In Buddhism, karma is seen as a moral law governing cause and effect that influences future rebirths and experiences. The focus is on intention behind actions. Jainism, however, has a more detailed understanding of karma, viewing it as a tangible substance that attaches to the soul based on one's actions, thoughts, and words. Jains believe that the accumulation of karma can be reduced through rigorous ascetic practices and adherence to their ethical code.
| 3. What are the key teachings of Jainism that differ from those of Buddhism? |  |
Ans. Jainism emphasizes five main ethical principles known as the Five Great Vows (Mahavratas): ahimsa (non-violence), satya (truthfulness), asteya (non-stealing), brahmacharya (celibacy), and aparigraha (non-possessiveness). These principles guide Jains in their daily lives and spiritual practices. In contrast, while Buddhism also values ethical conduct, it does not enforce strict vows in the same way. Instead, it encourages following the Eightfold Path, which includes aspects like right understanding, right intention, and right livelihood, focusing more on the attainment of enlightenment rather than strict asceticism.
| 4. What role does meditation play in Buddhism and Jainism? |  |
Ans. Meditation is a crucial practice in both Buddhism and Jainism but serves different purposes. In Buddhism, meditation is a means to develop mindfulness, concentration, and insight, ultimately leading to enlightenment (nirvana). Various forms of meditation, such as Vipassana and Zen, are practiced to cultivate awareness and understanding of the nature of reality. In Jainism, meditation is also important, primarily for self-purification and spiritual development. Jains may engage in practices like Samayika (a period of meditation and reflection) to foster a peaceful state of mind and deepen their commitment to ethical living.
| 5. How do Buddhism and Jainism approach the concept of liberation (moksha)? |  |
Ans. Both Buddhism and Jainism seek liberation (moksha) but have different understandings of it. In Buddhism, moksha is referred to as nirvana, a state of liberation from the cycle of birth and rebirth (samsara) characterized by the cessation of suffering and desire. It is achieved through the realization of the Four Noble Truths and practicing the Eightfold Path. Jainism views moksha as the liberation of the soul from the cycle of samsara, attained through the complete elimination of karma via strict adherence to the Five Great Vows and intense spiritual practices. Jains believe that once liberated, the soul resides in a state of eternal bliss and knowledge.
Related Searches






















