Mnemonics: Anatomy of Flowering Plants | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
1. Tissue Systems in Flowering Plants
Types: Epidermal Tissue System, Ground Tissue System, Vascular Tissue System
Mnemonic: "Elephants Graze Vigorously"
Breakdown:
- Elephants → Epidermal Tissue System
- Graze → Ground Tissue System
- Vigorously → Vascular Tissue System
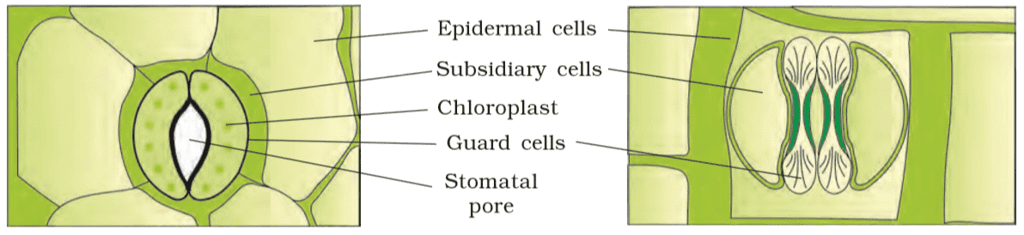
2. Components of Epidermal Tissue System
Components: Epidermal Cells, Stomata, Epidermal Appendages (Trichomes/Hairs)
Mnemonic: "Every Star Twinkles"
Breakdown:
- Every → Epidermal Cells
- Star → Stomata
- Twinkles → Trichomes/Hairs
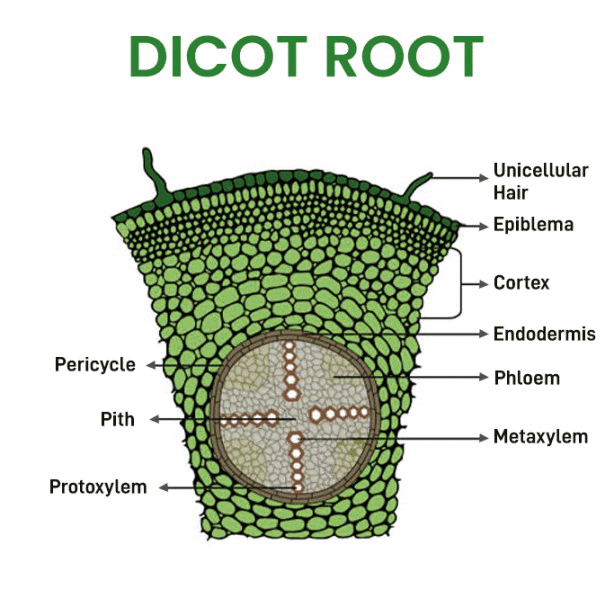
3. Parts of Dicot Root (Transverse Section)
Parts: Epiblema, Cortex, Endodermis, Pericycle, Vascular Bundles, Pith
Mnemonic: "Elephants Climb Every Peak Very Proudly"
Breakdown:
- Elephants → Epiblema
- Climb → Cortex
- Every → Endodermis
- Peak → Pericycle
- Very → Vascular Bundles
- Proudly → Pith
4. Parts of Monocot Root (Transverse Section)
Parts: Epidermis, Cortex, Endodermis, Pericycle, Vascular Bundles, Pith
Mnemonic: "Eager Cats Eat Plenty Very Often"
Breakdown:
- Eager → Epidermis
- Cats → Cortex
- Eat → Endodermis
- Plenty → Pericycle
- Very → Vascular Bundles
- Often → Pith
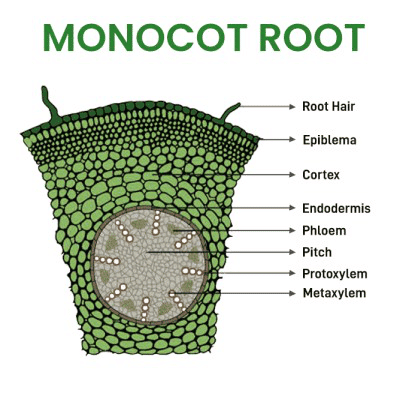
Note: Monocot and dicot roots have similar parts, but monocots have more xylem bundles (polyarch) and a large pith, which can be emphasized when recalling.
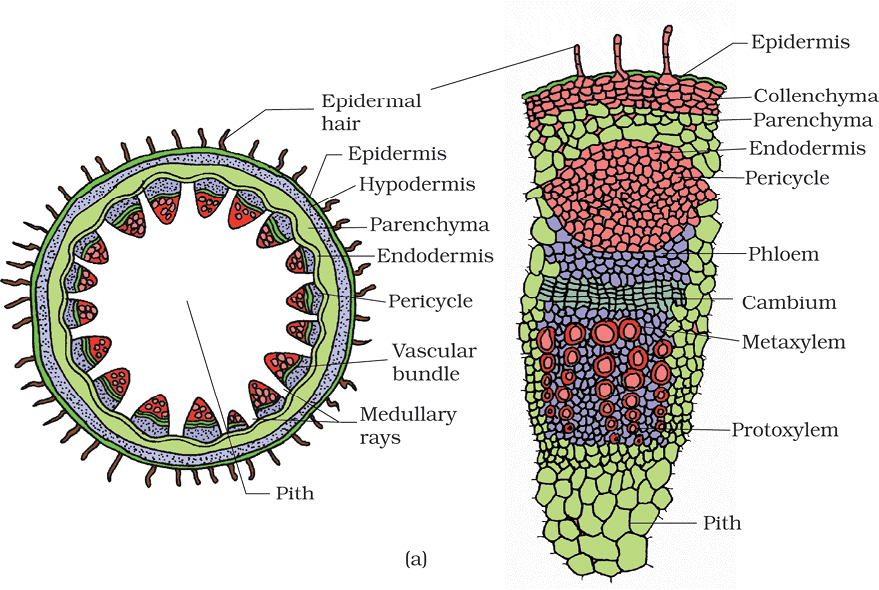
5. Parts of Dicot Stem (Transverse Section)
Parts: Epidermis, Hypodermis, Cortex, Endodermis (Starch Sheath), Pericycle, Vascular Bundles, Medullary Rays, Pith
Mnemonic: "Elephants Have Courage, Enduring Perils, Venturing Mighty Paths"
Breakdown:
- Elephants → Epidermis
- Have → Hypodermis
- Courage → Cortex
- Enduring → Endodermis (Starch Sheath)
- Perils → Pericycle
- Venturing → Vascular Bundles
- Mighty → Medullary Rays
- Paths → Pith
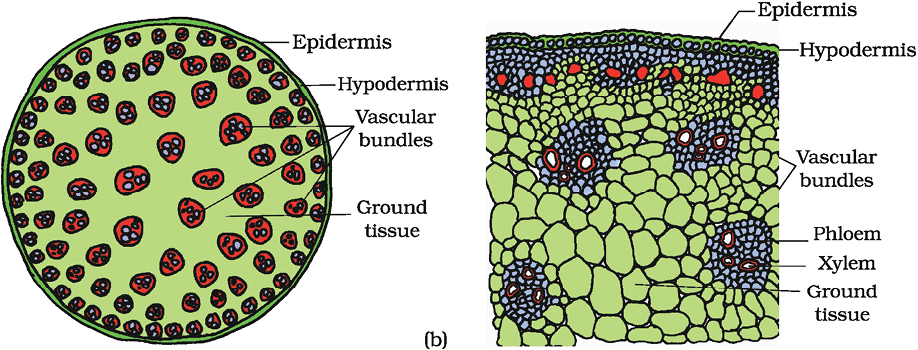
6. Parts of Monocot Stem (Transverse Section)
Parts: Hypodermis, Ground Tissue, Vascular Bundles, Bundle Sheath
Mnemonic: "Happy Goats Venture Boldly"
Breakdown:
- Happy → Hypodermis
- Goats → Ground Tissue
- Venture → Vascular Bundles
- Boldly → Bundle Sheath
7. Parts of Dicot (Dorsiventral) Leaf (Vertical Section)
Parts: Adaxial Epidermis, Abaxial Epidermis, Palisade Parenchyma, Spongy Parenchyma, Vascular Bundles, Bundle Sheath
Mnemonic: "Apples Attract Pretty Sponges, Very Beautiful"
Breakdown:
- Apples → Adaxial Epidermis
- Attract → Abaxial Epidermis
- Pretty → Palisade Parenchyma
- Sponges → Spongy Parenchyma
- Very → Vascular Bundles
- Beautiful → Bundle Sheath
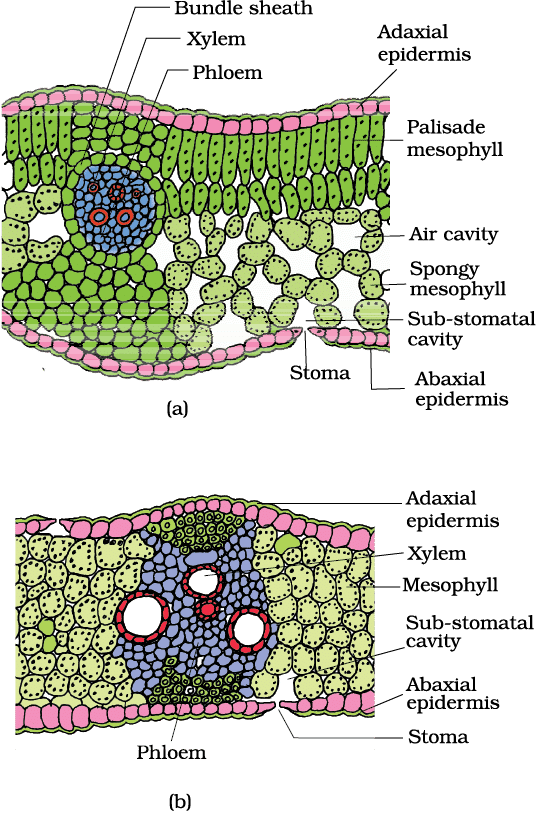 T.S. of leaf : (a) Dicot (b) Monocot
T.S. of leaf : (a) Dicot (b) Monocot
8. Parts of Monocot (Isobilateral) Leaf (Vertical Section)
Parts: Epidermis (Both Surfaces), Mesophyll (Undifferentiated), Vascular Bundles, Bundle Sheath, Bulliform Cells
Mnemonic: "Every Morning Vines Bloom Brightly"
Breakdown:
- Every → Epidermis (Both Surfaces)
- Morning → Mesophyll (Undifferentiated)
- Vines → Vascular Bundles
- Bloom → Bundle Sheath
- Brightly → Bulliform Cells
9. Types of Vascular Bundles
Types: Radial, Conjoint Open, Conjoint Closed
Mnemonic: "Rabbits Climb Cliffs"
Breakdown:
- Rabbits → Radial
- Climb → Conjoint Open
- Cliffs → Conjoint Closed
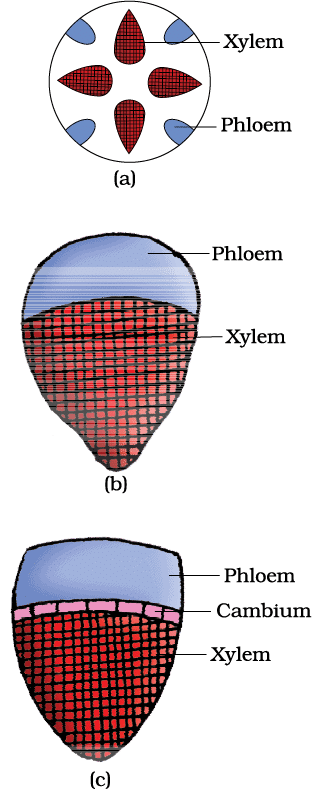 Various types of vascular bundles : (a) radial (b) conjoint closed (c) conjoint open
Various types of vascular bundles : (a) radial (b) conjoint closed (c) conjoint open
10. Key Differences Between Monocot and Dicot Anatomy
Features: Vascular Bundle Arrangement, Cambium Presence, Secondary Growth
Mnemonic: "Vines Can Sprout"
Breakdown:
- Vines → Vascular Bundle Arrangement (Scattered in monocots, Ring in dicots)
- Can → Cambium Presence (Absent in monocots, Present in dicots)
- Sprout → Secondary Growth (Absent in monocots, Present in dicots)
|
150 videos|398 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Anatomy of Flowering Plants - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What are the different types of meristematic tissues in plants? |  |
| 2. What are the characteristics of simple permanent tissues in plants? |  |
| 3. What are the main tissue systems found in plants? |  |
| 4. What are the components of a vascular bundle in plants? |  |
| 5. What are the different regions of the root, particularly at the root tip? |  |
















