Mnemonics: Current Electricity | Physics Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
1. Ohm’s Law
Types: Voltage (V), Current (I), Resistance (R)
Mnemonic: "Very Interesting Resistance"
Very – Voltage (V)
Interesting – Current (I)
Resistance – Resistance (R)
V = I R: Ohm’s law shows the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance. The voltage is directly proportional to the current and resistance.

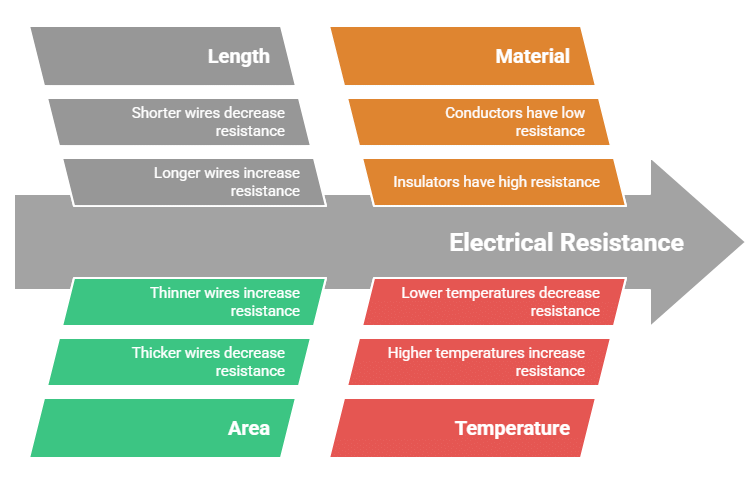
2. Factors Affecting Resistance
Types: Length, Area, Material, Temperature
Mnemonic: "Lazy Ants Make Tea"
- Lazy – Length
- Ants – Area
- Make – Material
- Tea – Temperature
Length (Lazy): The resistance of a conductor increases with length; longer wires have more resistance.
Area (Ants): The resistance decreases with cross-sectional area; thicker wires allow more current to flow.
Material (Make): Different materials have different resistivities. Conductors (like copper) have low resistance, while insulators (like rubber) have high resistance.
Temperature (Tea): Resistance generally increases with temperature for most conductors because higher temperatures cause more collisions between electrons and atoms.
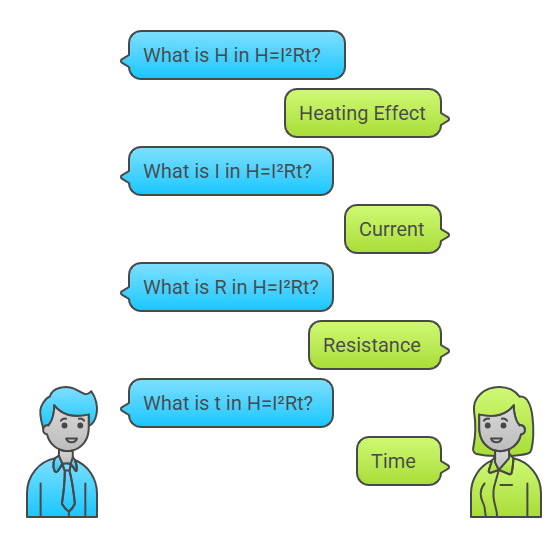
3. Heating Effect of Current (Joule’s Law)
Formula: H=I2Rt
Mnemonic: "Hot Iron Really Thrills"
Hot – Heating Effect (H)
Iron – Current (I)
Really – Resistance (R)
Thrills – Time (t)
H (Hot): The heating effect (H) is the energy converted into heat in a resistor when current flows through it.
I (Iron): The current (I) flowing through the conductor is squared in the formula, indicating the importance of current in heating.
R (Really): Resistance (R) represents the opposition to the current flow, which generates heat.
t (Thrills): The time (t) for which the current flows affects the total heat produced, as the longer the current flows, the more heat is generated.
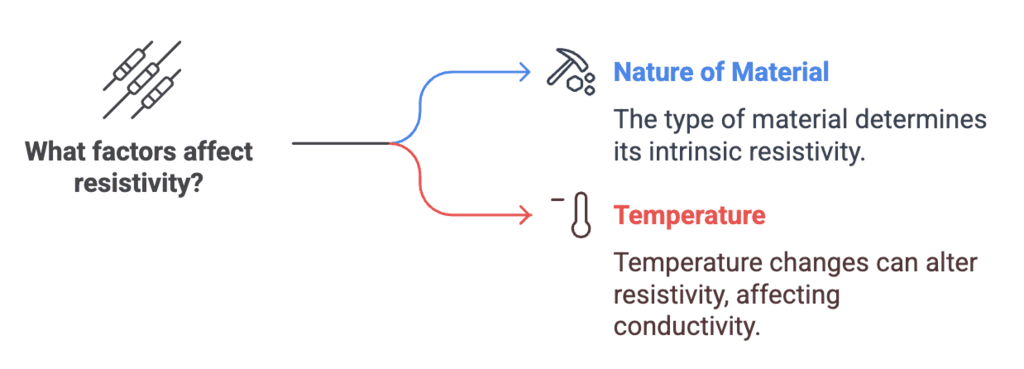
4. Resistivity Depends On
Types: Nature of Material, Temperature
Mnemonic: "Naughty Tiger"
- Naughty – Nature of Material
- Tiger – Temperature
Nature of Material (Naughty): The resistivity of a material depends on its intrinsic properties, like whether it's a conductor, insulator, or semiconductor. Different materials have different resistivities.
Temperature (Tiger): Resistivity typically increases with temperature for most materials. As temperature rises, the atoms in the material vibrate more, making it harder for electrons to move through, increasing resistance.
5. Combination of Resistors
Types: Series, Parallel
Mnemonic: "Silly Parrots"
- Silly – Series
- Parrots – Parallel
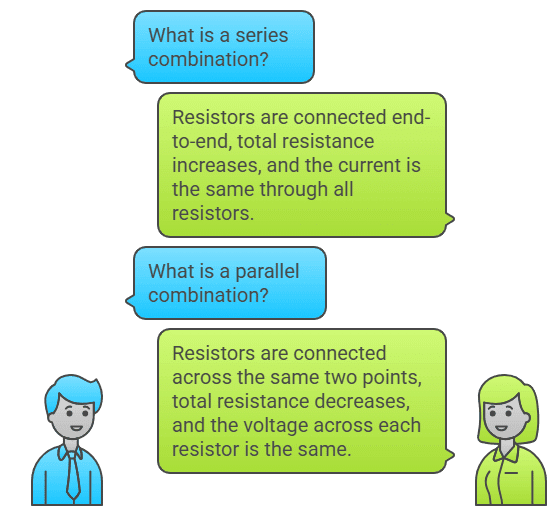
Series (Silly): In a series combination, resistors are connected end-to-end. The total resistance increases as you add more resistors, and the current is the same through all of them.
Parallel (Parrots): In a parallel combination, resistors are connected across the same two points. The total resistance decreases as you add more resistors, and the voltage across each resistor is the same.
6. Kirchhoff’s Laws
Types: Junction Rule, Loop Rule
Mnemonic: "Justice Loves Loops"
Justice – Junction Law (sum of currents at a junction)
Loves – Loop Law (sum of voltages in a loop is zero)
Junction Law (Justice):
At any junction in a circuit, the total current entering the junction is equal to the total current leaving the junction. This law ensures that no current is "lost" at any junction in a circuit.Loop Law (Loves):
The sum of the voltages (potential differences) around any closed loop in a circuit must be zero. This is because energy supplied by the sources is used up by the resistive elements in the loop, so there’s no net gain or loss of energy.

7. Common Electrical Units
Types: Ampere, Volt, Ohm, Watt, Coulomb
Mnemonic: "A Very Old Wise Cat"
- A – Ampere
- Very – Volt
- Old – Ohm
- Wise – Watt
- Cat – Coulomb
Ampere (A): The unit of electric current. It measures the flow of electric charge per unit of time.
Volt (Very): The unit of electric potential difference or voltage. It measures the force that pushes the electric current through a conductor.
Ohm (Old): The unit of electrical resistance. It measures how much a material resists the flow of current.
Watt (Wise): The unit of power. It measures the rate at which electrical energy is transferred or converted.
Coulomb (Cat): The unit of electric charge. It measures the quantity of electric charge.
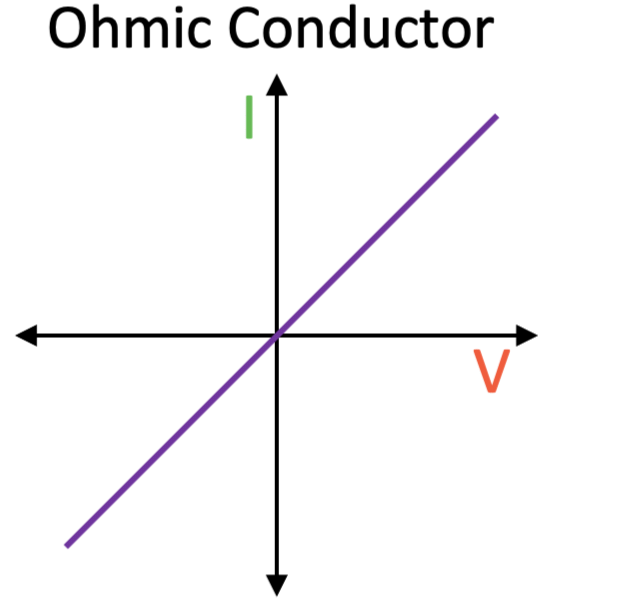
8. Important Graphs
Types: V-I Graph for Ohmic, V-I Graph for Non-Ohmic, Resistance-Temperature Graph
Mnemonic: "Very Nice Representation"
- Very – V-I Graph for Ohmic
- Nice – V-I Graph for Non-Ohmic
- Representation – Resistance-Temperature Graph
The V-I graph for Ohmic conductors is a straight line, showing that the current is directly proportional to the voltage (constant resistance).
The V-I graph for Non-Ohmic conductors is not a straight line, indicating that the resistance changes with voltage or current.
The Resistance-Temperature graphillustrates how resistance changes with temperature, typically increasing for most materials as temperature rises.
|
74 videos|314 docs|88 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Current Electricity - Physics Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is the concept of electric current in current electricity? |  |
| 2. How do you calculate the resistance in a circuit using Ohm's law? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of circuits in current electricity? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of Kirchhoff's laws in current electricity? |  |
| 5. How do capacitors work in an electric circuit? |  |