UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > UPSC Mains: Ethics, Integrity & Aptitude > Mind Map: Duties vs Rights
Mind Map: Duties vs Rights | UPSC Mains: Ethics, Integrity & Aptitude PDF Download
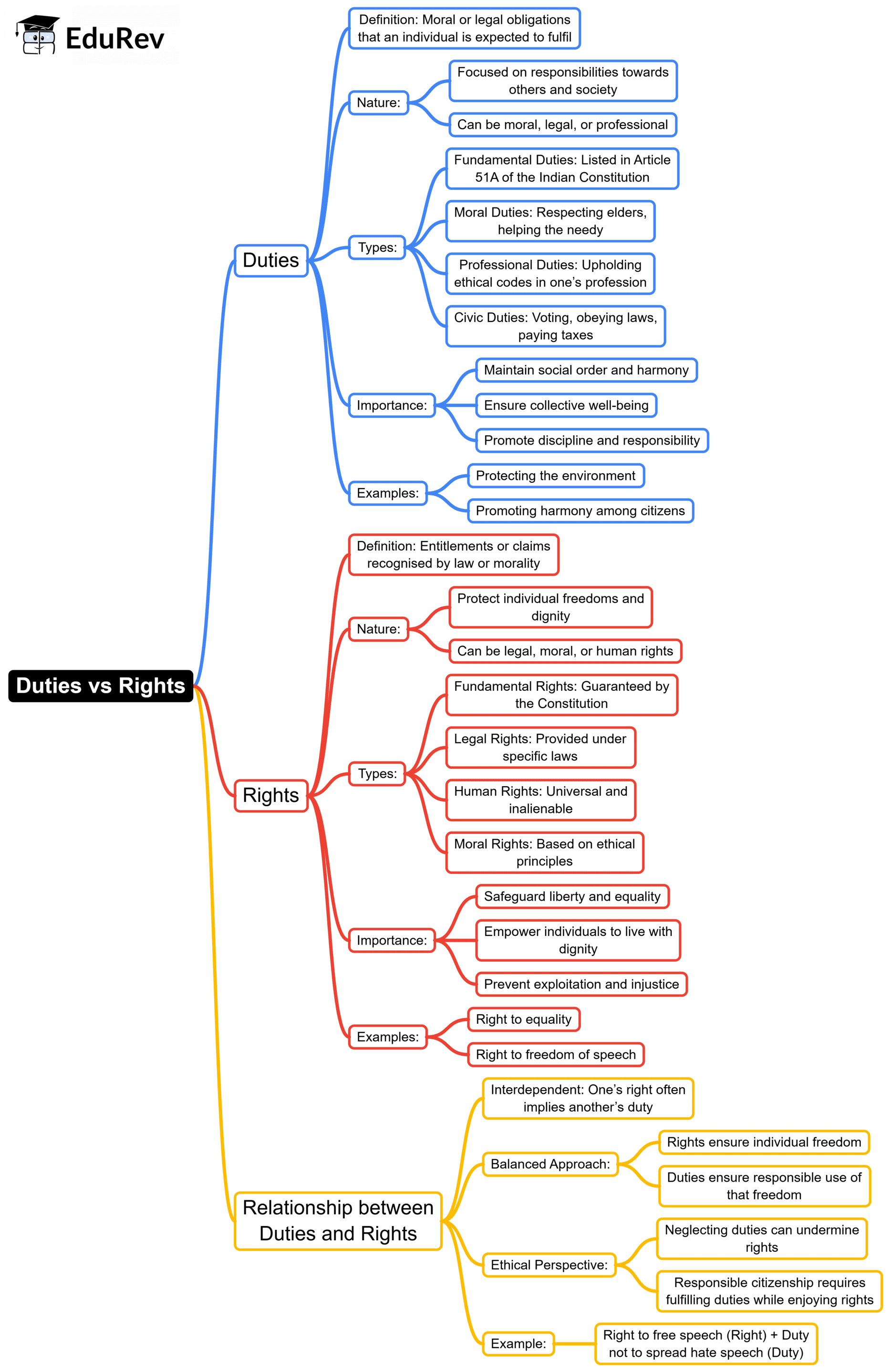
The document Mind Map: Duties vs Rights | UPSC Mains: Ethics, Integrity & Aptitude is a part of the UPSC Course UPSC Mains: Ethics, Integrity & Aptitude.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
78 videos|139 docs
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Duties vs Rights - UPSC Mains: Ethics, Integrity & Aptitude
| 1. What is the difference between duties and rights in the context of the Constitution? |  |
Ans. Duties refer to the responsibilities and obligations that individuals must fulfill as citizens, such as obeying laws, paying taxes, and respecting the rights of others. Rights, on the other hand, are the entitlements that individuals possess, allowing them to act in certain ways or to receive certain protections from the state, such as the right to free speech, the right to equality, and the right to privacy. Both duties and rights are essential to maintain a balanced and just society.
| 2. How do fundamental rights and duties complement each other in a democratic framework? |  |
Ans. Fundamental rights and duties are interrelated in a democracy. While fundamental rights empower individuals to pursue their interests and freedoms, fundamental duties remind citizens of their responsibilities towards society and the nation. This balance ensures that the exercise of rights does not infringe upon the rights of others and that citizens contribute positively to the societal framework, promoting harmony and cooperation.
| 3. Why are fundamental duties important for citizens in a democratic society? |  |
Ans. Fundamental duties are crucial because they promote responsible citizenship and encourage individuals to engage in activities that support the nation’s development. They foster a sense of belonging and accountability among citizens, ensuring that everyone contributes to the welfare of the community. By adhering to these duties, citizens help maintain law and order, promote social justice, and uphold the values enshrined in the Constitution.
| 4. Can fundamental rights be restricted, and under what circumstances? |  |
Ans. Yes, fundamental rights can be restricted under specific circumstances as outlined in the Constitution. Limitations may be imposed in the interest of public order, morality, health, or security of the state. However, such restrictions must be reasonable and cannot be arbitrary. The Constitution provides a framework for balancing individual rights with the collective interests of society.
| 5. What are the consequences of failing to fulfill one's duties as a citizen? |  |
Ans. Failing to fulfill one's duties as a citizen can lead to various consequences, including legal repercussions, social unrest, and a decline in civic responsibility. It may result in the erosion of rights, as the failure to uphold duties can compromise the rights of others and the stability of the state. Moreover, neglecting duties can weaken the democratic framework, making it challenging to address societal issues effectively.
Related Searches














