CLAT Exam > CLAT Notes > Legal Reasoning for CLAT > Mind Map: Contract Law- 1
Mind Map: Contract Law- 1 | Legal Reasoning for CLAT PDF Download
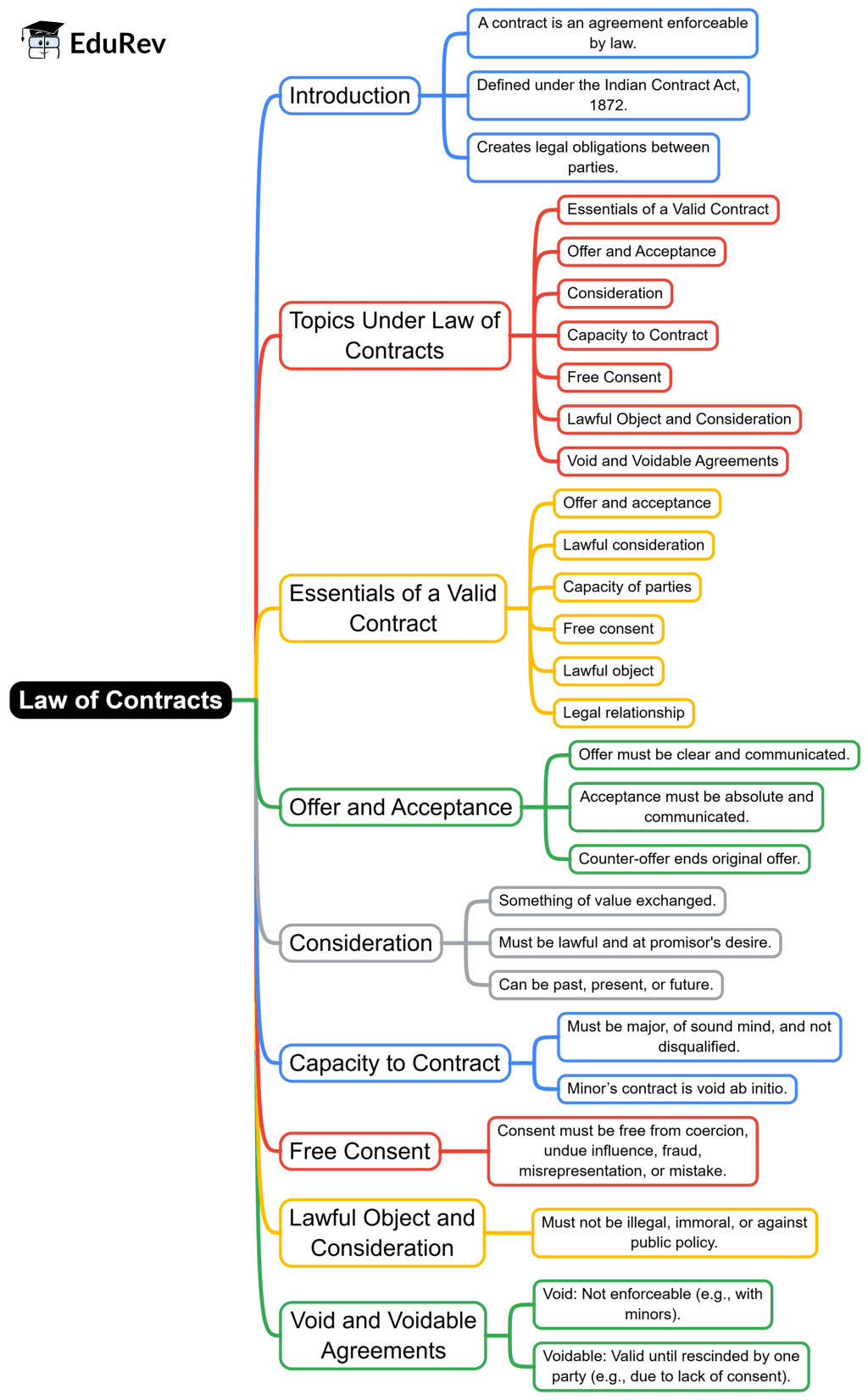
The document Mind Map: Contract Law- 1 | Legal Reasoning for CLAT is a part of the CLAT Course Legal Reasoning for CLAT.
All you need of CLAT at this link: CLAT
|
65 videos|181 docs|38 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Contract Law- 1 - Legal Reasoning for CLAT
| 1. What are the essential elements of a contract in contract law? |  |
Ans. The essential elements of a contract include offer, acceptance, consideration, capacity, and legality. An offer is a proposal made by one party to another, which must be clear and definite. Acceptance signifies agreement to the terms of the offer. Consideration refers to something of value exchanged between the parties. Both parties must have the capacity to enter into a contract, meaning they are of legal age and sound mind. Lastly, the contract's purpose must be legal and not against public policy.
| 2. How does the concept of consideration function in a contract? |  |
Ans. Consideration is a crucial element of a contract that involves a benefit or value exchanged between the parties. It can be in the form of money, services, goods, or a promise to do (or not do) something. For a contract to be valid, consideration must be present; it cannot be a gift or something that is not bargained for. Both parties must provide consideration for the contract to be enforceable.
| 3. What is the difference between void and voidable contracts? |  |
Ans. A void contract is one that is not legally enforceable from the moment it is created, meaning it has no legal effect. This can occur if the contract involves illegal activities or if one of the parties lacks the capacity to contract. A voidable contract, on the other hand, is valid and enforceable unless one party chooses to void it due to certain circumstances, such as misrepresentation or undue influence. In essence, a void contract is invalid, while a voidable contract can become invalid if one party decides to rescind it.
| 4. What are the common remedies for breach of contract? |  |
Ans. Common remedies for breach of contract include damages, specific performance, and rescission. Damages are a monetary compensation awarded to the injured party to cover losses incurred due to the breach. Specific performance is a court order requiring the breaching party to fulfill their contractual obligations. Rescission involves canceling the contract and restoring the parties to their pre-contractual positions. The chosen remedy often depends on the nature of the breach and the specific circumstances of the case.
| 5. How does the Statute of Frauds apply to contracts? |  |
Ans. The Statute of Frauds is a legal doctrine that requires certain types of contracts to be in writing to be enforceable. This generally includes contracts involving real estate, contracts that cannot be performed within one year, agreements to pay someone else's debt, and contracts for the sale of goods over a specified amount. The purpose of the Statute of Frauds is to prevent fraud and misunderstandings by ensuring that significant agreements are documented.
Related Searches





















