Mnemonics: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids | Chemistry Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
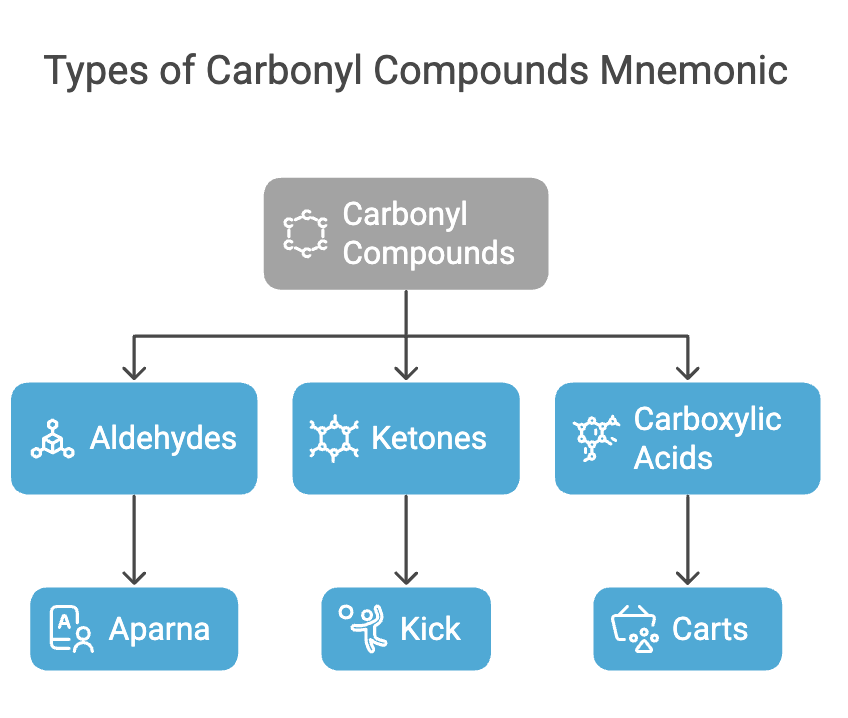
Types of Carbonyl Compounds
Types: Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids
Mnemonic: "Aparna Kick Carts"
Breakdown:
- Aparna - Aldehydes
- Kick - Ketones
- Carts - Carboxylic Acids
Methods of Preparation of Aldehydes
Types: From Alcohols, From Alkenes, From Nitriles
Mnemonic: "Ants Always Nibble"
Breakdown:
- Ants - From Alcohols
- Always - From Alkenes
- Nibble - From Nitriles
Methods of Preparation of Ketones
Types: From Alcohols, From Acyl Chlorides, From Nitriles
Mnemonic: "Apes Attack Nuts"
Breakdown:
- Apes - From Alcohols
- Attack - From Acyl Chlorides
- Nuts - From Nitriles
Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones
Types: Nucleophilic Addition, Reduction, Oxidation, Cannizzaro Reaction
Mnemonic: "Nervous Rats Overeat Candy"
Breakdown:
- Nervous - Nucleophilic Addition
- Rats - Reduction
- Overeat - Oxidation
- Candy - Cannizzaro Reaction
Tests to Distinguish Aldehydes and Ketones
Types: Fehling’s Test, Tollens’ Test, Schiff’s Test
Mnemonic: "Freddy Taste Sugar"
Breakdown:
- Freddy - Fehling’s Test
- Taste - Tollens’ Test
- Sugar - Schiff’s Test
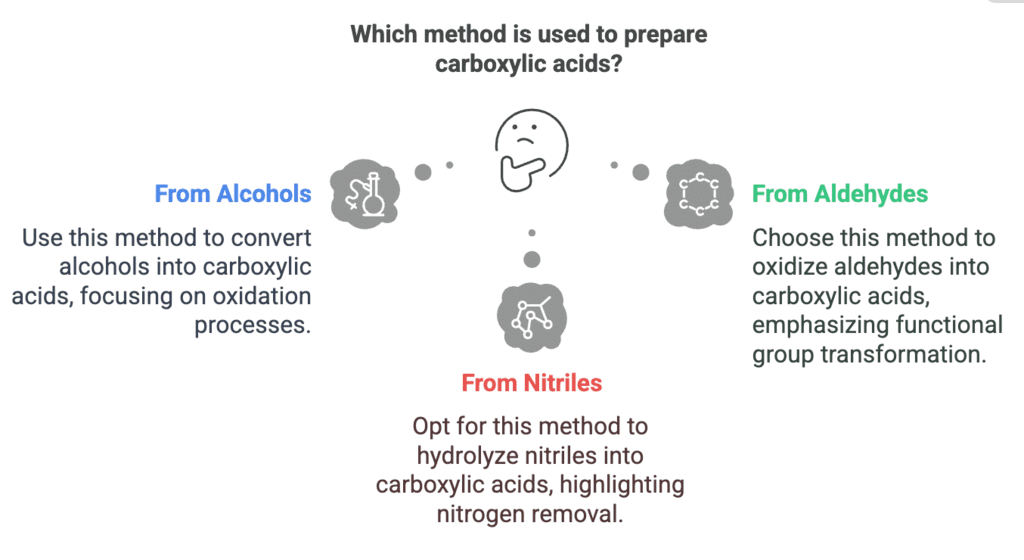
Methods of Preparation of Carboxylic Acids
Types: From Alcohols, From Aldehydes, From Nitriles
Mnemonic: "Alvin Annoys Nun"
Breakdown:
- Alvin- From Alcohols
- Annoys - From Aldehydes
- Nun - From Nitriles
Reactions of Carboxylic Acids
Types: Esterification, Decarboxylation, Reduction, Halogenation
Mnemonic: "Elephants Dance Rapidly High"
Breakdown:
- Elephants - Esterification
- Dance - Decarboxylation
- Rapidly - Reduction
- High - Halogenation
Physical Properties of Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids
Types: Boiling Point, Solubility, Odour
Mnemonic: "Brother Smells Odd"
Breakdown:
- Brother- Boiling Point
- Smells - Solubility
- Odd - Odour
|
75 videos|278 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids - Chemistry Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What are the key structural differences between aldehydes and ketones? |  |
| 2. How do you identify a carboxylic acid in a chemical structure? |  |
| 3. What are some common reactions that aldehydes undergo? |  |
| 4. What mnemonic can help remember the functional groups of aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids? |  |
| 5. Why are carboxylic acids considered more acidic than alcohols? |  |





















