NEET Exam > NEET Notes > Biology Class 11 > Mnemonics: Excretory Products & their Elimination
Mnemonics: Excretory Products & their Elimination | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
Let's learn the complex parts and processes of kidney by interlinking it with our daily words and never ever forgetting it again.
Types of Excretion Processes
Mnemonic: "All Urea Ultimately Evolves"
- All - Ammonotelism: Excretion of ammonia (e.g., bony fish, amphibians).
- Urea - Ureotelism: Excretion of urea (e.g., mammals, amphibians).
- Ultimately - Uricotelism: Excretion of uric acid (e.g., birds, reptiles).
- Evolves - Evolutionary Adaptation: Terrestrial animals produce less toxic forms like urea or uric acid for water conservation.
Types of Excretory Organs and Examples
Mnemonic: "Please Never Make Green Plants"
- Please - Protonephridia (e.g., Planaria): For osmoregulation in flatworms.
- Never- Nephridia (e.g., Earthworm): Remove nitrogenous wastes and maintain fluid balance.
- Make - Malpighian Tubules (e.g., Cockroach): For osmoregulation and nitrogen waste elimination in insects.
- Green - Green Glands (e.g., Prawns): Excretion in crustaceans.
- Plants- Plants: Use transpiration, guttation, and excretion through leaves for waste elimination.
Parts of the Kidney
Mnemonic: "Can Medics Handle Calm Patients?"
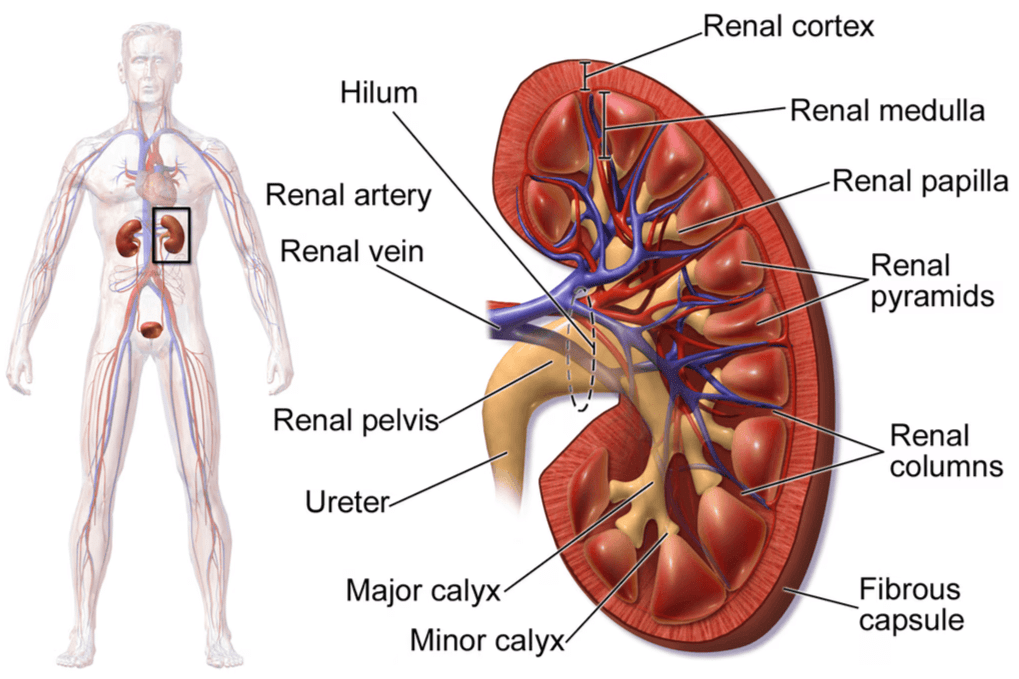
- Can - Cortex: Outer layer containing glomeruli and convoluted tubules.
- Medics - Medulla: Inner region with pyramids and loop of Henle.
- Handle - Hilum: Entry/exit for ureters, blood vessels, and nerves.
- Calm - Calyces: Funnel-shaped projections leading to the renal pelvis.
- Patients - Pelvis: Collects urine and passes it to the ureter.
Steps of Urine Formation
Mnemonic: "Good Rabbits Swim"
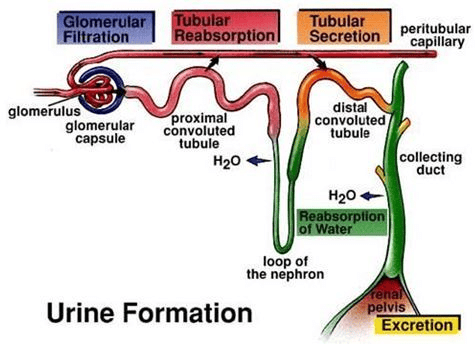
- Good - Glomerular Filtration: Ultrafiltration of blood in the glomerulus.
- Rabbits - Reabsorption: Active/passive absorption of nutrients, water, and ions in the tubules.
- Swim - Secretion: Elimination of H+, K+, and ammonia into the filtrate for pH and ionic balance.
Counter Current Mechanism
Mnemonic: "Henle's Loop Regulates Salts"
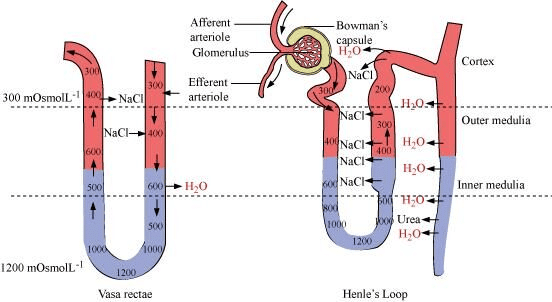
- Henle's Loop - Henle's Loop: Creates a gradient via descending (water permeable) and ascending limbs (impermeable to water, salt transport).
- Loop - Loop of Vasa Recta: Parallel capillaries help in exchange and retention of salts (NaCl and urea).
- Regulates - Regulation: Ensures concentrated urine with osmolarity up to 1200 mOsmol/L.
- Salts - Salts and Urea: Contribute to the osmotic gradient in the medulla.
Role of Other Organs in Excretion
Mnemonic: "Love Liver, Skin, and Sweat"
- Love - Lungs: Remove CO₂ and water vapor.
- Liver- Liver: Excretes bile pigments (bilirubin and biliverdin), drugs, and cholesterol.
- Skin - Skin: Eliminates salts, urea, and lactic acid via sweat.
- Sweat - Sebaceous Glands: Remove sterols and hydrocarbons through sebum.
Disorders of the Excretory System
Mnemonic: "U Really Shouldn't Get Kidney Glitches"
- U - Uremia: Accumulation of urea in blood due to kidney failure.
- Really - Renal Calculi: Kidney stones formed by crystallized salts.
- Shouldn't - Stone Formation: Includes oxalate stones causing pain and obstruction.
- Get - Glomerulonephritis: Inflammation of glomeruli, impairing filtration.
- Kidney - Kidney Failure: Treated by dialysis or kidney transplantation.
- Glitches - Glycosuria and Ketonuria: Presence of glucose and ketone bodies in urine, indicative of diabetes.
The document Mnemonics: Excretory Products & their Elimination | Biology Class 11 - NEET is a part of the NEET Course Biology Class 11.
All you need of NEET at this link: NEET
|
169 videos|531 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Excretory Products & their Elimination - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What are the main types of excretion processes in organisms? |  |
Ans. The main types of excretion processes in organisms include:
1. <b>Diffusion</b> - the movement of waste products from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration across cell membranes (e.g., gases like CO2).
2. <b>Exocytosis</b> - the process where cells expel waste materials in vesicles that fuse with the cell membrane.
3. <b>Active Transport</b> - the movement of ions or molecules against their concentration gradient, often using energy (e.g., reabsorption of ions in kidneys).
4. <b>Filtration</b> - the process of separating waste from blood, primarily occurring in the kidneys.
| 2. What are the different types of excretory organs and their examples? |  |
Ans. Different types of excretory organs include:
1. <b>Kidneys</b> - responsible for filtering blood and producing urine (e.g., human kidneys).
2. <b>Liver</b> - detoxifies and metabolizes substances, producing urea (e.g., human liver).
3. <b>Skin</b> - excretes sweat which contains water, salts, and urea (e.g., human skin).
4. <b>Lungs</b> - expel carbon dioxide and water vapor during respiration (e.g., human lungs).
| 3. What are the main parts of the kidney and their functions? |  |
Ans. The main parts of the kidney include:
1. <b>Cortex</b> - the outer region where blood filtration occurs.
2. <b>Medulla</b> - the inner region containing renal pyramids that help in urine formation.
3. <b>Renal Pelvis</b> - collects urine before it moves to the ureter.
4. <b>Nephrons</b> - the functional units of the kidney responsible for filtering blood and forming urine.
| 4. What are the steps involved in urine formation? |  |
Ans. The steps of urine formation include:
1. <b>Filtration</b> - blood is filtered in the glomerulus, allowing water, ions, and small molecules to pass into the Bowman's capsule.
2. <b>Reabsorption</b> - essential substances (water, glucose, ions) are reabsorbed back into the bloodstream from the renal tubules.
3. <b>Secretion</b> - additional waste products and excess ions are secreted from the blood into the renal tubules.
4. <b>Excretion</b> - the final urine is collected in the renal pelvis and transported to the bladder for elimination.
| 5. How does the counter-current mechanism work in the kidneys? |  |
Ans. The counter-current mechanism in the kidneys involves the interaction between the descending and ascending limbs of the loop of Henle.
- In the descending limb, water is reabsorbed, concentrating the filtrate.
- In the ascending limb, sodium and chloride ions are actively transported out, diluting the filtrate.
This mechanism creates a gradient that allows for efficient reabsorption of water in the collecting ducts, thus concentrating urine and conserving water in the body.
Related Searches
















