NEET Exam > NEET Notes > Biology Class 11 > Mnemonics: Body Fluids & Circulation
Mnemonics: Body Fluids & Circulation | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
Let's memorise the important components of Body Fluids and their Circulation: Types of WBCs , Sequence of Double Circulation, Layers of Arteries and Veins, Phases of Cardiac Cycle and ECG & Disorders of Circulatory System , linking with our daily usage of words and never forgetting.
1. Types of WBCs and Their Percentage ( In Decreasing Order)
Mnemonic: "Never Let Monkeys Eat Bananas"
Explanation:
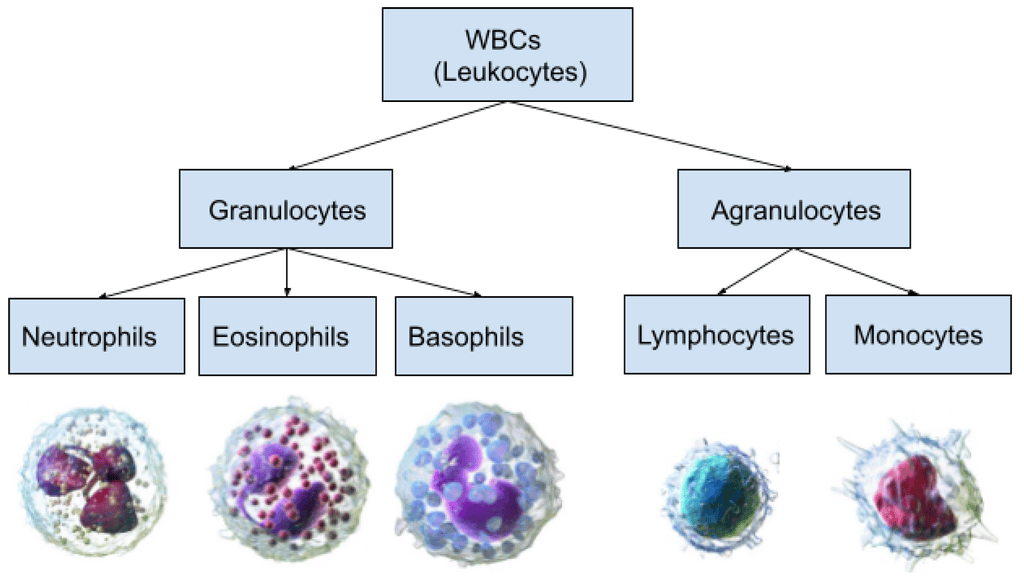 Types of WBCs
Types of WBCs
- Never - Neutrophils (60-65%): Most abundant, phagocytic.
- Let - Lymphocytes (20-25%): B and T cells, responsible for immunity.
- Monkeys - Monocytes (6-8%): Phagocytic, destroy pathogens.
- Eat - Eosinophils (2-3%): Resist infections, manage allergic reactions.
- Bananas - Basophils (0.5-1%): Least abundant, involved in inflammatory responses.
2. Sequence of Double Circulation: Pulmonary and Systemic Circulation
Mnemonic: "Right Pulmonary, Left Systemic"
Explanation:
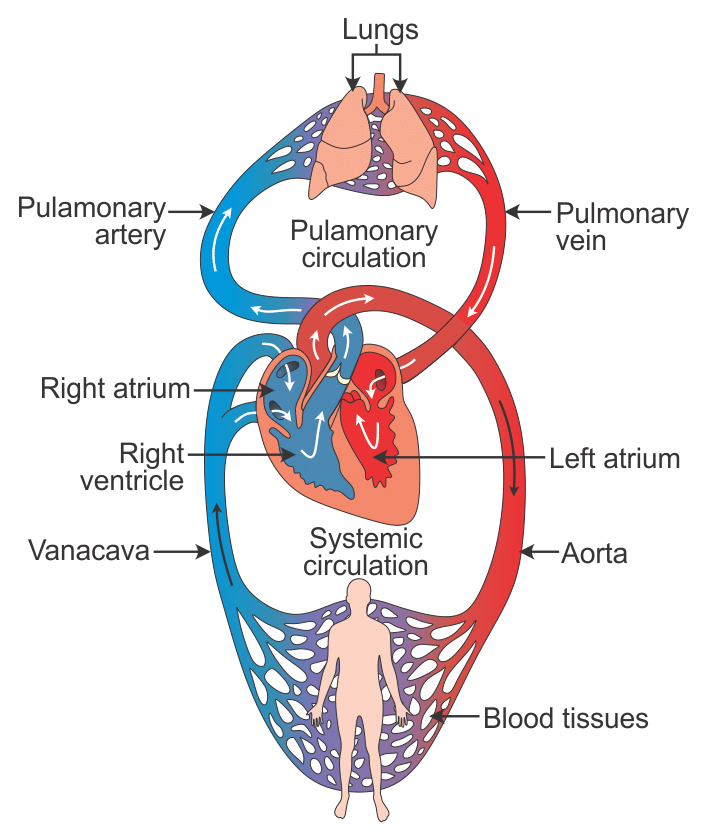 Double Circulation
Double Circulation
- Right denotes: Right auricle and ventricle & Pulmonary denotes : Pulmonary circulation involving lungs
Right Atrium → Right Ventricle → Pulmonary Artery → Lungs: Deoxygenated blood is oxygenated in the pulmonary circulation. - Left denotes: Left auricle & ventricle & Systemic denotes : Systemic circulation
Left Atrium → Left Ventricle → Aorta → Body Tissues: Oxygenated blood is circulated through systemic circulation to tissues.
3. Three Layers of Arteries and Veins
Mnemonic: "Intelligent Media Externally"
Explanation:
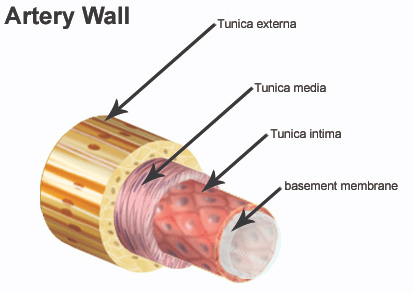
- Tunica Intima: Inner lining of squamous endothelium.
- Tunica Media: Middle layer with smooth muscle and elastic fibers.
- Tunica Externa: Outer fibrous connective tissue with collagen.
4. Phases of the Cardiac Cycle
Mnemonic: "Dolphins Swim Very Slow"
Explanation:
- D - Diastole (Joint diastole): All chambers relaxed, blood fills atria and ventricles.
- S - Systole (Atrial): Atria contract, pumping blood into ventricles.
- V - Ventricular systole: Ventricles contract, pumping blood into pulmonary artery and aorta.
- S - Semilunar valve closure: Prevents backflow, marking end of the cycle.
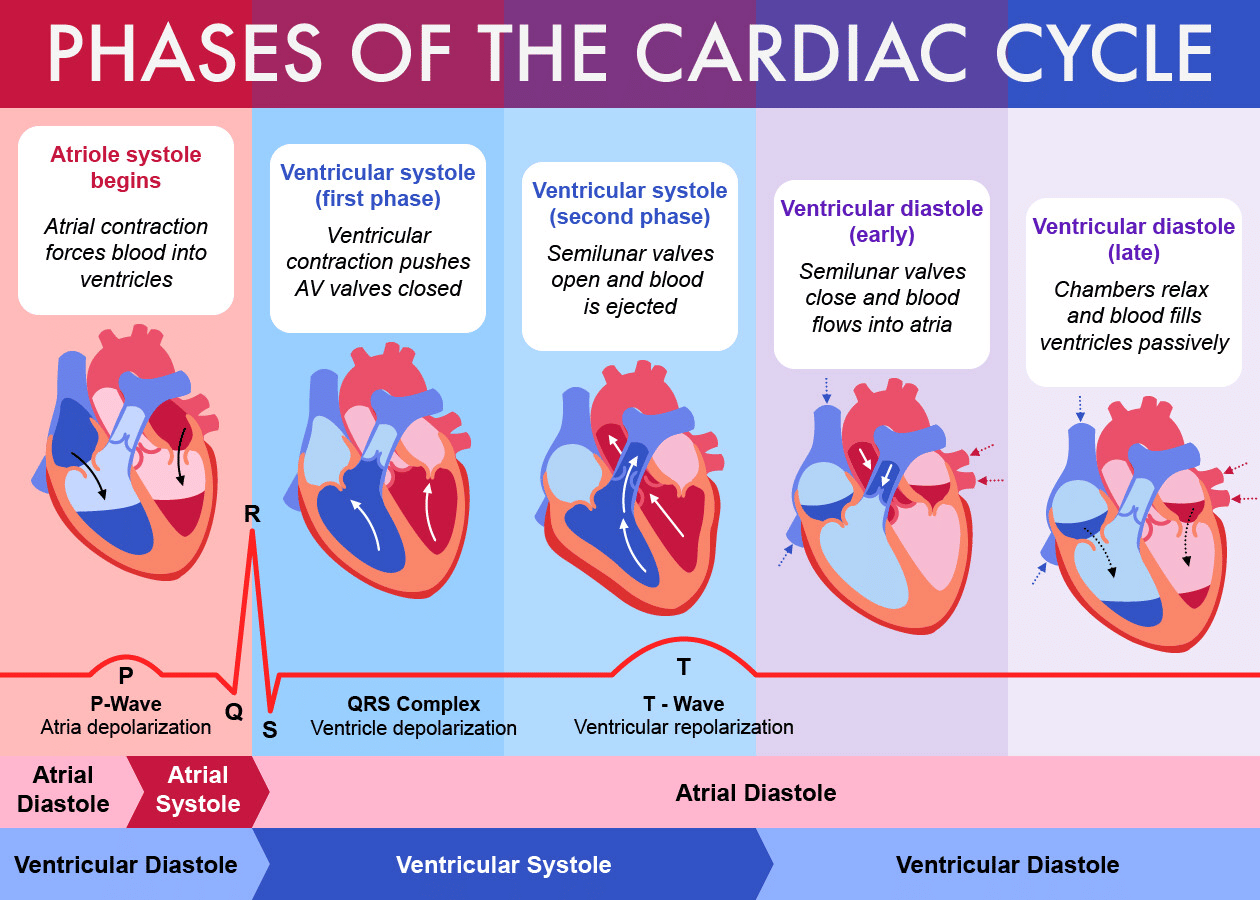
5. ECG Phases
Mnemonic: "P-QRS-T: Please Quit Robbing Steve & Tom"
Explanation:
- Please: P-Wave: Atrial depolarization (atria contract).
- Quit Robbing Steve : QRS Complex: Ventricular depolarization (ventricles contract).
- Tom: T-Wave: Ventricular repolarization (ventricles relax).
6. Disorders of Circulatory System
Mnemonic: "Hope Can Always Heal"
Explanation:
- Hope - Hypertension: Blood pressure above 140/90 mm Hg, affecting heart, brain, and kidneys.
- Can - Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Narrowing of coronary arteries due to fat and calcium deposits.
- Always - Angina: Acute chest pain caused by reduced oxygen to heart muscles.
- Heal - Heart Failure: Inadequate pumping of blood by the heart, leading to congestion in lungs.
The document Mnemonics: Body Fluids & Circulation | Biology Class 11 - NEET is a part of the NEET Course Biology Class 11.
All you need of NEET at this link: NEET
|
169 videos|531 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Body Fluids & Circulation - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What are the main types of leucocytes and their functions? |  |
Ans. The main types of leucocytes (white blood cells) include neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils. Neutrophils are essential for fighting bacterial infections. Lymphocytes play a crucial role in the immune response, with T cells attacking infected cells and B cells producing antibodies. Monocytes differentiate into macrophages and help in phagocytosis. Eosinophils are involved in combating parasitic infections and allergic reactions, while basophils release histamine during inflammatory responses.
| 2. How does blood circulation work in the human body? |  |
Ans. Blood circulation in the human body consists of two main circuits: the systemic circulation and the pulmonary circulation. In systemic circulation, oxygen-rich blood is pumped from the left ventricle through the aorta to supply the body tissues. After delivering oxygen, blood returns to the heart through the veins to the right atrium. In pulmonary circulation, deoxygenated blood is pumped from the right ventricle to the lungs via the pulmonary arteries, where it gets oxygenated and returns to the left atrium through the pulmonary veins.
| 3. What do the different waves in an ECG represent? |  |
Ans. An electrocardiogram (ECG) displays several waves that represent different electrical activities of the heart. The P wave indicates atrial depolarization, which leads to atrial contraction. The QRS complex represents ventricular depolarization, which leads to ventricular contraction. The T wave reflects ventricular repolarization, indicating the recovery phase of the ventricles. Each wave provides important information about the heart's rhythm and overall health.
| 4. What is the process of blood coagulation? |  |
Ans. Blood coagulation is a complex process that prevents excessive bleeding when a blood vessel is injured. It involves the activation of platelets and the clotting cascade, which comprises a series of proteins in the blood. When a vessel is damaged, platelets adhere to the injury site and release chemicals that attract more platelets. This forms a temporary plug. Simultaneously, clotting factors are activated, leading to the conversion of fibrinogen into fibrin, which stabilizes the clot, allowing healing to occur.
| 5. What are the phases of the cardiac cycle? |  |
Ans. The cardiac cycle consists of several phases: diastole and systole. During diastole, the heart muscle relaxes and the chambers fill with blood. This phase is further divided into early diastole (when the atria fill) and late diastole (when the atria contract and push blood into the ventricles). Systole follows, where the ventricles contract to pump blood to the lungs and the rest of the body. The cycle is crucial for maintaining an efficient blood flow and ensuring that oxygen is delivered to tissues.
Related Searches
















