NEET Exam > NEET Notes > Physics Class 11 > Mind Map: Systems of particles and Rotational Motion
Mind Map: Systems of particles and Rotational Motion | Physics Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
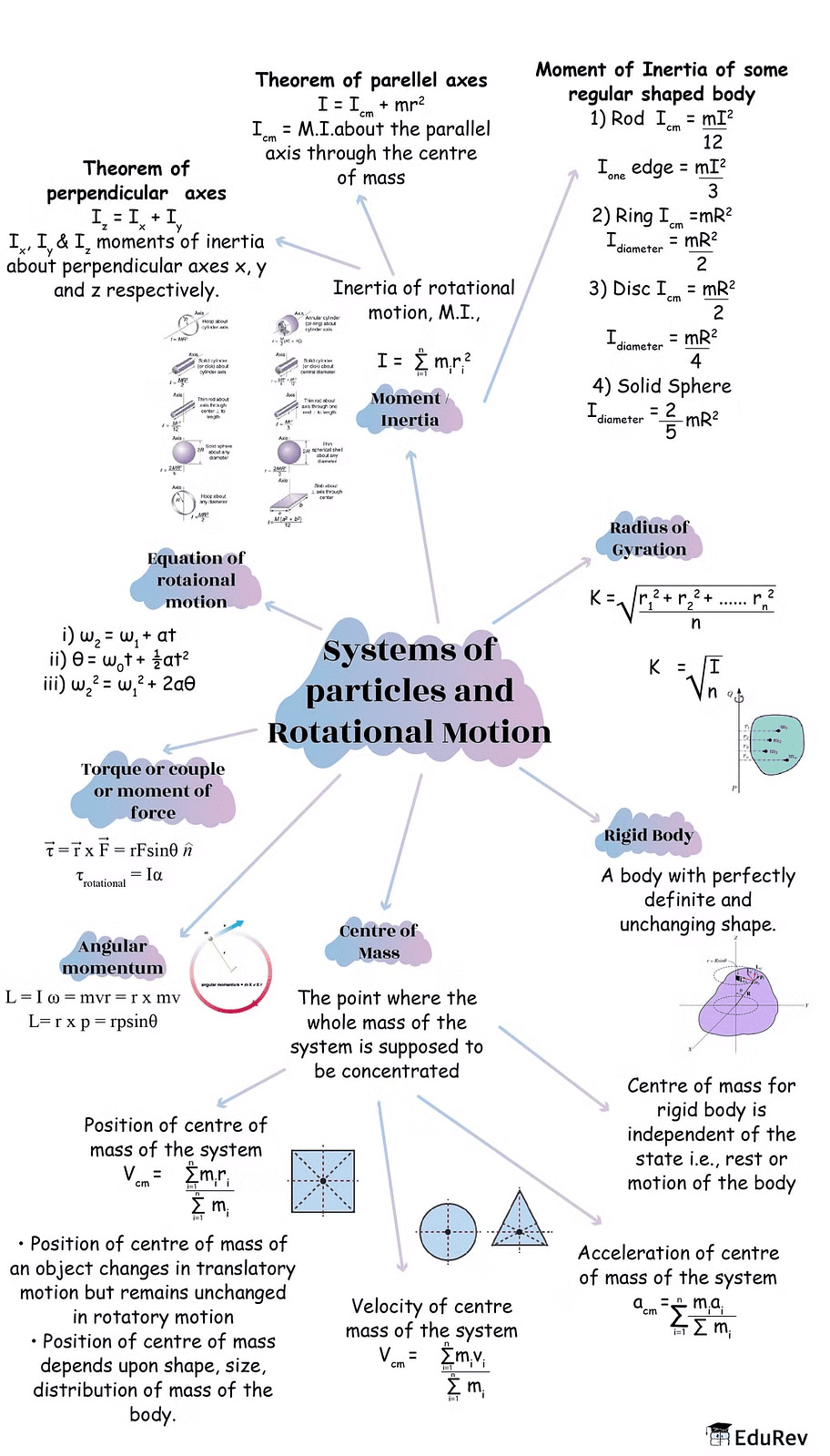
The document Mind Map: Systems of particles and Rotational Motion | Physics Class 11 - NEET is a part of the NEET Course Physics Class 11.
All you need of NEET at this link: NEET
|
119 videos|494 docs|98 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Systems of particles and Rotational Motion - Physics Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the significance of the center of mass in systems of particles? |  |
Ans. The center of mass is a crucial concept in systems of particles as it provides a point that represents the average position of all the mass in the system. It simplifies the analysis of motion, allowing us to treat a complex system as a single point particle for translational motion. The center of mass helps in understanding how external forces affect the motion of the entire system.
| 2. How do you calculate the moment of inertia for a system of particles? |  |
Ans. The moment of inertia (I) for a system of particles is calculated by summing the products of each particle's mass (m) and the square of its distance (r) from the axis of rotation. The formula is given by I = Σ(m * r²), where the summation runs over all particles in the system. This value is essential for analyzing rotational motion and determining angular acceleration when torque is applied.
| 3. What is the relationship between torque and angular acceleration in rotational motion? |  |
Ans. The relationship between torque (τ) and angular acceleration (α) in rotational motion is described by Newton's second law for rotation, which states τ = I * α, where I is the moment of inertia. This means that the torque applied to an object causes it to have angular acceleration proportional to the torque and inversely proportional to its moment of inertia. This relationship is fundamental for understanding how forces affect rotational dynamics.
| 4. How does conservation of angular momentum apply to systems of particles? |  |
Ans. The conservation of angular momentum states that if no external torque acts on a system of particles, the total angular momentum of the system remains constant over time. This principle is vital in analyzing collisions and interactions among particles, as it allows us to predict final states of motion based on initial conditions, even in complex systems.
| 5. What are the differences between translational and rotational motion in a system of particles? |  |
Ans. Translational motion refers to the movement of the entire system of particles from one location to another, characterized by linear displacement, velocity, and acceleration. In contrast, rotational motion involves the rotation of the system around an axis, characterized by angular displacement, angular velocity, and angular acceleration. While both types of motion can occur simultaneously, they are governed by different equations and principles, such as linear momentum for translational motion and angular momentum for rotational motion.
Related Searches

















