Mnemonics: Cell- The Unit of Life | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Cell Theory |

|
| Plasma Membrane |

|
| Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) |

|
| Golgi Apparatus |

|
| Nucleus |

|
| Mitochondria |

|
| Chloroplasts |

|
| Vacuoles |

|
This document will help you remember important information about Cell: The Unit of Life in a fun and easy way. Inside, you'll find mnemonics—memory tricks—that will make it easier for you to remember key concepts, examples, and organelles of a Cell.
Whether you're studying for an exam, preparing for a quiz, or simply looking to enhance your understanding of Cell: The Unit of Life, these mnemonics will serve as valuable memory tools. Utilize them alongside your regular study routine to reinforce your knowledge and increase your recall ability.
Happy mnemonic learning!
Cell Theory
"Come See Closely, Cells Create Life"
- Come: Represents the concept that cells come from pre-existing cells.
- See: Highlights the importance of observing and studying cells under a microscope.
- Closely: Emphasizes the need to examine cells closely to understand their structure and function.
- Cells: Reminds you that cells are the fundamental units that make up all living organisms.
- Create Life: Reinforces that cells are responsible for the creation and maintenance of life.
Plasma Membrane
"Secure Gates Guarding Cellular Entrances and Exits"
- Secure: Highlights the role of the plasma membrane in providing security and protection to the cell.
- Gates: Represents the selective permeability of the plasma membrane, controlling the movement of substances.
- Guarding: Reminds you that the plasma membrane acts as a barrier, guarding the cellular interior.
- Cellular: Relates to the cell, indicating that the plasma membrane is specific to cells.
- Entrances and Exits: Signifies the function of the plasma membrane in regulating the entry and exit of molecules.
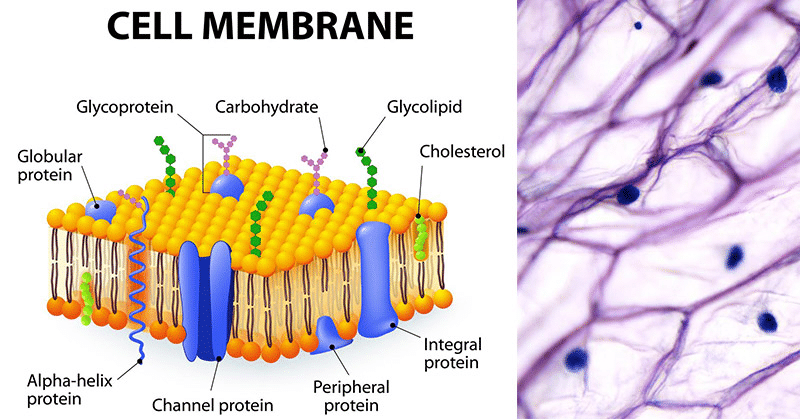 Plasma Membrane
Plasma Membrane
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
"Endless Road for Protein: Rough and Smooth ER"
- Endless Road: Illustrates the continuous network of membranes within the cell forming the ER.
- Protein: Highlights the main function of the ER, which is involved in protein synthesis and processing.
- Rough and Smooth: Distinguishes between the two types of ER - rough ER (with ribosomes) and smooth ER (without ribosomes).
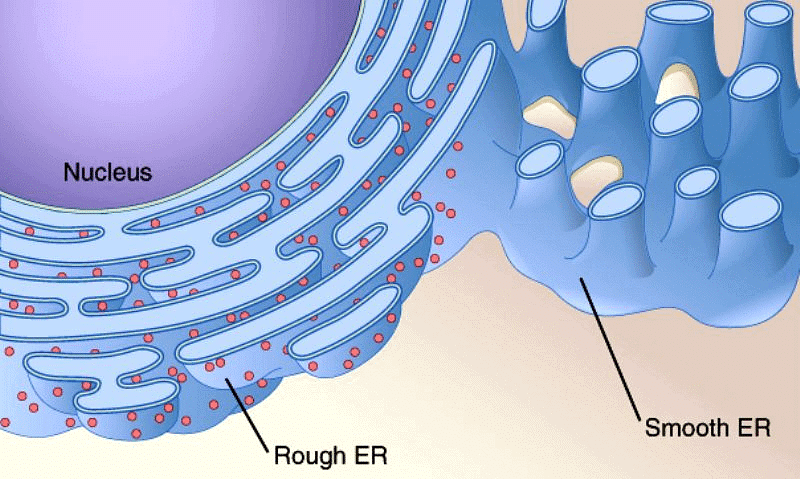 Endoplasmic Reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Golgi Apparatus
"Gift Assembly, Packaging, and Dispatching Operations"
- Gift: Represents the Golgi apparatus, responsible for modifying, processing, and packaging molecules.
- Assembly: Highlights the role of the Golgi apparatus in assembling and modifying complex molecules.
- Packaging: Reminds you that the Golgi apparatus packages molecules into vesicles for transportation.
- Dispatching Operations: Signifies that the Golgi apparatus dispatches vesicles to different cellular locations.
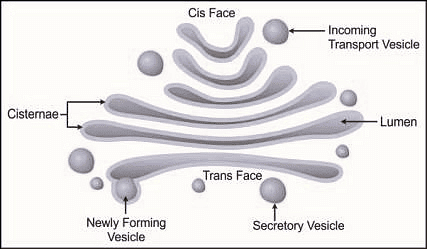 Golgi Apparatus
Golgi Apparatus
Nucleus
"Nucleus: Cell's Brain, Information Center"
- Nucleus: Represents the brain of the cell, responsible for controlling cell activities.
- Cell's Brain: Highlights its crucial role in regulating cell functions.
- Information Center: Reminds you that the nucleus stores and processes genetic information.
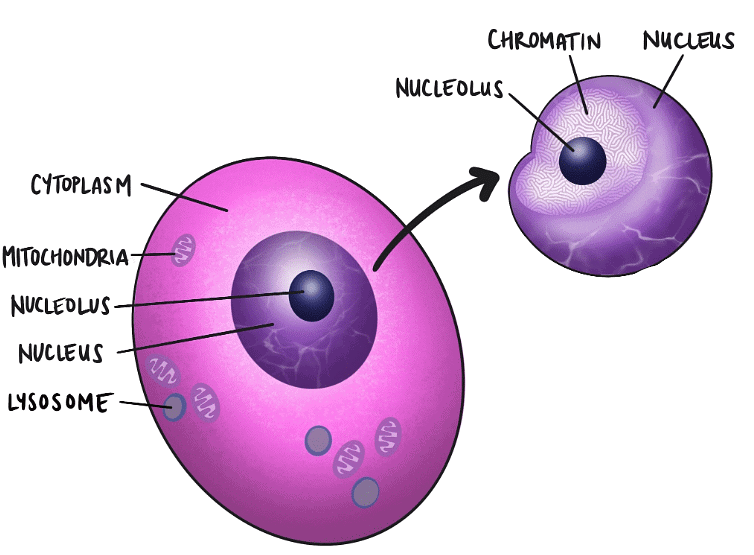 Nucleus
Nucleus
Mitochondria
"Mitochondria: Cell's Powerhouses, Energy Providers"
- Mitochondria: Symbolize powerhouses within the cell.
- Cell's Powerhouses: Emphasizes their function in generating energy.
- Energy Providers: Reminds you that mitochondria supply the cell with energy for its activities.
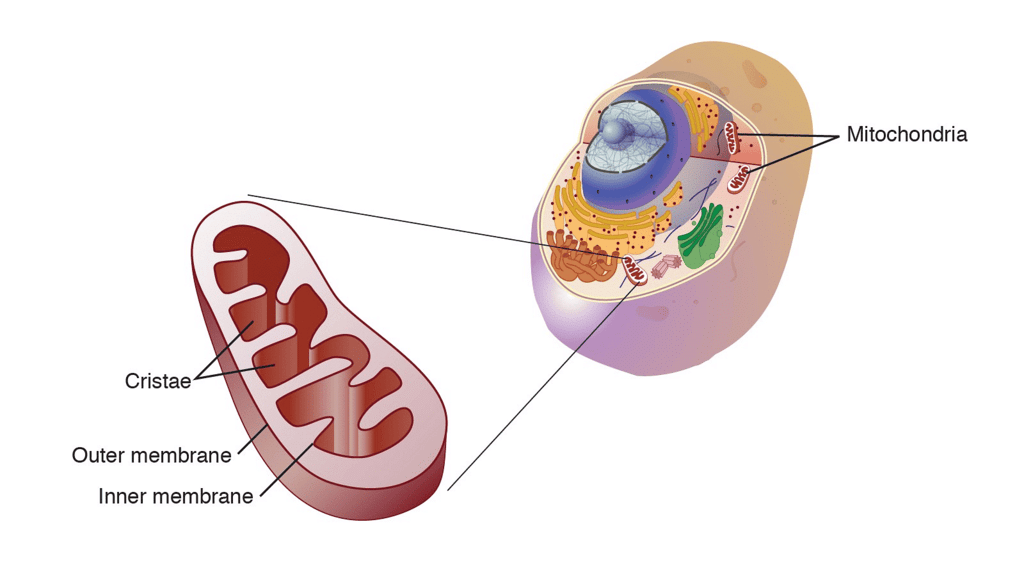 Mitochondria
Mitochondria
Chloroplasts
"Chloroplasts: Cell's Solar Panels, Sunlight Converters"
- Chloroplasts: Represent solar panels within plant cells.
- Cell's Solar Panels: Highlights their role in capturing sunlight.
- Sunlight Converters: Reminds you that chloroplasts convert sunlight into chemical energy during photosynthesis.
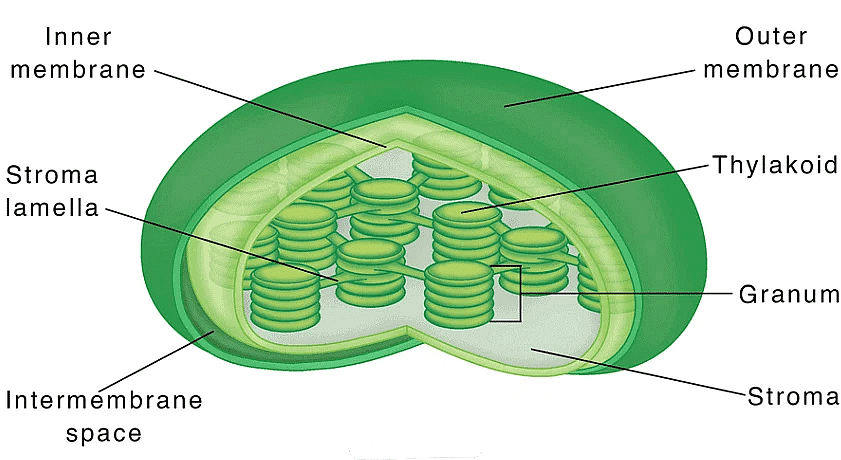 Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts
Vacuoles
"Vacuoles: Cell's Storage Units, Water Reservoirs"
- Vacuoles: Symbolize storage units within the cell.
- Cell's Storage Units: Emphasizes their function in storing various substances.
- Water Reservoirs: Reminds you that vacuoles can store water to maintain cellular hydration.
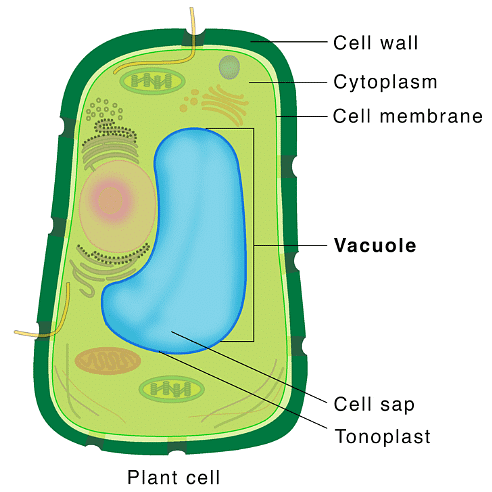 Vacuole
Vacuole
|
150 videos|398 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Cell- The Unit of Life - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the cell theory? |  |
| 2. What is the function of the plasma membrane? |  |
| 3. What is the role of the Golgi apparatus in the cell? |  |
| 4. What is the function of mitochondria in cells? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of chloroplasts in plant cells? |  |





















