Mnemonics: Atoms | Physics Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Atomic Models |

|
| Thomson Model Features |

|
| Rutherford Experiment Observations |

|
| Bohr Model Postulates |

|
Atomic Models
Types: Thomson, Rutherford, Bohr
Mnemonic: "The Real Beauty"
Breakdown:
- The - Thomson
Thomson Model: Also known as the "plum pudding" model, where electrons are spread throughout a positively charged sphere. It was the first model to suggest that atoms are made of smaller particles.
Example: J.J. Thomson’s cathode ray experiment led to the discovery of the electron.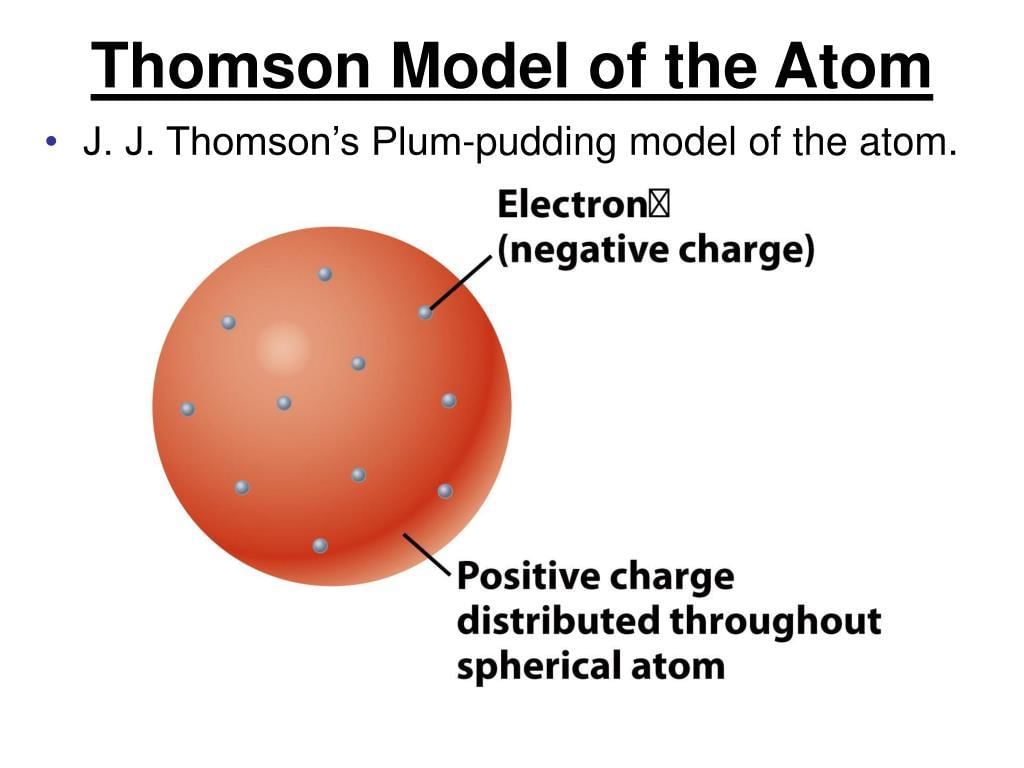
- Real - Rutherford
Rutherford Model: Proposed that the atom consists of a dense, positively charged nucleus with electrons orbiting around it, much like planets orbit the sun.
Example: Rutherford’s gold foil experiment revealed the existence of the atomic nucleus.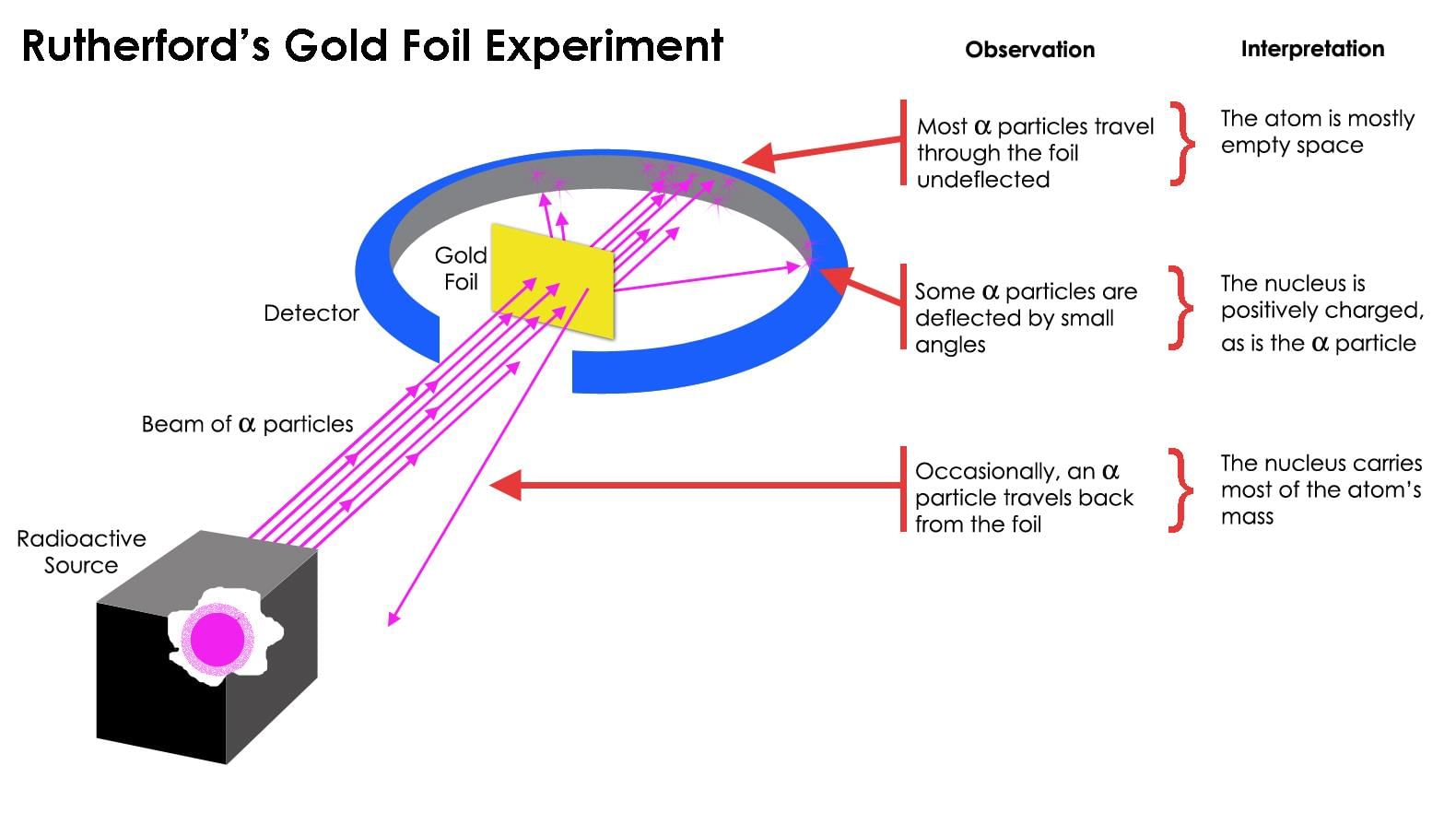
Beauty - Bohr
Bohr Model: Suggested that electrons move in fixed orbits around the nucleus, and energy is absorbed or emitted when electrons jump between these orbits.
Example: Bohr’s model of the hydrogen atom explained the discrete lines in its emission spectrum.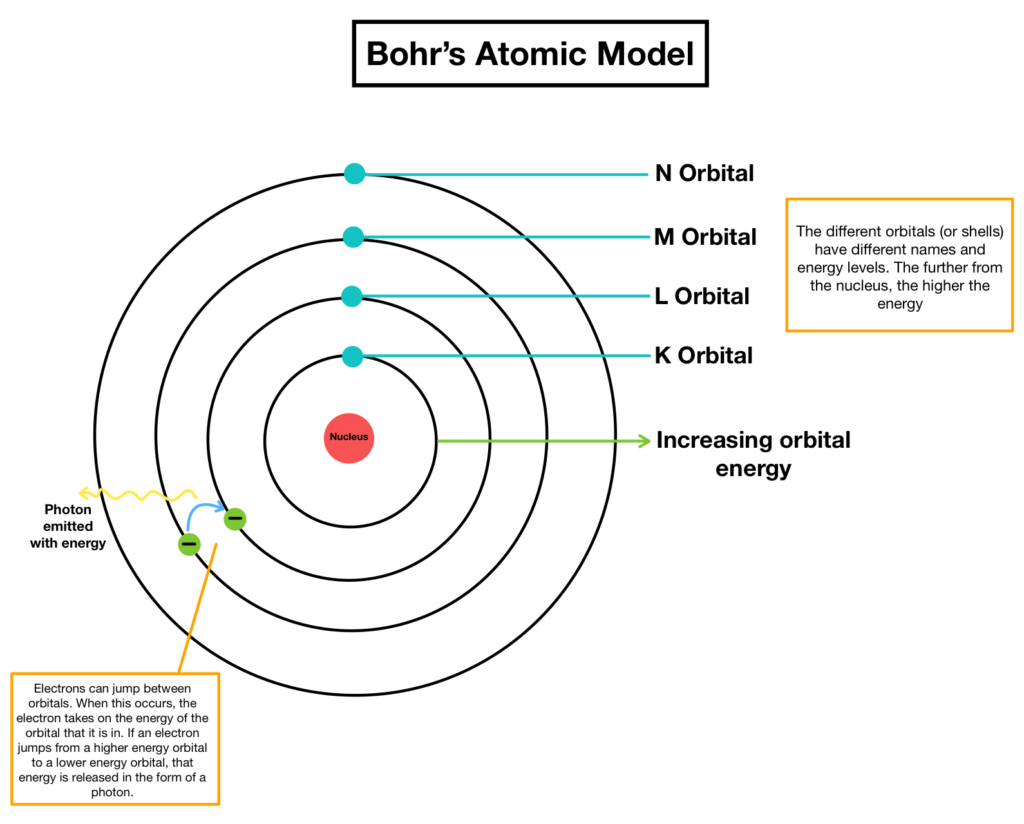
Thomson Model Features
Types: Plum Pudding, Positive Sphere, Embedded Electrons
Mnemonic: "Priya Pours Electric Power"
Breakdown:
Priya - Plum Pudding
Plum Pudding Model: Thomson proposed that the atom is like a "plum pudding," where negatively charged electrons are embedded in a positively charged "soup" or sphere.
Example: In this model, the positive charge is spread throughout the atom, with electrons scattered inside.Pours - Positive Sphere
Positive Sphere: In the Plum Pudding model, the atom’s positive charge is spread uniformly over the entire atom, like the pudding around the "plums" (electrons).
Example: The positive charge in the atom ensures the overall neutrality when combined with the negatively charged electrons.Electric Power - Embedded Electrons
Embedded Electrons: Electrons are embedded in the positive charge of the atom, much like plums in a pudding, and they move freely within this positively charged sphere.
Example: The electrons in Thomson’s model are held in place by the positive charge of the sphere, but can move freely inside.
Rutherford Experiment Observations
Types: Scattering, Nucleus, Empty Space
Mnemonic: "Some Nuclei Emit Signals"
Breakdown:
Some - Scattering
Scattering: Rutherford observed that most alpha particles passed through the gold foil with little or no deflection, but some were scattered at large angles, indicating that atoms have a dense core.
Example: The scattering of alpha particles helped demonstrate that the atom is not solid, but has a central nucleus.Nuclei - Nucleus
Nucleus: The experiment revealed that the atom has a tiny, dense, positively charged nucleus at its center, where most of the atom’s mass is concentrated.
Example: The nucleus holds protons and neutrons and is responsible for the atom’s overall mass.Emit Signals - Empty Space
Empty Space: Rutherford’s experiment showed that the majority of an atom is empty space, as most alpha particles passed through the gold foil without significant deflection.
Example: This empty space is the region between the dense nucleus and the orbiting electrons.
Bohr Model Postulates
Types: Quantized Orbits, Energy Levels, Electron Transitions
Mnemonic: "Quickly Elevating Every Thought "
Breakdown:
Quickly - Quantized Orbits
Quantized Orbits: Electrons revolve in specific, fixed orbits with quantized energies. They cannot exist between these orbits.
Example: Electrons move in these distinct orbits around the nucleus without radiating energy unless they transition to a different orbit.Elevating - Energy Levels
Energy Levels: The electron orbits correspond to different energy levels. The energy is lower closer to the nucleus and higher further away.
Example: Energy levels are discrete, meaning electrons can only have certain energy values depending on their orbit.Every Thought - Electron Transitions
Electron Transitions: When an electron moves between energy levels, it either absorbs or emits energy in the form of light. The energy change corresponds to the difference between the two energy levels.
Example: When an electron jumps to a higher energy level, it absorbs energy, and when it returns to a lower level, it emits light (specific wavelengths).
|
74 videos|314 docs|88 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Atoms - Physics Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What are atoms and why are they important in chemistry? |  |
| 2. How do atoms bond to form molecules? |  |
| 3. What is the structure of an atom? |  |
| 4. How are atomic number and mass number defined? |  |
| 5. What role do electrons play in chemical reactions? |  |















