UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > PSIR Optional for UPSC > Mind Map: India's Contribution to NAM
Mind Map: India's Contribution to NAM | PSIR Optional for UPSC PDF Download
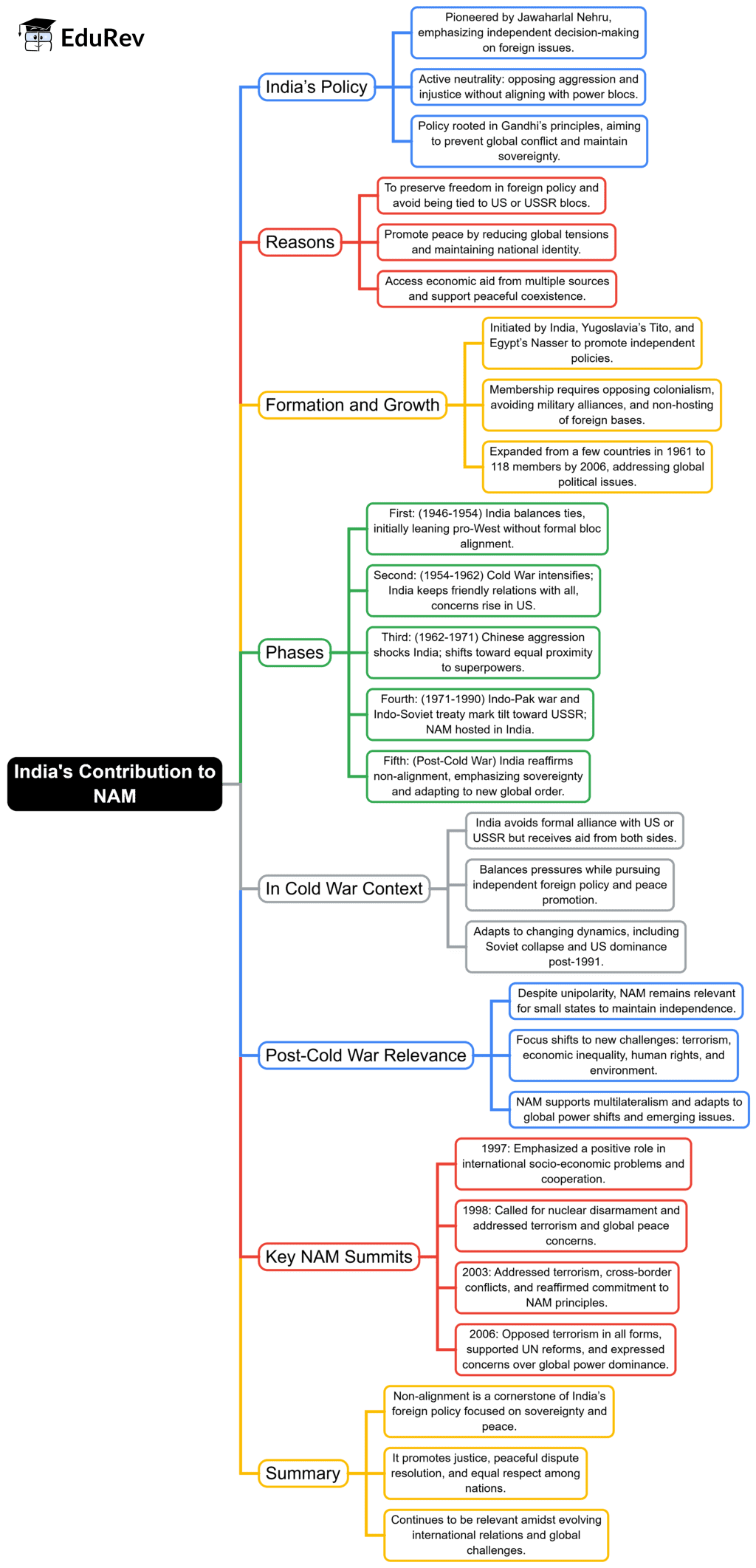
The document Mind Map: India's Contribution to NAM | PSIR Optional for UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course PSIR Optional for UPSC.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
173 videos|572 docs|148 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: India's Contribution to NAM - PSIR Optional for UPSC
| 1. What is the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) and what role has India played in it? |  |
Ans. The Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) is an international organization of states that are not formally aligned with or against any major power bloc. It was founded during the Cold War to provide a platform for countries that wanted to assert their independence and sovereignty while avoiding alignment with either the United States or the Soviet Union. India has been a founding member of NAM, playing a crucial role in shaping its principles and objectives, emphasizing peace, disarmament, and the pursuit of economic development.
| 2. How did India contribute to the establishment of NAM? |  |
Ans. India contributed to the establishment of NAM through its leadership under Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru, who, along with leaders from Egypt, Yugoslavia, and Indonesia, was instrumental in the formation of the movement. The first NAM summit was held in 1961 in Belgrade, where India advocated for the decolonization of nations, peaceful coexistence, and mutual respect among countries.
| 3. In what ways has India influenced NAM's agenda over the years? |  |
Ans. India has influenced NAM's agenda by consistently advocating for issues such as disarmament, anti-colonialism, and economic cooperation among developing nations. India has also pushed for reforms in international institutions to reflect the voices of developing countries. Through its active participation in NAM summits and initiatives, India has been able to shape discussions on global challenges like climate change, terrorism, and economic inequality.
| 4. What challenges does NAM face today, and how can India address them? |  |
Ans. NAM faces several challenges today, including geopolitical tensions, the rise of new power blocs, and the impact of globalization. India can address these challenges by reinforcing its leadership role within the movement, advocating for a collective approach to global issues, and promoting dialogue among member states. India can also enhance cooperation in areas such as technology transfer, trade, and sustainable development to strengthen NAM's relevance.
| 5. How has India's foreign policy towards NAM evolved in recent years? |  |
Ans. India's foreign policy towards NAM has evolved to reflect its broader strategic interests while maintaining its commitment to the movement's core principles. In recent years, India has sought to balance its relationships with major powers while engaging more actively with NAM countries on issues like climate change, health, and security. This evolution demonstrates India's commitment to multilateralism and its desire to play a key role in shaping a more equitable global order.
Related Searches





















