CLAT Exam > CLAT Notes > Legal Reasoning for CLAT > Mind Map: General Data Protection Regulation
Mind Map: General Data Protection Regulation | Legal Reasoning for CLAT PDF Download
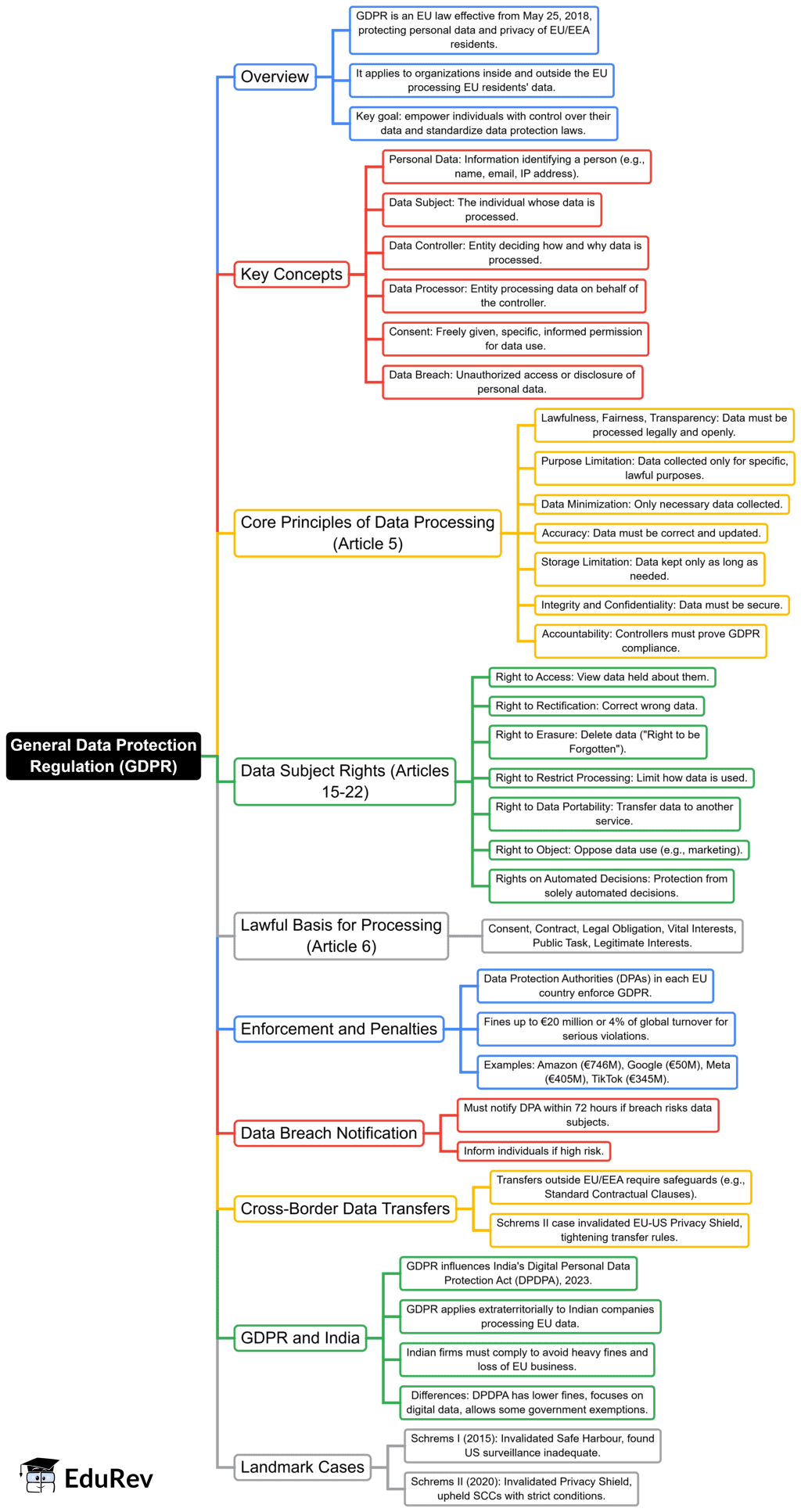
The document Mind Map: General Data Protection Regulation | Legal Reasoning for CLAT is a part of the CLAT Course Legal Reasoning for CLAT.
All you need of CLAT at this link: CLAT
|
65 videos|181 docs|38 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: General Data Protection Regulation - Legal Reasoning for CLAT
| 1. What is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)? |  |
Ans. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a comprehensive data protection law in the European Union that came into effect on May 25, 2018. It aims to enhance individuals' control over their personal data and unify data protection regulations across Europe. The GDPR sets strict guidelines for the collection, storage, processing, and sharing of personal data, ensuring transparency and privacy for EU citizens.
| 2. Who does the GDPR apply to? |  |
Ans. The GDPR applies to all organizations that process the personal data of individuals residing in the European Union, regardless of where the organization is based. This includes businesses, government agencies, and non-profits. It also applies to entities outside the EU if they offer goods or services to, or monitor the behavior of, EU residents.
| 3. What are the main rights granted to individuals under the GDPR? |  |
Ans. The GDPR grants several key rights to individuals, including the right to access their personal data, the right to rectification (correcting inaccurate data), the right to erasure (the “right to be forgotten”), the right to restrict processing, the right to data portability, and the right to object to processing. These rights aim to empower individuals and give them more control over their personal information.
| 4. What are the penalties for non-compliance with the GDPR? |  |
Ans. Organizations that fail to comply with the GDPR can face hefty fines of up to €20 million or 4% of their annual global revenue, whichever is higher. In addition to financial penalties, non-compliance can also result in reputational damage and loss of customer trust.
| 5. How does the GDPR affect businesses operating in multiple countries? |  |
Ans. Businesses operating in multiple countries must ensure compliance with the GDPR when processing personal data of EU residents. This means they need to implement data protection measures in accordance with GDPR standards, regardless of their physical location. Organizations may also need to appoint a representative in the EU if they are not established there, to ensure they can respond to inquiries from EU regulators.
Related Searches
















