UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Indian Polity for UPSC CSE > Mind Map: Judicial Review
Mind Map: Judicial Review | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
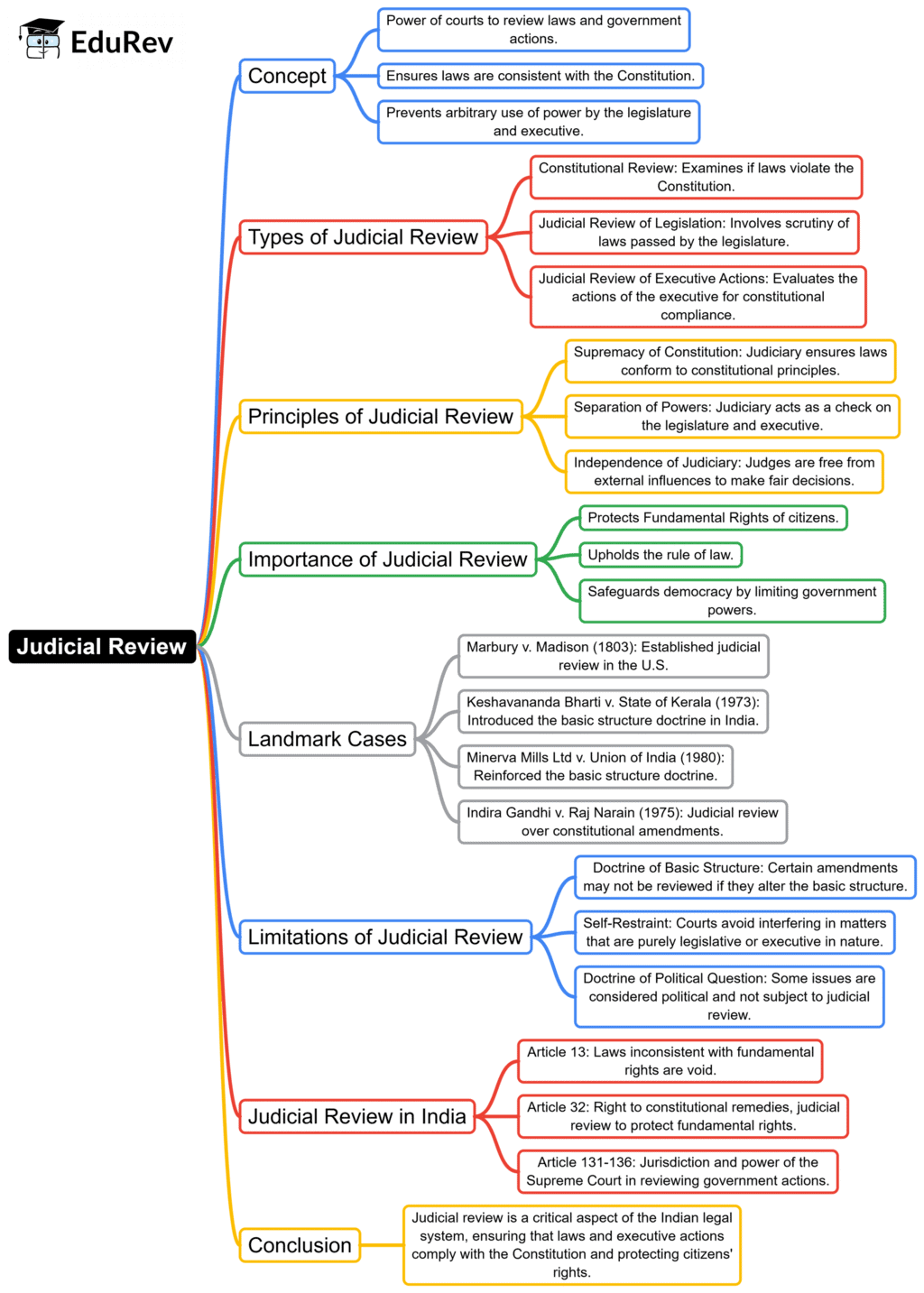
The document Mind Map: Judicial Review | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Indian Polity for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
154 videos|998 docs|260 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Judicial Review - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is judicial review and why is it important in a democratic system? |  |
Ans. Judicial review is the power of courts to assess the constitutionality of legislative and executive actions. It is crucial in a democratic system as it ensures that laws and policies comply with the constitution, protecting citizens' rights and maintaining the rule of law. By allowing courts to invalidate unconstitutional laws, judicial review serves as a check on government power, preventing abuse and safeguarding democracy.
| 2. How does the process of judicial review work in the context of the Indian legal system? |  |
Ans. In the Indian legal system, judicial review is exercised by the Supreme Court and High Courts. When a law or executive order is challenged, the courts review the case to determine its compliance with the Constitution. If found unconstitutional, the court can strike down the law. This process involves petitions filed by individuals or groups, and the courts may interpret constitutional provisions to uphold fundamental rights or assess the legality of government actions.
| 3. What are the key landmark cases that shaped judicial review in India? |  |
Ans. Several landmark cases have significantly shaped judicial review in India. Notable among them are the Kesavananda Bharati case, which established the Basic Structure doctrine, and the Minerva Mills case, which reinforced the importance of judicial review in protecting fundamental rights. These cases underscored the judiciary's role in maintaining the balance of power among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches of government.
| 4. What are the limitations of judicial review in India? |  |
Ans. While judicial review is a vital aspect of the Indian legal framework, it has limitations. The judiciary cannot interfere in matters of policy or legislation that fall within the purview of the legislature unless they violate constitutional provisions. Additionally, the principle of separation of powers restricts the judiciary from overstepping its authority, ensuring that it does not encroach upon the functions of the other branches of government.
| 5. How does judicial review differ from constitutional interpretation? |  |
Ans. Judicial review and constitutional interpretation are related but distinct concepts. Judicial review involves evaluating the legality of laws and government actions against the Constitution, while constitutional interpretation refers to the process of elucidating the meaning and scope of constitutional provisions. Judicial review can involve constitutional interpretation, but it specifically focuses on the validity of actions or laws rather than merely explaining constitutional texts.
Related Searches





















