Mnemonics: Electromagnetic Waves | Physics Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
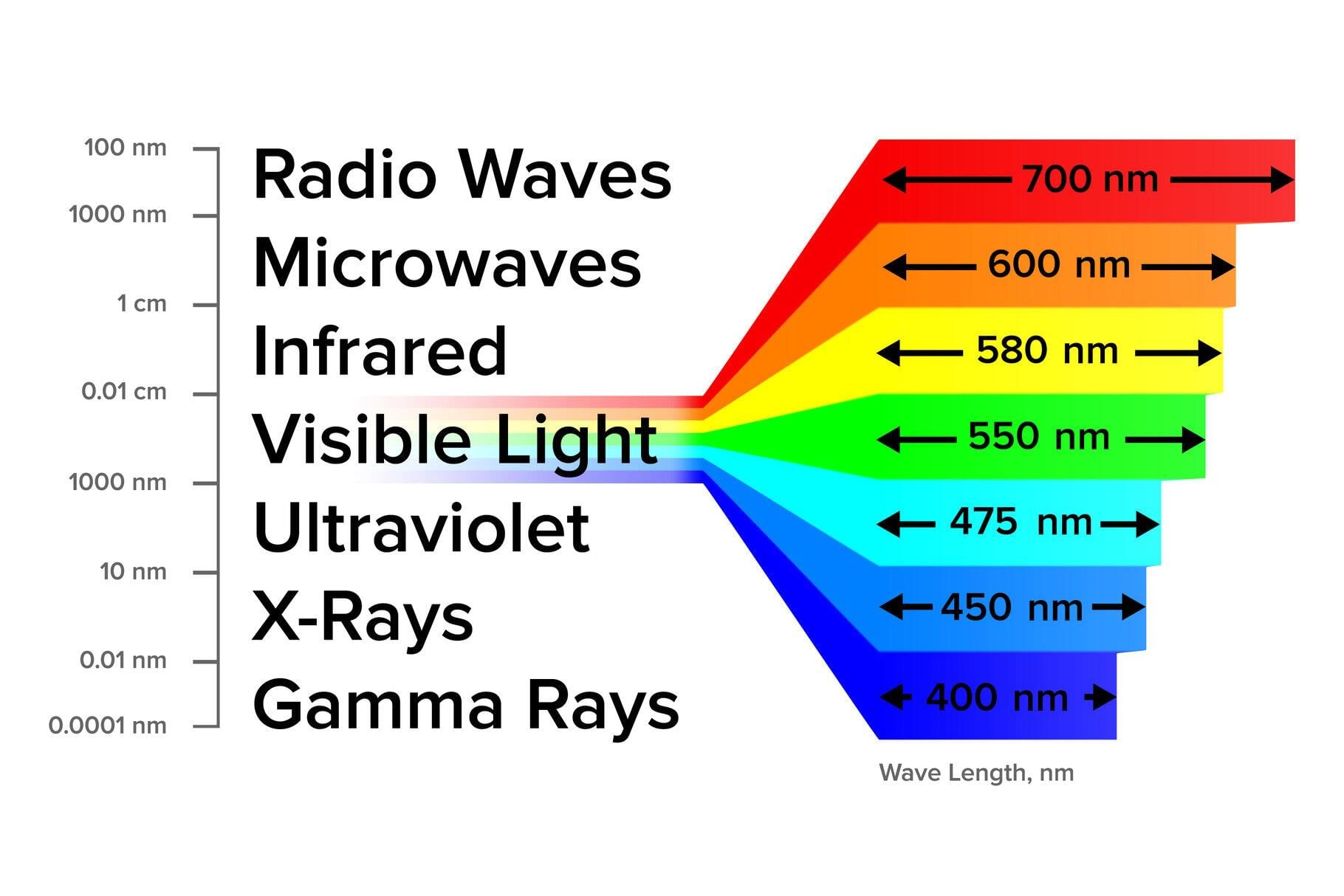
1. Electromagnetic Spectrum (From Long Wavelength to Short)
Types: Radio Waves, Microwaves, Infrared, Visible, Ultraviolet, X-Rays, Gamma Rays
Mnemonic: "Rabbits March In Very Unusual Xtreme Gardens"
Breakdown:
Rabbits – Radio Waves: These have the longest wavelength and the lowest frequency in the electromagnetic spectrum.
March – Microwaves: Used in communication and heating food, with shorter wavelengths than radio waves.
In – Infrared: Wavelengths longer than visible light, felt as heat.
Very – Visible: The range of light visible to the human eye, including all colors of the rainbow.
Unusual – Ultraviolet: Wavelengths shorter than visible light; ultraviolet rays are responsible for tanning and sunburns.
Xtreme – X-Rays: High-energy waves used in medical imaging, with very short wavelengths.
Gardens – Gamma Rays: The shortest wavelength and the highest frequency, produced by radioactive decay and certain cosmic events.
This mnemonic helps you remember the order of electromagnetic waves from long to short wavelength. The spectrum starts with Radio Waves (longest wavelength) and ends with Gamma Rays (shortest wavelength). Each type of wave has unique uses and properties, from communication in radio waves to high-energy applications like gamma rays in medicine and radiation therapy.
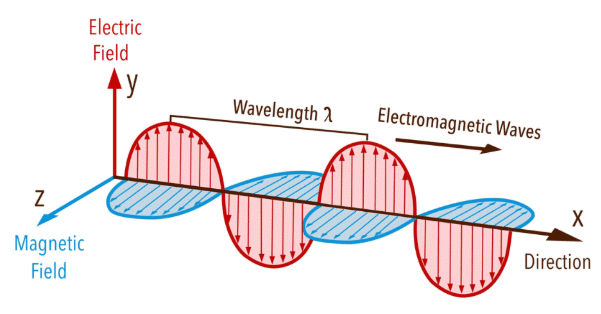
2. Properties of Electromagnetic Waves
Types: Transverse Nature, Travel in Vacuum, Perpendicular Electric and Magnetic Fields, Carry Energy and Momentum, Constant Speed in Vacuum
Mnemonic: "Tall Trees Protect Every Creature"
- Breakdown:
Tall – Transverse Nature: Electromagnetic waves are transverse, meaning their oscillations occur perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation.
Trees – Travel in Vacuum: Electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum (space) without the need for a medium.
Protect – Perpendicular Electric and Magnetic Fields: The electric and magnetic fields in electromagnetic waves are perpendicular to each other and to the direction of wave propagation.
Every – Energy and Momentum: Electromagnetic waves carry both energy and momentum as they travel.
Creature – Constant Speed in Vacuum: In a vacuum, electromagnetic waves travel at a constant speed of m/s, which is the speed of light.
This mnemonic helps you recall the key properties of electromagnetic waves. These waves have a transverse nature, they can travel in a vacuum, their electric and magnetic fields are perpendicular, they carry energy and momentum, and they travel at a constant speed in vacuum, specifically the speed of light.
|
74 videos|314 docs|88 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Electromagnetic Waves - Physics Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What are electromagnetic waves and how are they classified? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of the electromagnetic spectrum in NEET? |  |
| 3. How do electromagnetic waves propagate through different media? |  |
| 4. What are some real-life applications of electromagnetic waves? |  |
| 5. How can mnemonics help in remembering the order of electromagnetic waves? |  |
















