UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Indian Economy for UPSC CSE > Mind Map: Security Market in India
Mind Map: Security Market in India | Indian Economy for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Security Market in India - 1
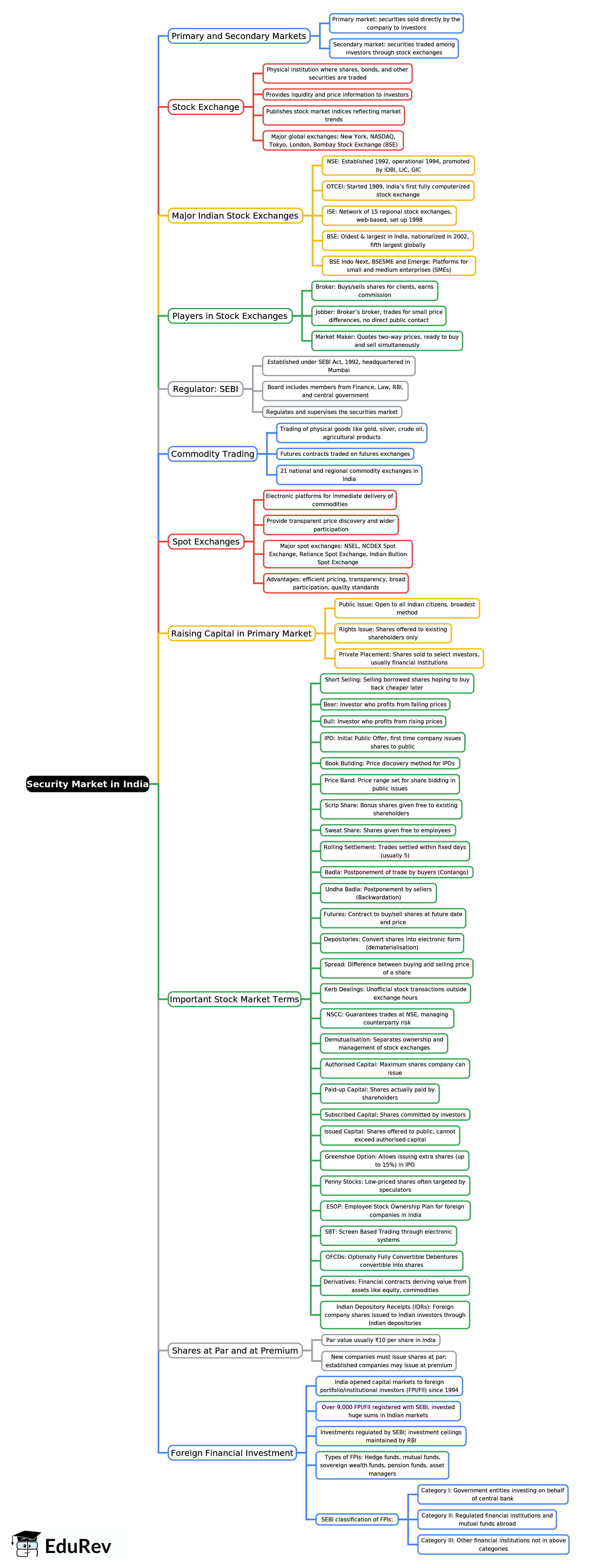
Security Market in India - 2
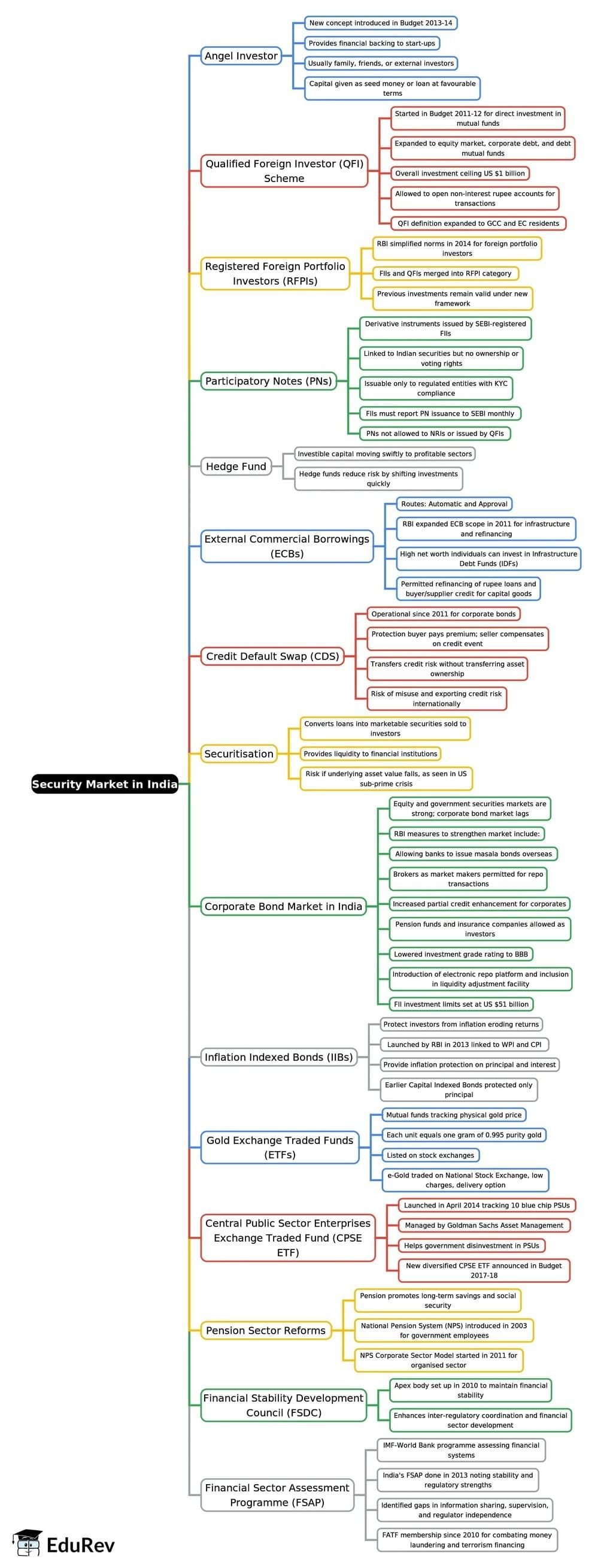
Security Market in India - 3
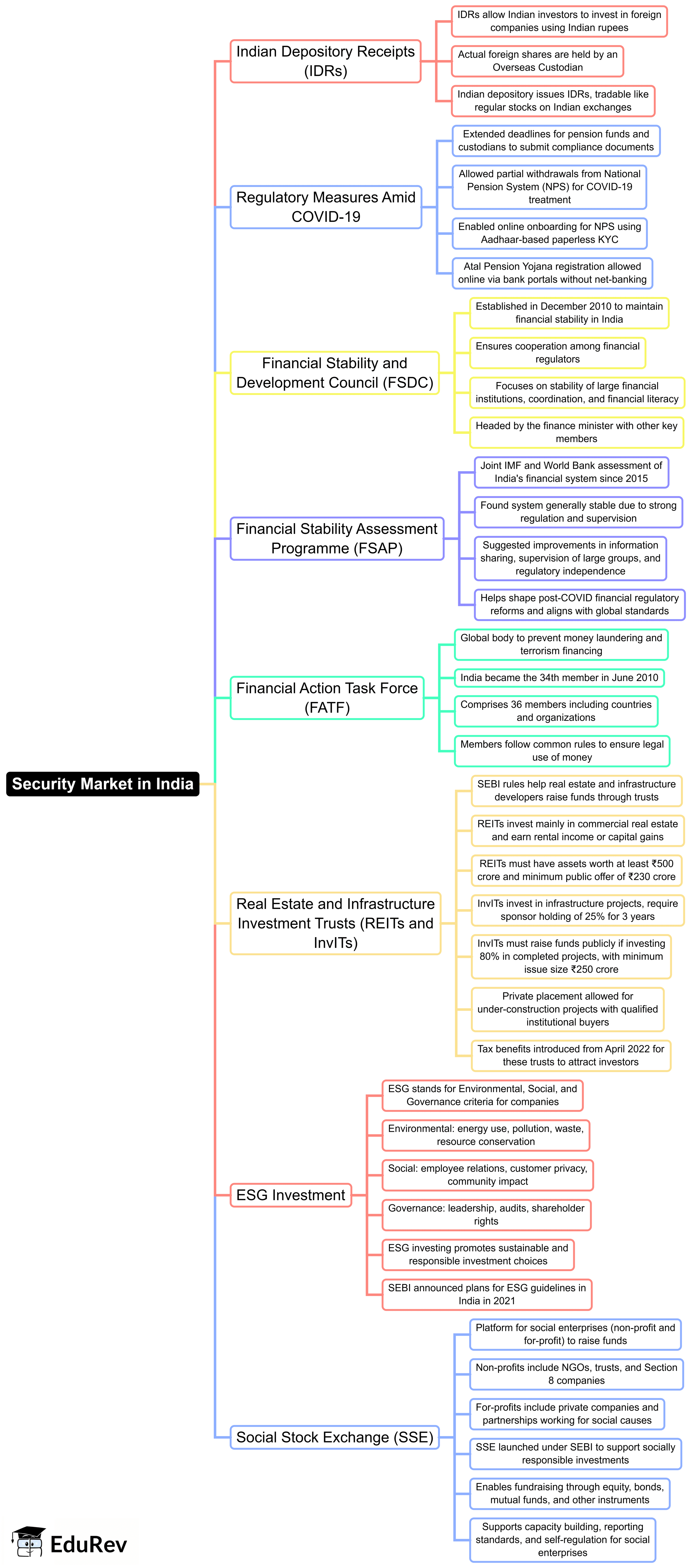
The document Mind Map: Security Market in India | Indian Economy for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Indian Economy for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
108 videos|425 docs|128 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Security Market in India - Indian Economy for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the key components of the security market in India? |  |
Ans. The key components of the security market in India include stock exchanges, stockbrokers, investors, and various financial instruments such as stocks, bonds, and derivatives. The primary stock exchanges in India are the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) and the National Stock Exchange (NSE). These platforms facilitate the buying and selling of securities, contributing to capital formation and liquidity in the market.
| 2. How is the regulatory framework structured for the security market in India? |  |
Ans. The regulatory framework for the security market in India is primarily governed by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI). SEBI was established to protect investor interests, regulate the securities market, and promote its development. It formulates rules and regulations for market participants, oversees stock exchanges, and enforces compliance to ensure transparency and fairness in trading activities.
| 3. What role do Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) play in the Indian security market? |  |
Ans. Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) play a significant role in the Indian security market by providing capital and liquidity. Their investments can lead to increased market depth and can positively influence stock prices. FIIs are subject to certain regulations and limits on their investments, and their participation often reflects international confidence in the Indian economy.
| 4. What are the risks associated with investing in the security market in India? |  |
Ans. Investing in the security market in India involves various risks, including market risk, credit risk, liquidity risk, and regulatory risk. Market risk arises from fluctuations in stock prices due to economic changes or investor sentiment. Credit risk pertains to the possibility of default by issuers of securities, while liquidity risk involves the difficulty of selling securities without affecting their price. Regulatory risk involves changes in laws or regulations that could impact market operations.
| 5. How has the security market in India evolved over the years? |  |
Ans. The security market in India has evolved significantly, particularly since the liberalization of the economy. Key milestones include the introduction of electronic trading, the establishment of the National Stock Exchange, and the implementation of various reforms by SEBI to enhance transparency and investor protection. This evolution has led to increased participation from retail and institutional investors, making the market more dynamic and accessible.
Related Searches





















