UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests) > Mind Map: Nazism and the rise of Hitler
Mind Map: Nazism and the rise of Hitler | Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests) PDF Download
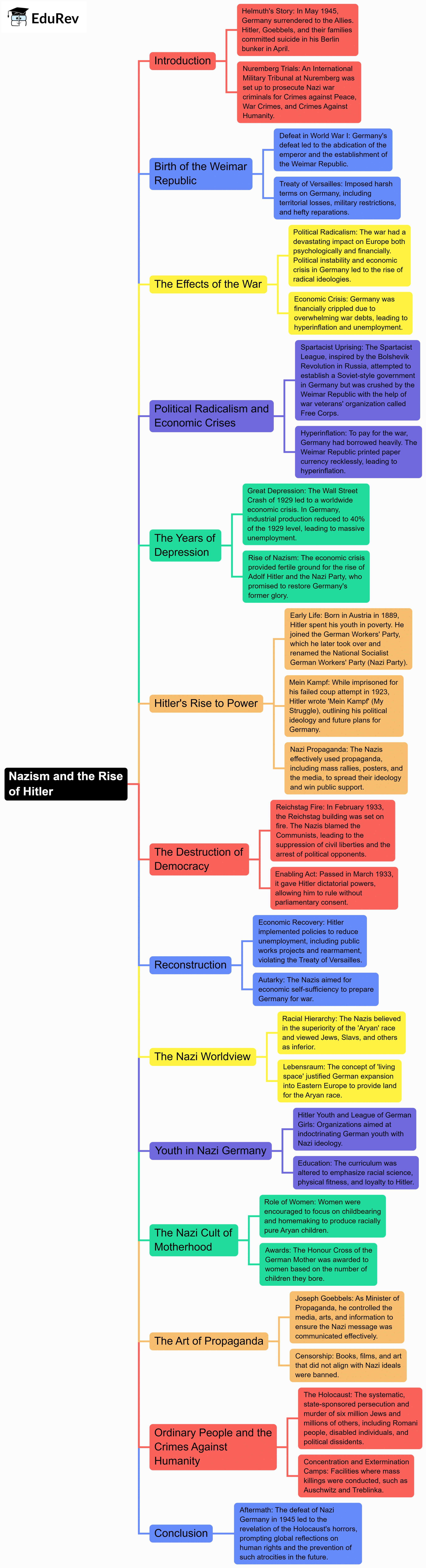
The document Mind Map: Nazism and the rise of Hitler | Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests) is a part of the UPSC Course Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests).
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
743 videos|1444 docs|633 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Nazism and the rise of Hitler - Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests)
| 1. What were the main factors that led to the rise of Nazism in Germany? |  |
Ans. The rise of Nazism in Germany can be attributed to several key factors, including the economic devastation caused by World War I, the harsh terms of the Treaty of Versailles, and widespread social unrest. Hyperinflation in the early 1920s and the Great Depression in 1929 further exacerbated economic hardships, leading many Germans to lose faith in traditional political parties. The Nazi Party, led by Adolf Hitler, capitalized on this discontent by promoting nationalistic and anti-Semitic ideologies, promising to restore Germany's former glory.
| 2. How did Adolf Hitler gain power in Germany? |  |
Ans. Adolf Hitler gained power through a combination of political maneuvering and the exploitation of economic and social crises. Initially, he was appointed Chancellor in January 1933. Following the Reichstag Fire, he pushed through the Reichstag Fire Decree and the Enabling Act, which allowed him to legislate without parliamentary consent. These actions effectively dismantled the democratic framework of the Weimar Republic, enabling Hitler to establish a totalitarian regime.
| 3. What role did propaganda play in the rise of Nazism? |  |
Ans. Propaganda was crucial to the rise of Nazism, as it was used to manipulate public perception and consolidate power. The Nazi regime employed various media, including newspapers, films, and rallies, to spread its ideologies and create a cult of personality around Hitler. Joseph Goebbels, the Minister of Propaganda, orchestrated campaigns that glorified the Nazi Party and demonized its enemies, particularly Jews, which helped garner widespread support for their policies.
| 4. What were the consequences of Hitler's policies for Germany and Europe? |  |
Ans. Hitler's policies led to catastrophic consequences for Germany and Europe, including the instigation of World War II, which resulted in the deaths of millions. The aggressive expansionist policies and military conquests devastated numerous countries. Furthermore, the implementation of anti-Semitic laws culminated in the Holocaust, where six million Jews were systematically murdered. Ultimately, these actions led to Germany's defeat in 1945 and significant geopolitical changes in Europe.
| 5. How did the international community respond to the rise of Nazism? |  |
Ans. The international community's response to the rise of Nazism was initially marked by appeasement and inaction. Many countries, still reeling from World War I, were reluctant to confront Hitler's aggressive policies. The Munich Agreement of 1938, which allowed Hitler to annex parts of Czechoslovakia, exemplified this approach. However, as Nazi actions became increasingly aggressive and expansionist, culminating in the invasion of Poland in 1939, the international community was forced to respond, leading to the outbreak of World War II.
Related Searches






















