UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Geography for UPSC CSE > Mind Map: Vulcanism and Earth Quakes
Mind Map: Vulcanism and Earth Quakes | Geography for UPSC CSE PDF Download
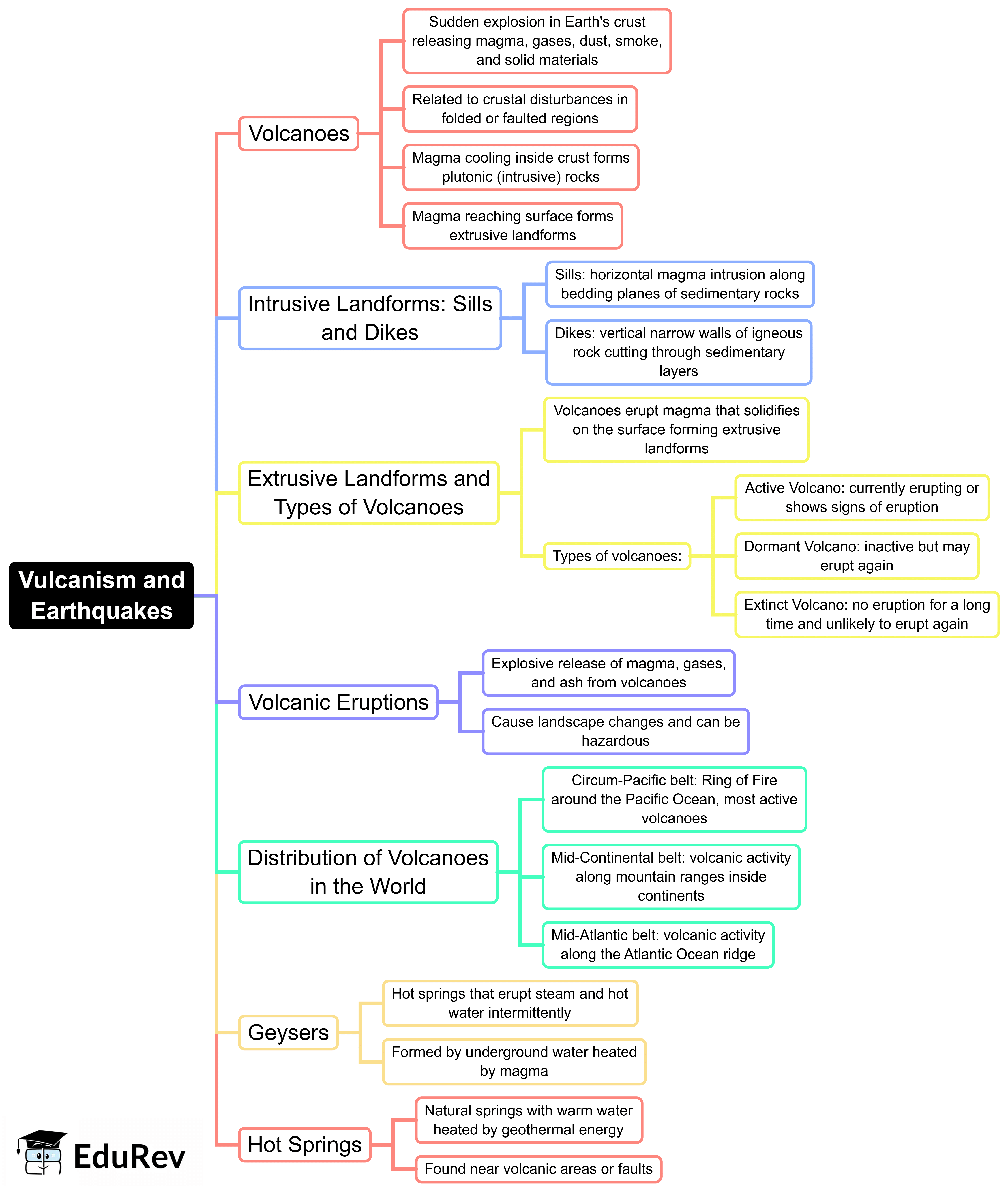
The document Mind Map: Vulcanism and Earth Quakes | Geography for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Geography for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
175 videos|619 docs|192 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Vulcanism and Earth Quakes - Geography for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the difference between volcanism and earthquakes? |  |
Ans. Volcanism refers to the processes and phenomena associated with the movement of molten rock (magma) from beneath the Earth's crust to its surface, resulting in volcanic eruptions. Earthquakes, on the other hand, occur due to the sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust, creating seismic waves. While volcanism is primarily linked to tectonic activity and magma movement, earthquakes are often caused by tectonic plate movements, faults, and other geological stresses.
| 2. What are the main types of volcanic eruptions? |  |
Ans. The main types of volcanic eruptions include effusive eruptions, explosive eruptions, and phreatomagmatic eruptions. Effusive eruptions involve the steady flow of lava, resulting in the formation of shield volcanoes. Explosive eruptions are characterized by violent explosions that can produce ash clouds and pyroclastic flows, often associated with stratovolcanoes. Phreatomagmatic eruptions occur when magma interacts with water, leading to steam explosions and the fragmentation of the magma.
| 3. How are earthquakes measured and classified? |  |
Ans. Earthquakes are measured using seismographs, which record the seismic waves generated by the earthquake. The magnitude of an earthquake is commonly classified using the Richter scale or the moment magnitude scale (Mw). The Richter scale measures the amplitude of seismic waves, while the moment magnitude scale takes into account the area of the fault that slipped and the amount of slip. Earthquakes are classified into categories such as minor, light, moderate, strong, major, and great based on their magnitude.
| 4. What are the primary causes of earthquakes? |  |
Ans. The primary causes of earthquakes include tectonic plate movements, volcanic activity, and human activities such as mining and reservoir-induced seismicity. Tectonic earthquakes occur when stress builds up along fault lines due to the movement of tectonic plates. Volcanic earthquakes are associated with volcanic activity, where magma movement creates seismic waves. Human-induced earthquakes can result from activities like drilling, fracking, and the filling of large reservoirs.
| 5. What are the impacts of volcanic eruptions and earthquakes on human life and the environment? |  |
Ans. Volcanic eruptions can lead to devastating effects, including loss of life, destruction of infrastructure, and long-term environmental changes such as ash fallout and climate alteration. Earthquakes can cause widespread damage, including building collapses, landslides, and tsunamis, depending on their magnitude and location. Both phenomena can result in significant economic losses, displacement of populations, and long-lasting ecological impacts, necessitating disaster preparedness and response strategies.
Related Searches
















