UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Indian Economy for UPSC CSE > Mind Map: External Sector in India
Mind Map: External Sector in India | Indian Economy for UPSC CSE PDF Download
External Sector in India - 1
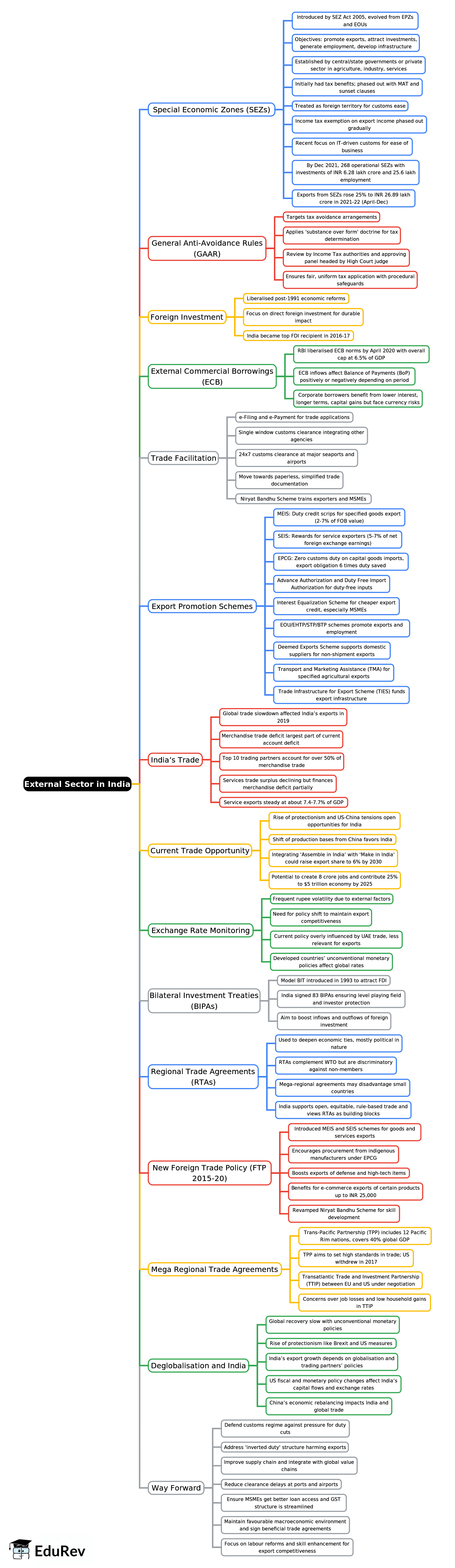
External Sector in India - 2
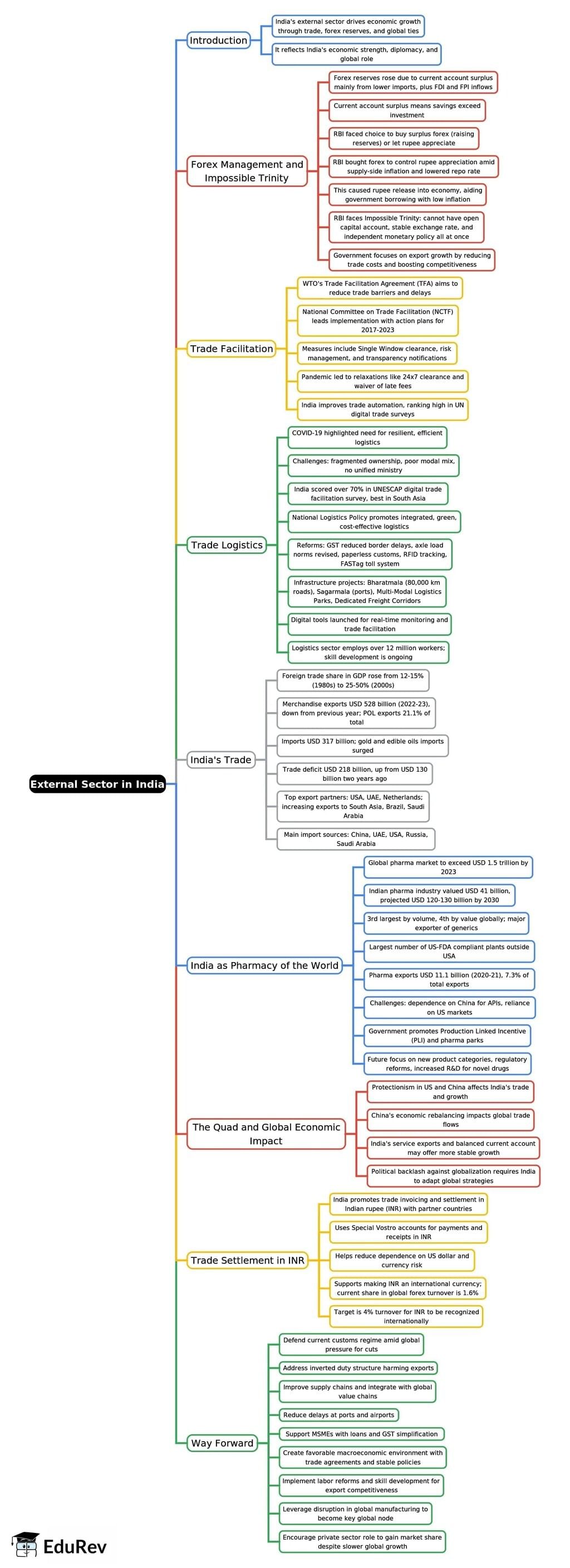
External Sector in India - 3
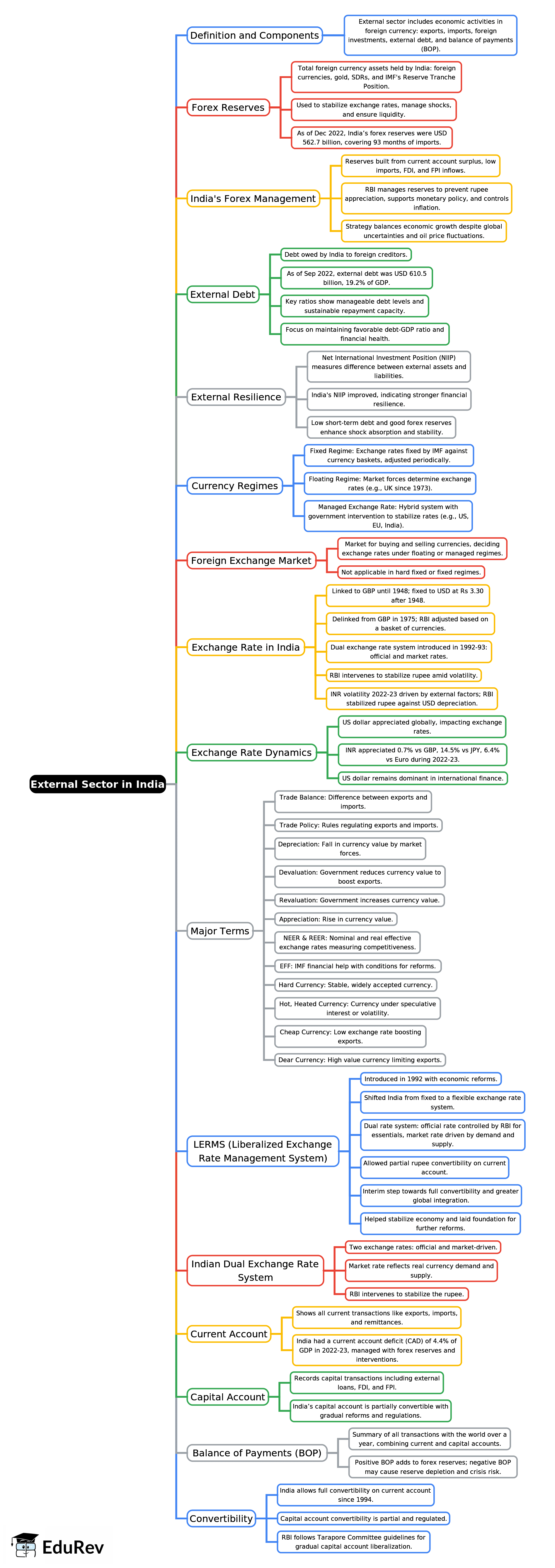
The document Mind Map: External Sector in India | Indian Economy for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Indian Economy for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
108 videos|430 docs|128 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: External Sector in India - Indian Economy for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the significance of the external sector in India's economy? |  |
Ans. The external sector plays a crucial role in India's economy as it encompasses international trade, foreign investment, and remittances. It influences the country’s balance of payments, foreign exchange reserves, and overall economic growth. A strong external sector can enhance foreign exchange availability, create job opportunities, and foster economic development through increased capital inflow.
| 2. How does India's balance of payments work? |  |
Ans. India's balance of payments (BOP) is a comprehensive record of all economic transactions between residents of India and the rest of the world over a specific period. It consists of the current account, which includes trade in goods and services, income, and current transfers, and the capital account, which records capital transfers and transactions in financial assets. A surplus in the current account indicates more foreign exchange inflow than outflow, while a deficit may require financing through capital account surpluses.
| 3. What are the main components of India's foreign trade? |  |
Ans. The main components of India's foreign trade include exports and imports of goods and services, which can be categorized into various sectors such as agriculture, textiles, machinery, and technology. Services, especially IT and software services, constitute a significant portion of exports. Imports primarily consist of crude oil, machinery, electronic goods, and precious metals. The trade balance, which is the difference between exports and imports, is a key indicator of economic health.
| 4. What role do remittances play in the external sector of India? |  |
Ans. Remittances are a vital component of India's external sector, significantly contributing to the national economy. They refer to the money sent back home by Indians working abroad. Remittances help in boosting household incomes, enhancing purchasing power, and providing a stable source of foreign exchange. They also play a critical role in reducing poverty and improving living standards in many regions of India.
| 5. How has India’s foreign direct investment (FDI) policy evolved over time? |  |
Ans. India’s foreign direct investment (FDI) policy has evolved to encourage foreign investments by liberalizing regulations and simplifying procedures. Initially, FDI was restricted to specific sectors and required government approval. Over time, policies have been relaxed, allowing 100% FDI in various sectors like retail, telecommunications, and defense under the automatic route. This evolution aims to attract more foreign capital, technology transfer, and enhance overall economic growth.
Related Searches





















