UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Geography for UPSC CSE > Mind Map: Volcanism
Mind Map: Volcanism | Geography for UPSC CSE PDF Download
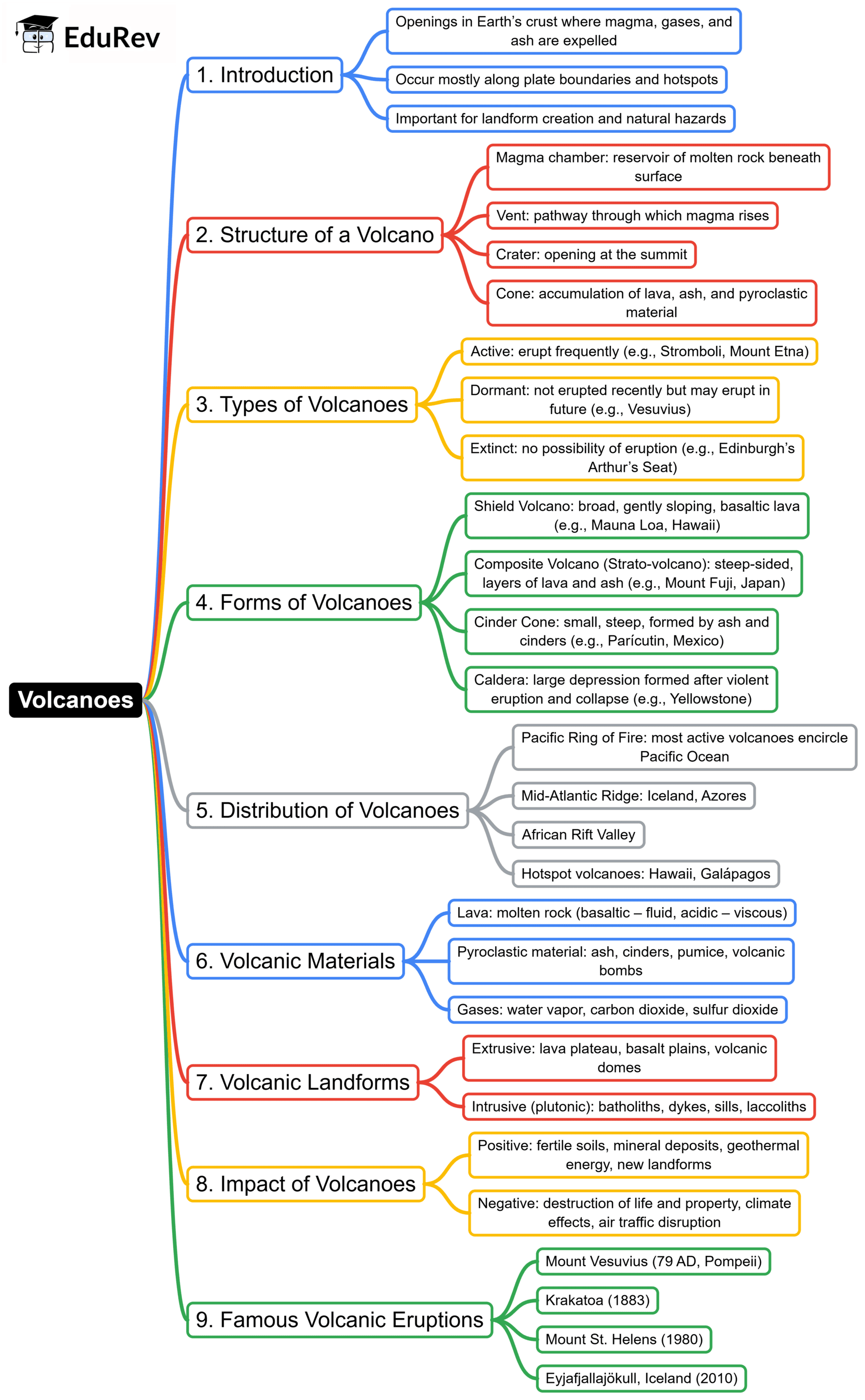
The document Mind Map: Volcanism | Geography for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Geography for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
263 videos|872 docs|232 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Volcanism - Geography for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is volcanism? |  |
Ans. Volcanism refers to the process of magma and volcanic gases being discharged onto the Earth's surface through volcanic eruptions. It involves the movement of molten rock, known as magma, from beneath the Earth's crust to the surface.
| 2. How are volcanoes formed? |  |
Ans. Volcanoes are formed when there is a weak spot in the Earth's crust, allowing magma to rise to the surface. This weak spot is often associated with tectonic plate boundaries, such as divergent or convergent plate boundaries. The magma eventually solidifies and builds up, forming a volcano.
| 3. What are the different types of volcanoes? |  |
Ans. There are several types of volcanoes, including stratovolcanoes (composite volcanoes), shield volcanoes, cinder cone volcanoes, and calderas. Stratovolcanoes are tall, steep-sided volcanoes made up of layers of ash, lava, and volcanic rocks. Shield volcanoes, on the other hand, have gentle slopes and are primarily composed of lava. Cinder cone volcanoes are small and are formed by explosive eruptions, while calderas are large volcanic craters formed by the collapse of a volcano after a massive eruption.
| 4. What are the main hazards associated with volcanic eruptions? |  |
Ans. Volcanic eruptions can pose various hazards, including ashfall, pyroclastic flows, lava flows, lahars (mudflows), and volcanic gases. Ashfall can disrupt air travel, cause respiratory problems, and damage crops and infrastructure. Pyroclastic flows are fast-moving currents of hot gas, ash, and volcanic fragments that can devastate everything in their path. Lava flows can destroy buildings and infrastructure, while lahars can result in flash floods and debris flows. Volcanic gases, such as sulfur dioxide, can have detrimental effects on human health and the environment.
| 5. Can volcanic eruptions be predicted? |  |
Ans. While scientists can monitor volcanic activity and detect signs of an impending eruption, accurately predicting when a volcano will erupt is extremely challenging. Monitoring techniques involve the use of seismometers to detect ground vibrations, gas sensors to measure volcanic gases, and satellite imagery to monitor changes in the volcano's shape. However, volcanic eruptions are complex geological events influenced by numerous factors, making precise predictions difficult.
Related Searches






















