UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Indian Polity for UPSC CSE > Mind Map: Subordinate Courts
Mind Map: Subordinate Courts | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
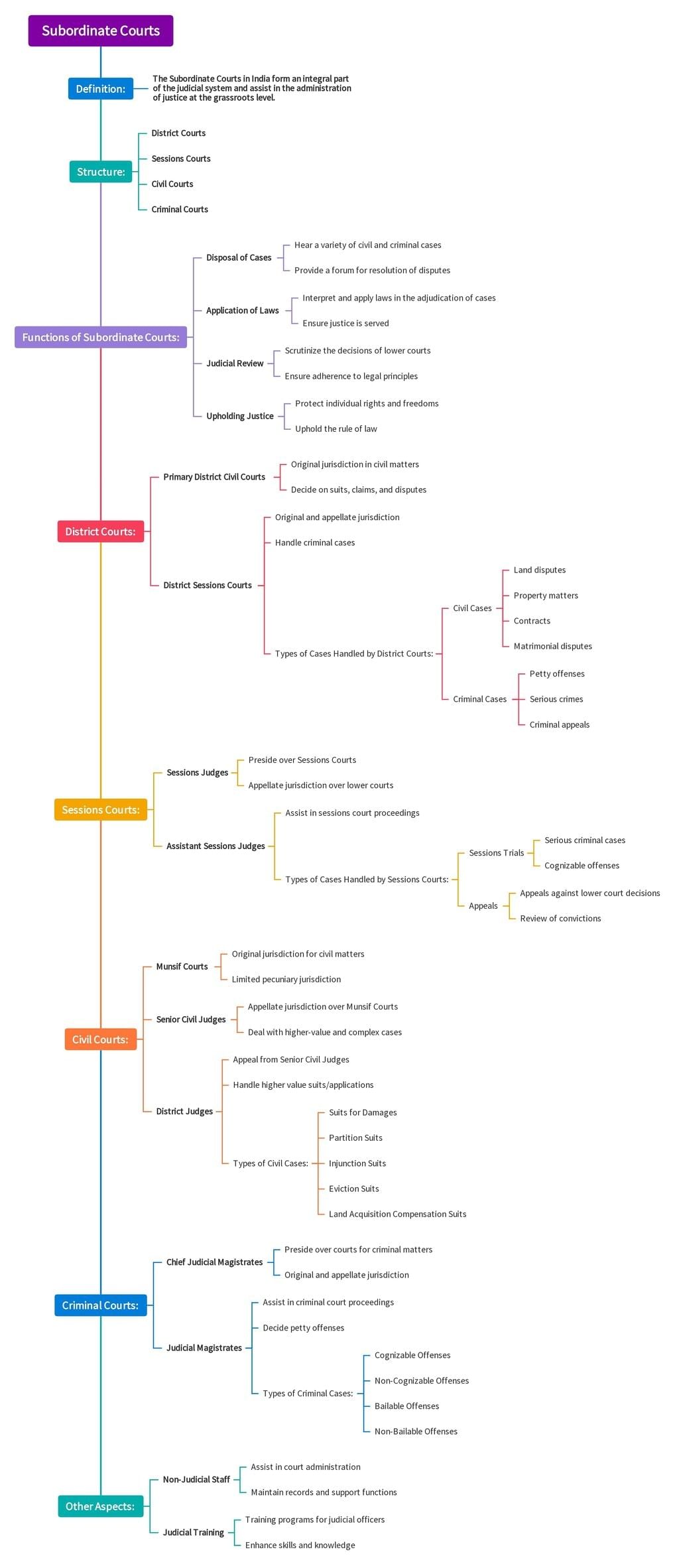
The document Mind Map: Subordinate Courts | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Indian Polity for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
154 videos|973 docs|260 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Subordinate Courts - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are subordinate courts? |  |
Ans. Subordinate courts are lower courts that exist below the higher or appellate courts in the judicial hierarchy. They primarily handle less serious criminal cases, civil disputes, and other legal matters that do not fall within the jurisdiction of higher courts.
| 2. What types of cases are typically heard in subordinate courts? |  |
Ans. Subordinate courts typically handle cases such as small claims, traffic violations, misdemeanor offenses, family disputes, and civil cases with lower monetary values. They play a crucial role in providing access to justice for the general public.
| 3. How are judges appointed in subordinate courts? |  |
Ans. The appointment of judges in subordinate courts varies from country to country. In some jurisdictions, judges are appointed by the executive branch or relevant judicial authorities, while in others, they may be elected or appointed through a combination of methods. The selection process aims to ensure the competence, impartiality, and integrity of the judges.
| 4. Can decisions made in subordinate courts be appealed? |  |
Ans. Yes, decisions made in subordinate courts can be appealed. If a party is dissatisfied with the judgment or ruling of a subordinate court, they can usually file an appeal to a higher court within a specified timeframe. The higher court will then review the case and determine whether any errors were made in the subordinate court's decision.
| 5. How do subordinate courts contribute to the overall judicial system? |  |
Ans. Subordinate courts play a critical role in the overall judicial system by providing a first level of legal recourse for individuals. They help alleviate the burden on higher courts by handling a large volume of cases, resolving disputes at a local level, and ensuring access to justice for all members of society.
Related Searches





















