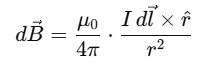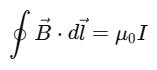Mnemonics: Moving Charges and Magnetism | Physics Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
1. Magnetic Force on Moving Charge
Formula: 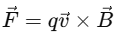
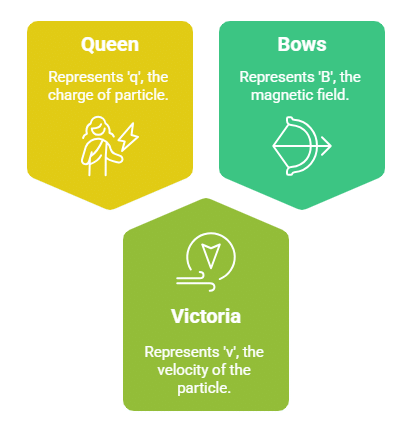
Mnemonic: "Queen Victoria Bows"
Breakdown:
Queen – q (charge)
Victoria – v (velocity)
Bows – B (magnetic field)
This mnemonic helps you recall the magnetic force formula where:
A charged particle (Queen) moving with a velocity (Victoria) in a magnetic field (Bows) experiences a magnetic force.
The direction of the force is given by the right-hand rule (thumb for velocity, fingers for magnetic field, palm gives the force direction for a positive charge).
2. Biot–Savart Law Elements
Mnemonic: "Tiny Current Makes Field"
Breakdown:
Tiny –
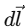 (tiny element of wire)
(tiny element of wire)Current – Current
Makes – Magnetic field
Field –
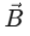
The Biot–Savart Law describes how a small segment of current-carrying conductor creates a magnetic field around it. The law is given by:
This mnemonic helps you recall the essential components involved in generating a magnetic field from a current element. "Tiny Current Makes Field" paints the picture of a small current element influencing its magnetic surroundings.
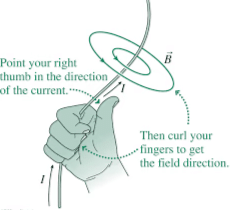
3. Ampere’s Circuital Law
Mnemonic: "I Am Beautiful"
Breakdown:
I – Current enclosed
Am – Ampere's Law
Beautiful –
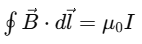 (the mathematical expression of the law)
(the mathematical expression of the law)
This mnemonic helps you recall Ampere’s Circuital Law, which connects the magnetic field along a closed loop to the electric current passing through that loop.
The word "Beautiful" represents the elegant and symmetrical equation:
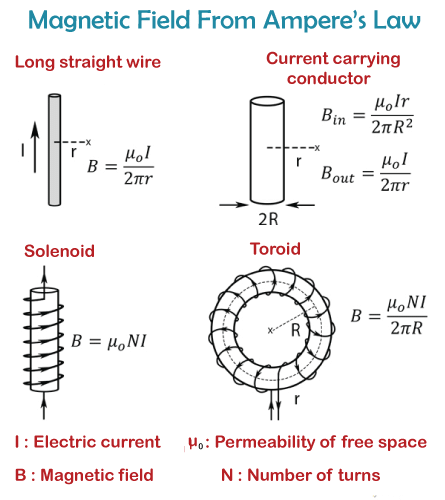
4. Ampere’s Circuital Law Applications
Types: Infinite Straight Wire, Solenoid, Toroid
Mnemonic: "Incredible Super Tunnel"
Breakdown:
Incredible – Infinite Straight Wire
Super – Solenoid
Tunnel – Toroid
This creative mnemonic helps you recall where Ampere’s Circuital Law is typically applied:
Infinite Straight Wire – To find the magnetic field around a long current-carrying conductor
Solenoid – To analyze the magnetic field inside a coil of wire
Toroid – For calculating the magnetic field in a donut-shaped coil.
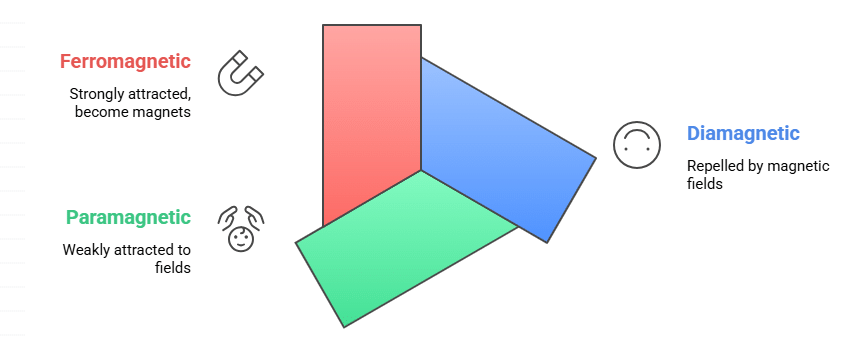
5. Magnetic Properties of Materials
Types: Diamagnetic, Paramagnetic, Ferromagnetic
Mnemonic: "Don’t Panic, Friend!"
Breakdown:
Don’t – Diamagnetic
Panic – Paramagnetic
Friend – Ferromagnetic
This mnemonic gives a sense of increasing magnetic behavior:
Diamagnetic → Very weak and repelled by magnetic fields (stay calm = don’t react)
Paramagnetic → Weakly attracted (mild response = slight panic)
Ferromagnetic → Strongly attracted and can become magnets (reliable = strong friend!)
6. Forces Between Two Parallel Currents
Types: Attraction, Repulsion, Dependence on Direction
Mnemonic: "Ants Run Downhill"
Ants – Attraction (currents in the same direction attract each other)
Run – Repulsion (currents in opposite directions repel each other)
Downhill – Direction Dependence (the force depends on the direction of the currents)
Ants (Attraction): When the currents are flowing in the same direction, they attract each other, similar to how ants might gather together.
Run (Repulsion): When the currents flow in opposite directions, they repel each other, just like how things would move away if they were in opposition.
Downhill (Direction Dependence): The force between the two currents depends on the direction in which they are flowing (either attracting or repelling based on their relative direction).
|
74 videos|314 docs|88 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Moving Charges and Magnetism - Physics Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is the relationship between moving charges and magnetic fields? |  |
| 2. How do magnetic fields affect the motion of charged particles? |  |
| 3. What are the applications of moving charges and magnetism in daily life? |  |
| 4. What is electromagnetic induction and its significance? |  |
| 5. How can the right-hand rule be used to determine the direction of the magnetic field? |  |