Mnemonics: Magnetism and Matter | Physics Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
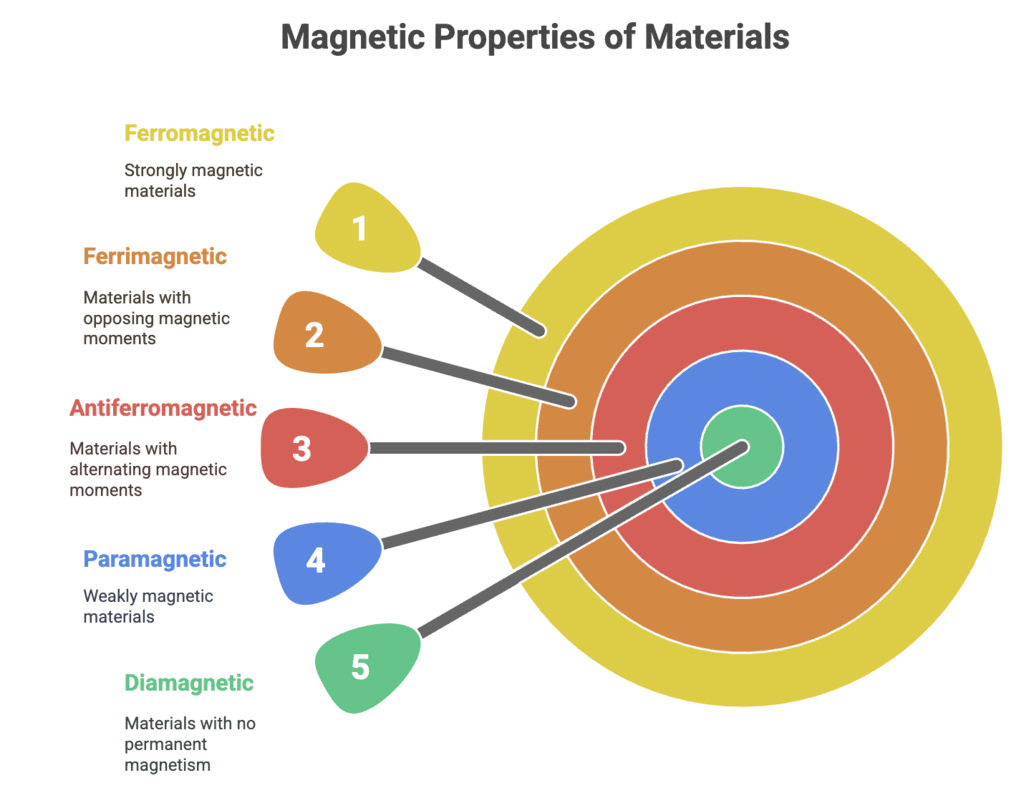
1. Magnetic Properties of Materials
Types: Diamagnetic, Paramagnetic, Ferromagnetic, Antiferromagnetic, Ferrimagnetic
Mnemonic: "Don’t Play Football After Fights"
Don’t – Diamagnetic
Play – Paramagnetic
Football – Ferromagnetic
After – Antiferromagnetic
Fights – Ferrimagnetic
This mnemonic makes it easier to remember the order of magnetic material types:
Diamagnetic – Weakly repelled by magnetic fields
Paramagnetic – Slightly attracted to magnetic fields
Ferromagnetic – Strongly attracted and retains magnetism
Antiferromagnetic – Opposing magnetic moments cancel out
Ferrimagnetic – Unequal opposing magnetic moments lead to net magnetism
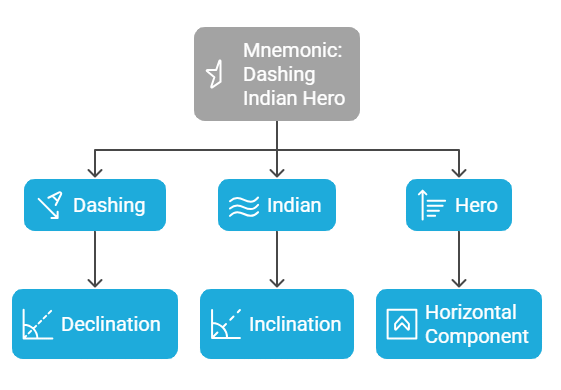
2. Magnetic Elements of Earth
Mnemonic: "Dashing Indian Hero"
Dashing – Declination
Indian – Inclination
Hero – Horizontal Component
This mnemonic helps you recall the three important magnetic elements of the Earth:
Declination – The angle between the magnetic north and true north (difference in direction).
Inclination – The angle between the magnetic field lines and the horizontal plane (also known as dip).
Horizontal Component – The component of the Earth's magnetic field that lies in the horizontal plane.
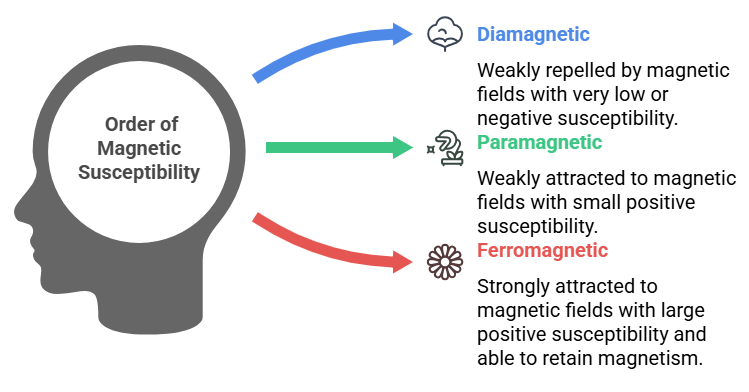
3. Order of Magnetic Susceptibility
Types: Diamagnetic < Paramagnetic < Ferromagnetic
Mnemonic: "Dull Plants Flourish"
Dull – Diamagnetic (very low or negative susceptibility)
Plants – Paramagnetic (positive but small susceptibility)
Flourish – Ferromagnetic (large and positive susceptibility)
This mnemonic helps you remember the order of magnetic susceptibility for different materials:
Diamagnetic materials are weakly repelled by magnetic fields and have very low or negative susceptibility.
Paramagnetic materials are weakly attracted to magnetic fields with a small positive susceptibility.
Ferromagnetic materials have a large positive susceptibility, making them strongly attracted to magnetic fields and able to retain magnetism.
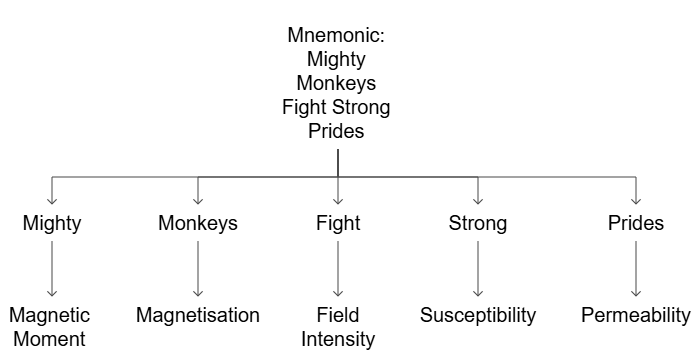
4. Magnetic Quantities and Their Meaning
Types: Magnetic Moment, Magnetisation, Magnetic Field Intensity, Magnetic Susceptibility, Relative Permeability
Mnemonic: "Mighty Monkeys Fight Strong Prides"
Mighty – Magnetic Moment
Monkeys – Magnetisation
Fight – Field Intensity
Strong – Susceptibility
Prides – Permeability (Relative)
This mnemonic uses an image of "Mighty Monkeys Fighting Strong Prides" to help you recall the magnetic quantities:
Magnetic Moment – The strength and orientation of a magnet’s field.
Magnetisation – The degree of magnetization a material achieves in response to an external magnetic field.
Magnetic Field Intensity – The strength of the magnetic field produced by a current or magnet.
Magnetic Susceptibility – How easily a material becomes magnetized in the presence of a magnetic field.
Relative Permeability – The ratio of a material's permeability to that of free space.
[Question: 0]
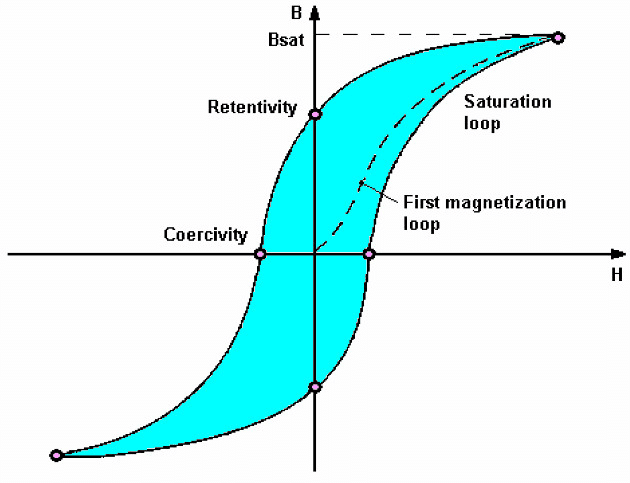
5. Magnetic Behaviour Based on Hysteresis
Types: Retentivity, Coercivity, Hysteresis Loss, Saturation
Mnemonic: "Rita Cooks Hot Soup"
- Rita – Retentivity
- Cooks – Coercivity
- Hot – Hysteresis Loss
- Soup – Saturation
This mnemonic helps you easily remember the key concepts related to hysteresis in magnetic materials:
Retentivity – The ability of a material to retain magnetization after the external magnetic field is removed.
Coercivity – The measure of the resistance of a material to becoming demagnetized.
Hysteresis Loss – Energy lost in the form of heat when a magnetic material is magnetized and demagnetized.
Saturation – The point at which an increase in the magnetic field does not result in any further increase in magnetization.
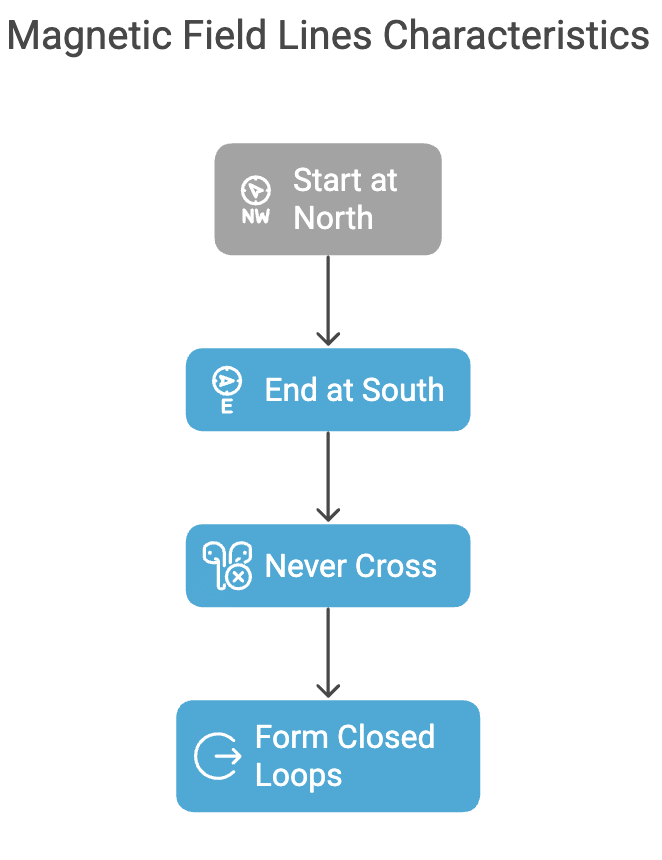
6. Magnetic Field Lines Characteristics
Types: Start from North, End at South, Never Cross, Form Closed Loops
Mnemonic: "Snakes Enter Narrow Caves"
- Snakes – Start at North
- Enter – End at South
- Narrow – Never Cross
- Caves – Closed Loops
This mnemonic helps you remember the important characteristics of magnetic field lines:
Start at North – Magnetic field lines begin at the north pole of a magnet.
End at South – Magnetic field lines end at the south pole of a magnet.
Never Cross – Magnetic field lines never intersect or cross each other.
Closed Loops – Magnetic field lines form closed loops, meaning they travel from the north pole to the south pole outside the magnet and loop back inside.
7. Units Related to Magnetism
Types: Ampere, Tesla, Weber, Henry
Mnemonic: "Ali Took Warm Hats"
- Ali – Ampere
- Took – Tesla
- Warm – Weber
- Hats – Henry
This mnemonic helps you remember the key units used in the study of magnetism:
Ampere – Unit of electric current.
Tesla – Unit of magnetic flux density (magnetic field strength).
Weber – Unit of magnetic flux.
Henry – Unit of inductance.
[Question: 0]
|
74 videos|314 docs|88 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Magnetism and Matter - Physics Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is the difference between magnetism and matter? |  |
| 2. How do magnetic fields interact with magnetic materials? |  |
| 3. What are the types of magnetic materials? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of the magnetic field lines? |  |
| 5. How can the concept of magnetism be applied in everyday life? |  |





















