UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Public Administration Optional for UPSC (Notes) > Mind Map: Evolution of Indian Administration
Mind Map: Evolution of Indian Administration | Public Administration Optional for UPSC (Notes) PDF Download
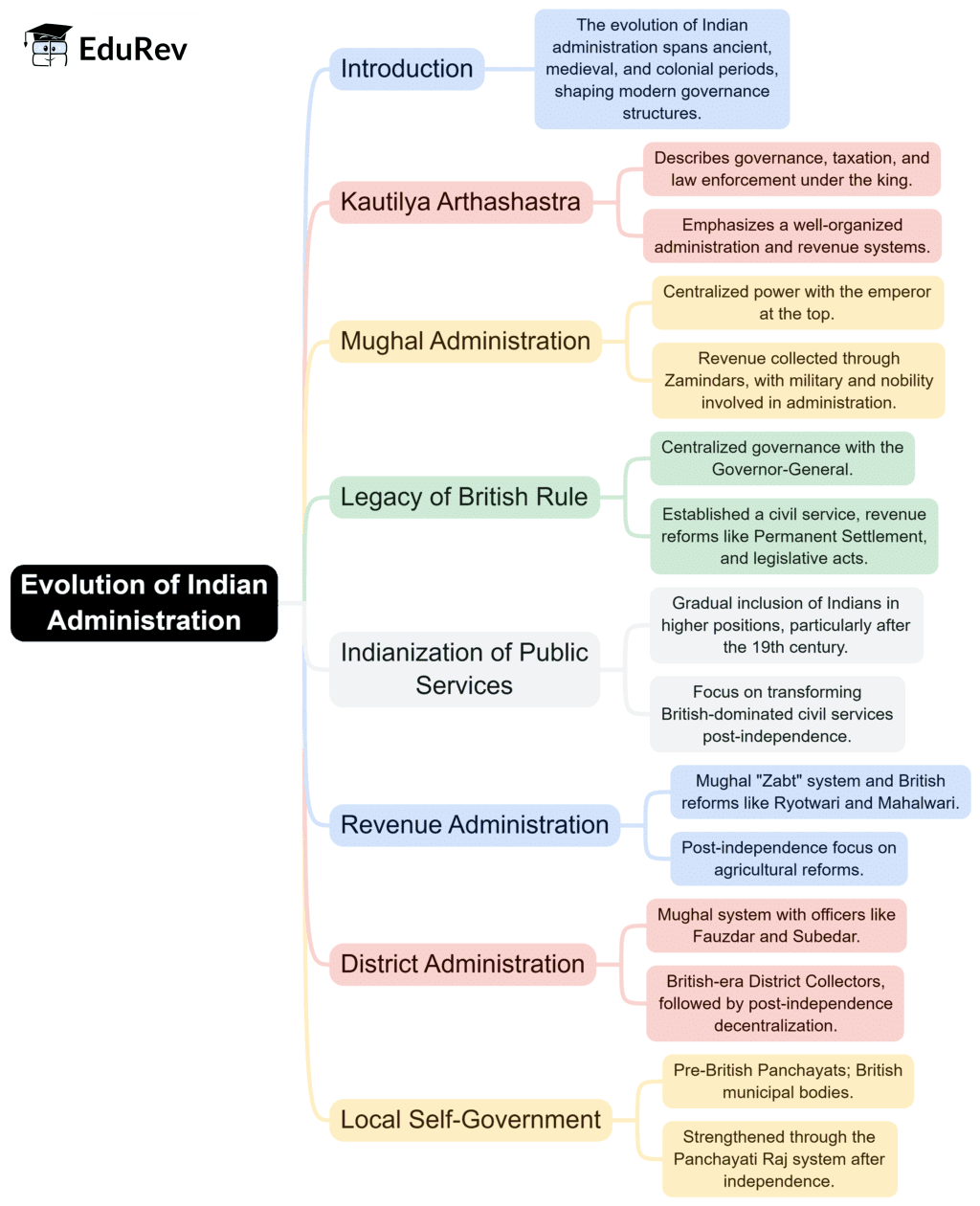
The document Mind Map: Evolution of Indian Administration | Public Administration Optional for UPSC (Notes) is a part of the UPSC Course Public Administration Optional for UPSC (Notes).
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
58 videos|242 docs
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Evolution of Indian Administration - Public Administration Optional for UPSC (Notes)
| 1. What are the key phases in the evolution of Indian administration? |  |
Ans. The evolution of Indian administration can be broadly divided into several key phases:
1. Ancient Period: Administrative systems were largely influenced by the Mauryan and Gupta empires, focusing on centralized governance and local self-governance.
2. Medieval Period: The administration saw the introduction of various regional kingdoms, with diverse administrative practices under rulers like the Mughals, who emphasized a bureaucratic structure.
3. Colonial Period: The British Raj introduced significant changes, including the establishment of a centralized administration, codification of laws, and the introduction of various civil services.
4. Post-Independence: After 1947, India adopted a democratic framework, leading to a reformation of the administrative structure to align with constitutional mandates, focusing on decentralization and public service.
| 2. How did the British Raj influence Indian administration? |  |
Ans. The British Raj had a profound influence on Indian administration through the introduction of a structured bureaucratic system, the establishment of the Indian Civil Service (ICS), and the codification of laws. The British emphasized a centralized administration that often disregarded local traditions and governance structures. This led to the introduction of new legal frameworks and policies that affected various aspects of governance, including revenue collection, law enforcement, and civil rights. The legacy of these changes is still evident in contemporary Indian administrative practices.
| 3. What is the role of the Indian Civil Service in the evolution of administration? |  |
Ans. The Indian Civil Service (ICS) was established during the British colonial period and has played a crucial role in shaping the administrative landscape of India. It was responsible for implementing policies, maintaining law and order, and managing public services. After independence, the ICS was restructured into the Indian Administrative Service (IAS), which continues to be pivotal in governance. The IAS is responsible for policy formulation, implementation, and administration at various levels of government, ensuring that the democratic principles of the Constitution are upheld.
| 4. What are the major reforms in Indian administration post-independence? |  |
Ans. Post-independence, several major reforms were initiated to improve Indian administration, including:
1. Constitutional Framework: Establishment of a democratic framework with the Constitution of India, emphasizing fundamental rights and duties.
2. Decentralization: Introduction of Panchayati Raj institutions to empower local governance and enhance grassroots participation.
3. Administrative Reforms: Various committees, such as the Kothari Commission, recommended improvements in education and bureaucracy.
4. E-Governance: The adoption of technology in administration for better service delivery and transparency.
These reforms aimed to create a more responsive, accountable, and efficient administrative system.
| 5. How has technology impacted Indian administration in recent years? |  |
Ans. Technology has significantly impacted Indian administration by enhancing efficiency and transparency. The introduction of e-governance initiatives has made public services more accessible to citizens. Online platforms for services such as land records, tax payments, and grievance redressal have streamlined processes and reduced corruption. Additionally, data analytics and digital tools have improved decision-making and policy implementation, allowing for better resource management and citizen engagement in governance.
Related Searches





















