Occurrence of Metals: Extraction & Metallurgy | Science Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Minerals and Ores |

|
| Metallurgy |

|
| 1. Crushing and Grinding of the Ore |

|
| 2. Enrichment of Ores |

|
| 4. Purification of Metals |

|
| 5. Refining of Metals |

|
Minerals and Ores
The natural substances (elements or compounds) in which metals and their compounds occur either in their native state or combined state are called minerals.
Example: Aluminium occurs in the earth's crust in the form of two well-known minerals, bauxite (Al2O3.2H2O) and clay (Al2O3 . 2SiO2 . 2H2O).  Aluminium Ore: Bauxite
Aluminium Ore: Bauxite
- In some places, minerals may contain a large percentage of metal whereas others may contain only a small percentage of the metal.
- The mineral from which metal can be conveniently and profitably extracted is called an ore.
- All ores are minerals but all the minerals are not ores.
Example:Copper occurs in nature in the form of several minerals like copper pyrites, copper glance (Cu2S), and cuprite (Cu2O).
 Copper Ore
Copper Ore
- But copper can be conveniently extracted from copper pyrites (CuFeS2). Therefore, the ore of copper is copper pyrites. Some common ores are listed below:
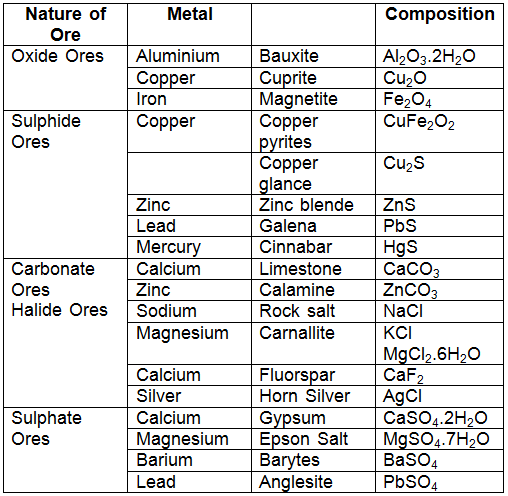
- Since ores of many metals are oxides due to the high reactivity of oxygen and they are very abundant on the earth's crust.
Metallurgy
The various processes involved in the extraction of metals from their ores and refining for use are known as metallurgy.
Various steps are involved in the extraction of metals or metallurgical process :
- Crushing and grinding of the ore.
- Concentration of the ore or enrichment of the ore.
- Extraction of metal from the concentrated ore.
- Refining or purification of the impure metal.
1. Crushing and Grinding of the Ore
- Most of the ores in nature occur as big rocks. They are broken into small pieces with the help of crushers. These pieces are then reduced to a fine powder with the help of a ball mill or a stamp mill. This process is known as pulverization.
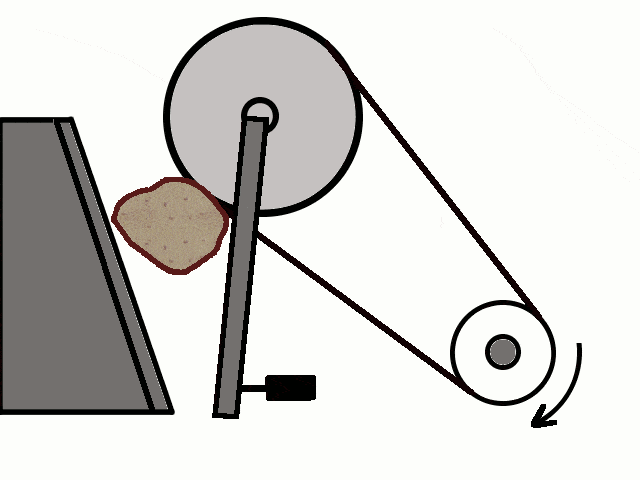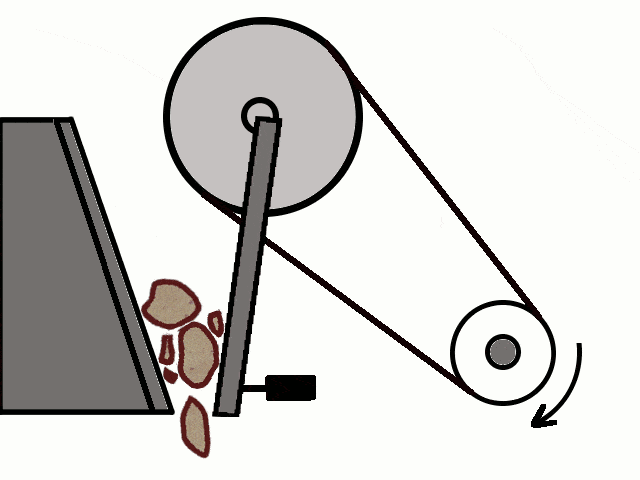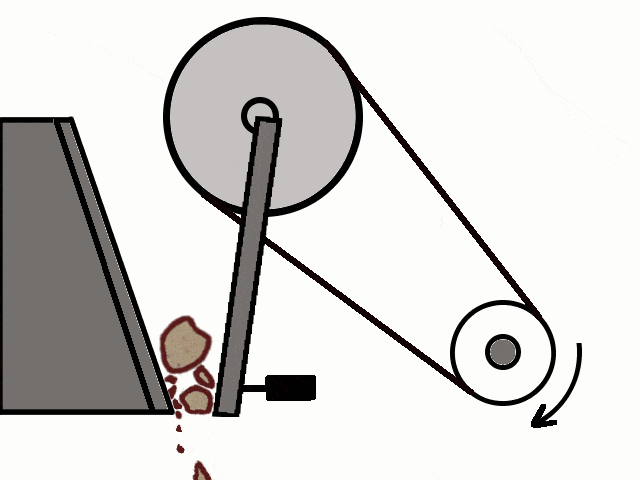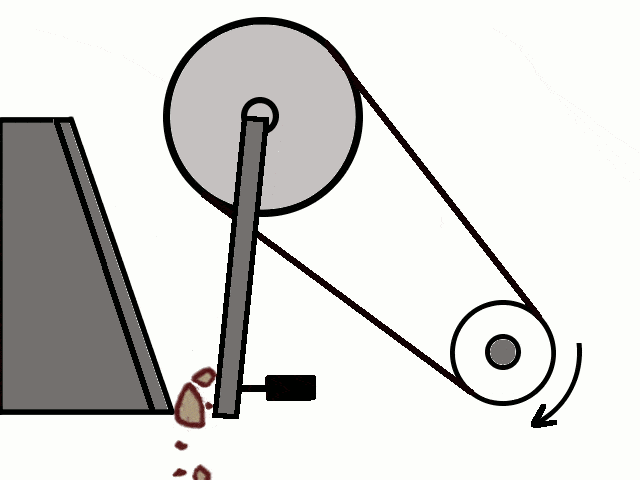 Crushing of Ores
Crushing of Ores Crushed Ore converted into fine powder by Stamp Mill
Crushed Ore converted into fine powder by Stamp Mill
2. Enrichment of Ores
- The ores mined from the earth's crust contain a number of impurities, such as soil, sand, etc. called gangue and matrix.
- The process of removal of impurities (gangue) from the ore is called enrichment of ore or concentration of ore.
Enrichment of ore is carried out by the following methods :
(i) Levigation
- This method is based upon the difference in the densities of the ore particles and impurities (gangue).
- The powdered ore is washed in a jet of water. The lighter, rocky and earthy impurities are washed away by water, while heavier particles are left behind to settle down at the bottom. This process is also called hydraulic washing.
- This method of concentration is usually applicable to oxides ore.
Example:Ores of iron, tin, and lead are very heavy and therefore they are concentrated by this method.
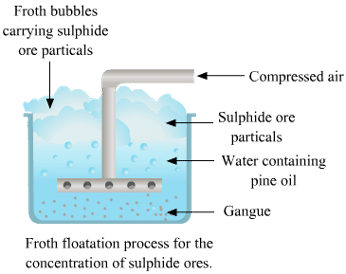
(ii) Froth Flotation
- This method is based on the principle of difference in the wetting properties of the ore and gangue particles with water and oil.
- This method is commonly used for sulphide ores (such as copper-zinc and lead).
- In this method, the finely powdered ore is mixed with water and a small amount of oil (pine oil or eucalyptus oil) tank. Air is blown into the mixture. The ore particle floats in the froth on the surface. So, this process is known as a froth floatation process.
- The heavier impurities (gangue) settle to the bottom. The froth at the surface is transferred into another tank and some acid is added to break up the froth. The concentrated ore particles are separated by filtration and dried.
(iii) Liquation
- This process is used to concentrate the ore whose melting point is lower than that of the impurities. Stibnite an ore of antimony, is concentrated by this method.
- The impure ore is heated. The ore melts and flows along the surface. The impurities are left behind.
 Liquation Process
Liquation Process
(iv) Magnetic Separation
- This method depends upon the difference in the magnetic properties of the ores and gangue.
- The ores which are attracted by a magnet can be separated from the non-magnetic impurities with the help of the magnetic separation method. It consists of a leather belt moving over two rollers.
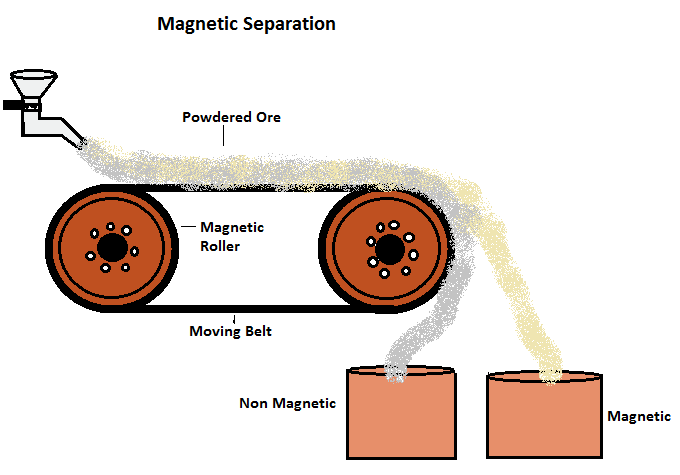
- The powdered ore is dropped over the moving belt at one end. At the other end, the magnetic portion of the ore is attracted by the magnetic roller and falls nearer to the roller while the non-magnetic impurities fall further off.
For example,This method is used for the concentration of iron ores (Haematite)
(v) Leaching or Chemical Separation Method
- It is based on the difference in some chemical properties of the metal and the impurities. This method of concentration is also known as leaching.
- In the chemical method, the powdered ore is treated with a suitable solvent. The ore dissolves in it while the impurities are not soluble.
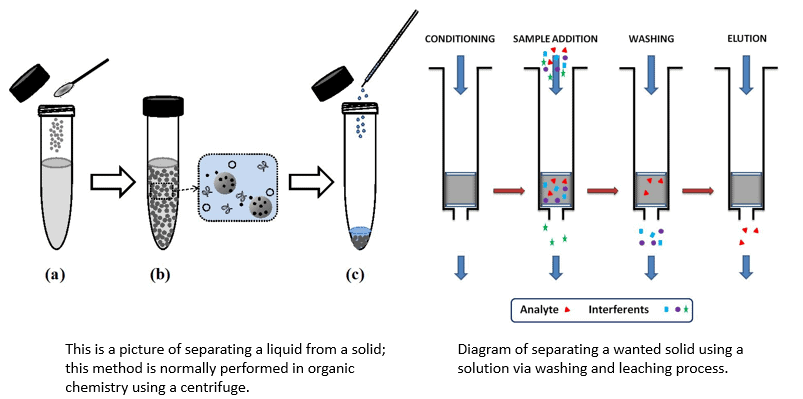 Sample diagram of leaching process
Sample diagram of leaching process
- For Example, Bauxite ore contains Fe2O3, SiO2, etc as impurities. Bayer's method is used to obtain pure aluminium oxide from bauxite ore.
- This process of chemical separation of aluminium by the chemical method is known as Bayer's process.
This method involves the following steps.
(i)The finely powdered ore is treated with hot sodium hydroxide solution which reacts with Al2O3 present in bauxite ore to form sodium meta aluminate. (soluble in water).
(ii) The filtrate (containing NaAlO2 and sodium silicate (Na2SiO3)) is then stirred with a small amount of freshly prepared Al(OH)3.
The aluminium hydroxide (Al(OH)3) is added to induce the precipitation of Al(OH)3. It acts as a seeding agent and helps in quick precipitation.
(iii)The precipitate is separated by filtration. It is dried and heated to get pure aluminium oxide which is also known as alumina.
3. Extraction of the metal from the concentrated ore or enriched ore
The metal is extracted from the concentrated ore by the following steps:
Conversion of the concentrated ore into its oxides
- The production of metal from concentrated ore mainly involves the reduction process.
- This can be usually done by two processes known as calcinationand roastingprocess. The method depends upon the nature of the ore.
- A carbonate ore is converted into oxide by calcination while a sulphide ore is converted into oxide by roasting. These two methods are discussed briefly as below:
(a) Calcination
The process in which concentrated ore is heated in the absence of air is called calcination.
This process is used for the following changes:
(i)To convert carbonates ores into metal oxide.
(ii) To remove water from the hydrated ores.
(iii)To remove volatile impurities from the ore.
For example, Calamine (ZnCO3) is the ore of zinc that calcined i.e. heated strongly in the absence of air to convert into zinc oxide. During calcination, carbon dioxide gas is expelled.
Similarly, in case carbonate ore of Fe, siderite (FeCO3), and ore of calcium and magnesium, are:
Dolomite (CaCO3.MgCO3)
Calcination converts into oxide as:
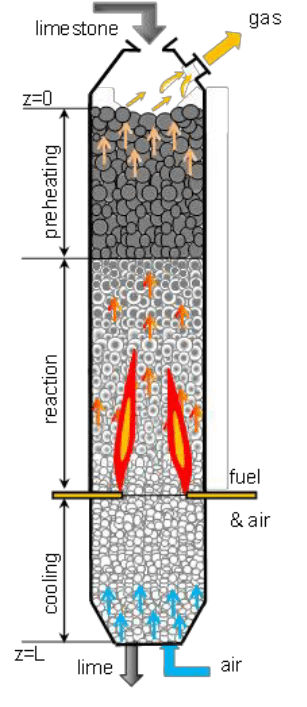 Process of Calcination
Process of Calcination
(b) Roasting
The process in which concentrated ore is heated strongly in the presence of excess air is called roasting.
This process is used for converting sulphide ores to metal oxide. In this process, the following changes take place :
1.
(i)The sulphide ores undergo oxidation to form their oxides.
(ii)Moisture is used.
(iii) Volatile impurities are removed.
For example (i) Zinc blende (ZnS) is the ore of zinc that heated strongly in the presence of excess air to convert zinc oxide and sulphur dioxide gas is expelled.
2. Iron pyrite (FeS2) is converted into ferric oxide (Fe2O3) by roasting.
3. Galena (PbS) is converted into litharge (PbO) by roasting.
4. Cinnabar (HgS) is roasted to convert it directly into mercury.
Extraction of metal from metal oxide or conversion of metal oxide to metalThe metal oxide formed after calcination or roasting is converted into metal by reduction. The method used for the reduction of metal oxide depends upon the nature and chemical reactivity of the metal.
The different metals are extracted by different techniques. The different steps are discussed below:
(a) Extracting the metals low in the activity series
- The metals which are low in the activity series are very unreactive. The oxides of these metals can be reduced to metal by heating alone.
For example, Copper is obtained from its copper sulphide (Cu2S) are by this method.
This involves the following steps :
(i)The concentrated copper sulphide is roasted in the air to form copper oxide.
2Cu2S(s) + 3SO2(g) 2Cu2O(s) + 2SO2(g)
(ii)Copper oxide is again heated with Cu2S to obtain reduced copper and SO2 gas is evolved.
2Cu2O(s) + Cu2S(g) 6Cu(s) + SO2(g)
Similarly, when cinnabar ore (HgS) is heated in air it is first gets converted into mercuric oxide (HgO), which is then reduced to mercury on further heating.
HgS(s) + 3O2(g) HgO(s) + SO2(g)
HgO(s) 2Hg(l) + O2(g)
(b) Extracting metals in the middle of the activity series
- The metals in the middle of the activity series such as iron, zinc, lead, etc are moderately reactive. There are usually present as sulphides or carbonates and which are must be converted to oxides by roasting or calcination.
- The oxides of these metals can not be reduced by heating alone. Therefore, these metal oxides are reduced to free metal by using suitable reducing agents such as carbon, carbon monoxide, aluminium, sodium, or calcium. This is known as smelting.
(i) Reduction with Carbon
When zinc oxide is heated with carbon, zinc metal is produced.
Similarly, Iron and lead are obtained from their oxides by heating with carbon.
Fe2O3(s) + 3C(s) 2Fe(s) + 3CO(g)
PbO(s) + C(s) Pb(s) + CO(g)
(ii) Reduction with CO
Iron is obtained from ferric oxide by heating with CO.
Fe2O3(s) + 3CO(g) 2Fe(s) + 3CO2(g)
(iii) Reduction with Aluminium
Certain metal oxides are reduced by aluminium to metals. This method is known as aluminothermyor thermite process.
For example,Chromium, manganese, titanium, and vanadium metal are obtained by the reduction of their oxides with Al powder. The following reaction takes place.
3MnO2(g) + 4Al(s) 3Mn(s) + 2Al2O3(s)
Cr2O3(g) + 2Al(s) 2Cr(s) + Al2O3(s)
These displacement reactions are highly exothermic, so, a large amount of heat is evolved and metals are produced in the molten state.
In fact the reaction of iron(III) oxide (Fe2O3) with aluminium. The mixture of iron oxide and aluminium powder is called thermite is used to repair railway tracks or cracked machine parts.
This reaction is known as a thermite reaction.
Fe2O3(g) + 2Al(s) 2Fe(l) + Al2O3(s) + Heat
Note: Al is an expensive metal and so, it is not used to reduce metals that are less expensive than aluminium.
(c) Extracting metals towards the top of the activity series
- Electrolytic reduction or reduction by electrolysis. The reactive metals (which are high up in the activity series) cannot be produced by any of the above methods. They are obtained by electrolytic reduction of their molten oxides or chlorides.
- During electrolysis, the cathode supplies electrons to metal ions for their reduction to the metal. The process of extracting metals by electrolysis process is called electrometallurgy.
For example:
(i) Aluminium oxide (Al2O3) is reduced to aluminium by the electrolysis of molten aluminium oxide.
Al2O3 → 2Al3+ + 3O2–
The aluminium ions present in aluminium oxide go to the cathode and are reduced there to aluminium atoms.
Al3+ + 3e- → Al
(ii) Sodium metal is obtained by the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride.
2NaCl 2Na+ + 2Cl–
2Cl– → Cl2 + 2e- (at anode)
2Na+ + 2e- → 2Na (at cathode)
2NaCl 2Na + Cl2
4. Purification of Metals
- The metal obtained by any of the above methods is usually impure and is known as crudemetal. The process of purifying the crude metal is called refining.
- The method of refining depends upon the nature of the metal and the impurities which are present in the metal.
Some of the methods generally applied for refining metals are discussed below:
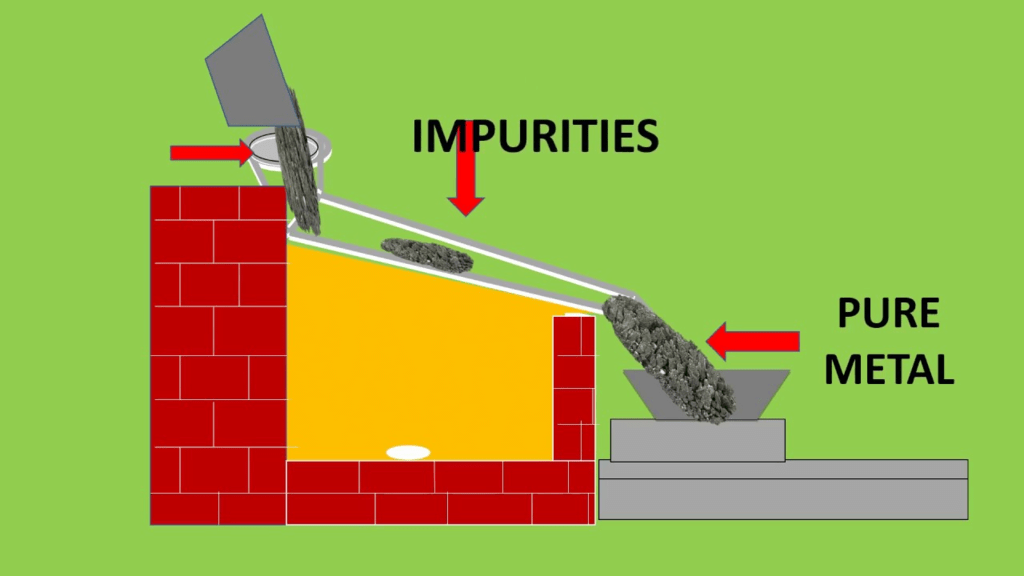
(a) Liquation
- This process is used for refining metals having low melting points. Such as tin, lead, bismuth. etc.
- This is based on the principle that the metal to be refined is easily fusible (melt easily) but the impurities do not fuse easily.
- In this process, the impure metal is placed on the sloping hearth of the furnace and is gently heated.
- The hearth is maintained at a temperature slightly above the melting point of the metal. The metal melts and flows down to the bottom of the sloping hearth and the impurities are left behind. The pure metal is collected at the bottom of the sloping hearth.
(b) Distillation
- This method is used for the purification of volatile metals (which form vapours readily). Such as mercury and zinc.
- In this method, the impure metal is heated strongly in a vessel (called a retort). The pure metal distils over and its vapours are condensed separately in a receiver to get pure metal. The non-volatile impurities are left behind in the retort.
5. Refining of Metals
(a) Oxidation method (Oxidative refining)
- This method is used for the refining of metal in those cases in which the impurities have a greater tendency to get oxidised than the metal itself.
For example,Impure iron (Pig or cast iron) is refined by oxidative refining method. - Pig iron contains Carbon, Sulphur, phosphorous, silicon, and manganese as impurities. When a blast of air is blown over molten pig iron these impurities are oxidised to their oxides (CO2, SO2, P2O5, etc.) and get removed. The pure iron is left behind.
- Similarly, Silver is refined by this method.
(b) Electrolytic Refining
- This is the most widely used method for the refining of impure metals. Many metals such as copper, zinc, tin, nickel, silver, gold, etc. are refined electrolytically. It is based upon the phenomenon of electrolysis.
- In this process, the impure metal is made of the anode and a thin strip of pure metal is the cathode. A solution of the metal salt is used as an electrolyte. On passing the electric current through the electrolyte, the pure metal from the anode dissolves into the electrolyte. An equivalent amount of pure metal gets deposited on the cathode. The soluble impurities go into the solution, whereas, the insoluble impurities settle down at the bottom of the anode and are known as anode mud.
For example: In the electrolytic refining of copper (The apparatus is set up as shown in the figure below) 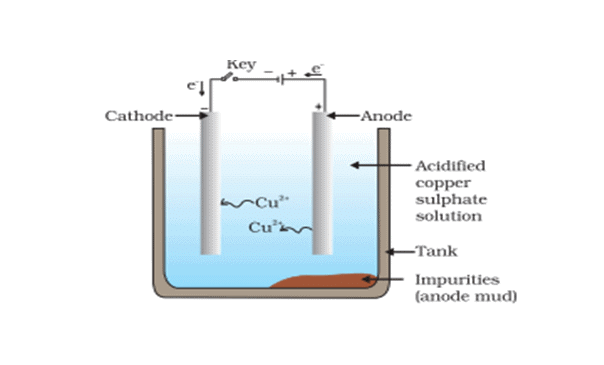 Crude copper is made as the anode, and a thin sheet of pure copper is made as the cathode. The electrolyte is a solution of copper sulphate containing a small amount of dilute H2SO4 acid. On passing the electric current copper dissolve from the anode into the electrolyte. An equivalent amount of copper is deposited at the cathode in the form of pure metal.
Crude copper is made as the anode, and a thin sheet of pure copper is made as the cathode. The electrolyte is a solution of copper sulphate containing a small amount of dilute H2SO4 acid. On passing the electric current copper dissolve from the anode into the electrolyte. An equivalent amount of copper is deposited at the cathode in the form of pure metal.
The following reactions occur at the electrodes.
At anode:
At cathode:
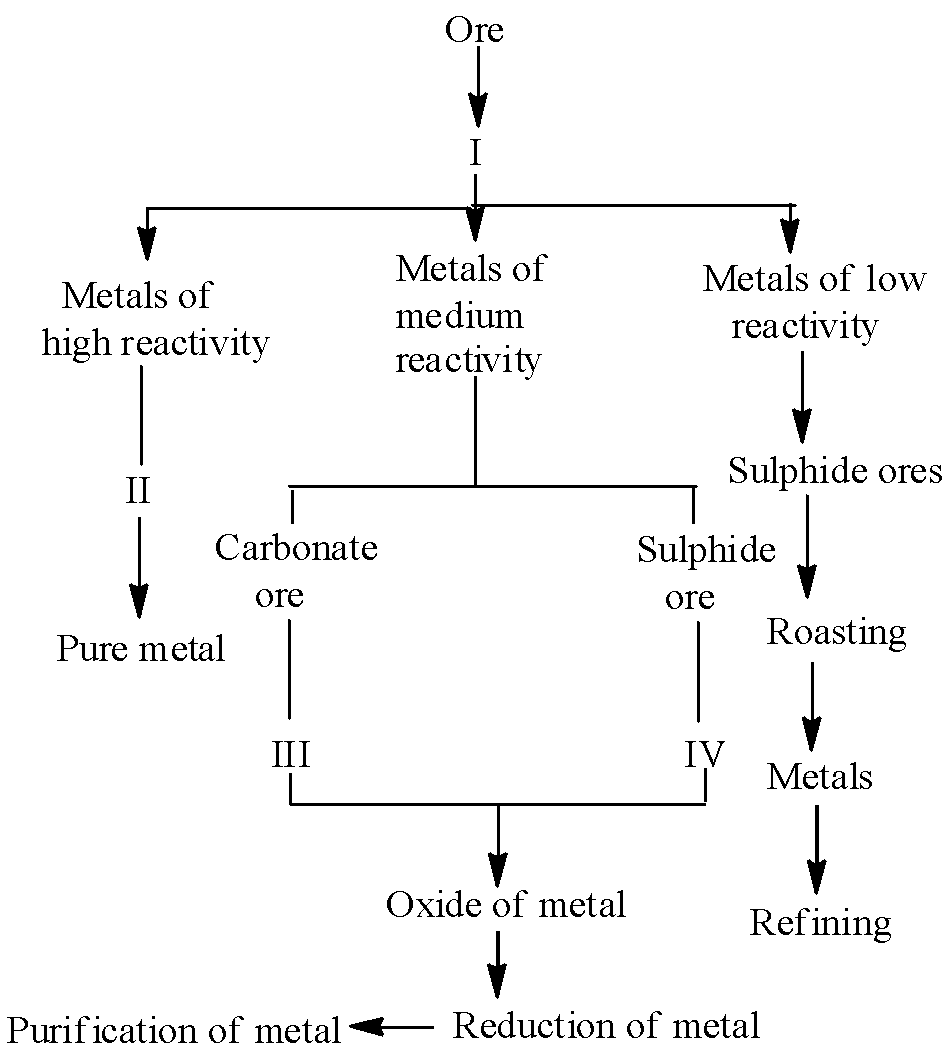
The summary or flow sheet of different steps involved for three types of extraction of metals is given below :
 Electrolytic Refining
Electrolytic Refining
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Occurrence of Metals: Extraction & Metallurgy - Science Class 10
| 1. What is the process of crushing and grinding in metallurgy? |  |
| 2. How is the enrichment of ores achieved? |  |
| 3. What are the common methods for extracting metals from concentrated ores? |  |
| 4. Why is the purification of metals important in metallurgy? |  |
| 5. What is the difference between refining and purification of metals? |  |
















