Mnemonics: Nuclei | Physics Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
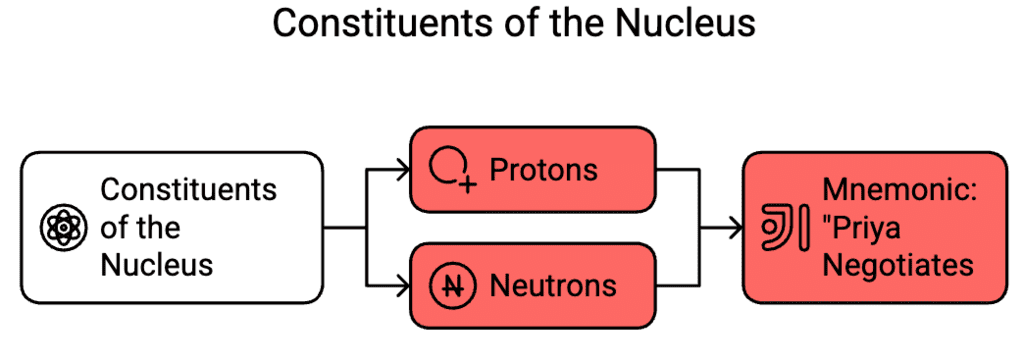
Constituents of the Nucleus
Types: Protons, Neutrons
Mnemonic: "Priya Negotiates "
Breakdown:
- Priya - Protons
- Negotiates - Neutrons
The nucleus of an atom is made up of two types of particles:
Protons are positively charged particles that determine the atomic number and identity of an element.
Neutrons are neutral particles that add mass to the nucleus and help stabilize it by reducing repulsive forces between protons.
Together, protons and neutrons are called nucleons, and they are held together by strong nuclear forces within the nucleus.
Nuclear Properties
Types: Mass Number, Atomic Number, Size
Mnemonic: "Mona Adds Shiny Zingers"
Breakdown:
- Mona - Mass Number
- Adds - Atomic Number
- Shiny Zingers - Size
These three properties are essential to understanding the characteristics of any nucleus:
Mass Number (A): Total number of nucleons (protons + neutrons) in the nucleus. It represents the mass of the atom (approximately).
Atomic Number (Z): Number of protons in the nucleus, which determines the identity and position of the element in the periodic table.
Size: Refers to the nuclear radius, which increases slightly with mass number, roughly following the formula R∝A1/3. The nucleus is incredibly small—about 10−15 meters.
Radioactive Decay Types
Types: Alpha, Beta, Gamma
Mnemonic: "Amit Blasts Glass"
Breakdown:
- Amit - Alpha
- Blasts - Beta
- Glass - Gamma
Alpha Decay (α/He²⁺): Emits 2 protons + 2 neutrons → Z ↓ by 2, A ↓ by 4.
Example: U-238 → Th-234.Beta Decay (β⁻/β⁺): Neutron → proton + electron (β⁻) or proton → neutron + positron (β⁺) → Z changes ±1, A unchanged.
Example: C-14 → N-14.Gamma Decay (γ): Emits high-energy photon → No change in Z or A, just energy release.
Often follows α or β decay.
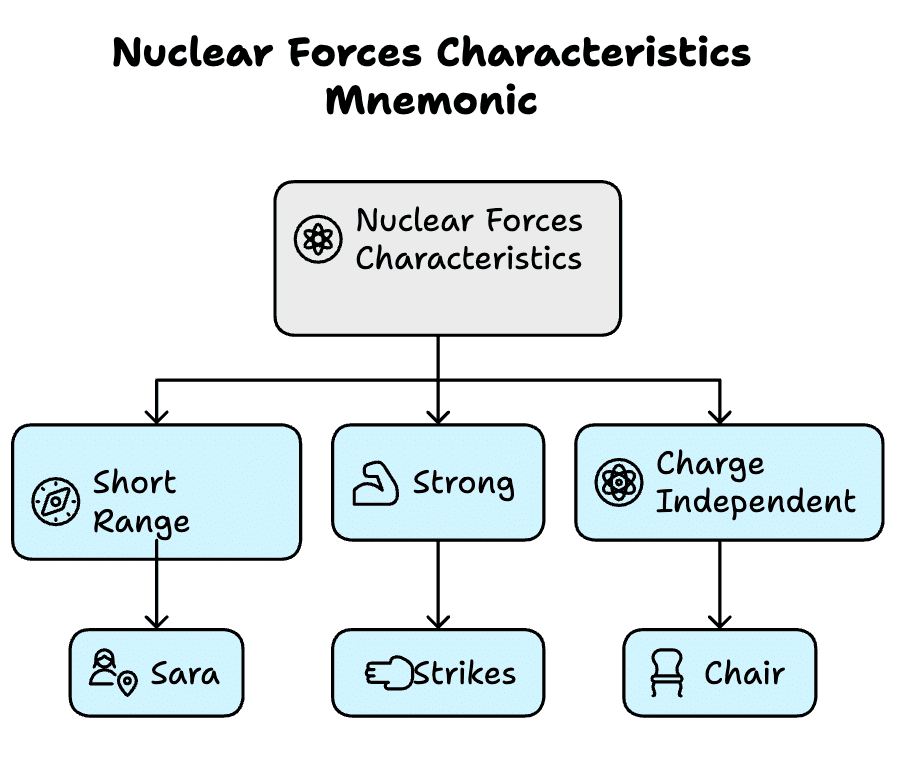
Nuclear Forces Characteristics
Types: Short Range, Strong, Charge Independent
Mnemonic: "Sara Strikes Chair"
Breakdown:
- Sara - Short Range
- Strikes - Strong
- Chair - Charge Independent
The nuclear force binds protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
Short Range: Acts only within ~1–2 femtometers; negligible beyond.
Strong: Strongest fundamental force; overcomes proton repulsion.
Charge Independent: Same effect between p–p, n–n, or p–n.
Radioactive Decay Law Components
Types: Activity, Half-Life, Decay Constant
Mnemonic: "Acids Have Dangerous Consequences "
Breakdown:
- Acids - Activity
- Have - Half-Life
- Dangerous consequences - Decay Constant
Activity (A): Rate of decay → A = λN
Half-Life (T₁/₂): Time for half the nuclei to decay → T₁/₂ = ln2 / λ
Decay Constant (λ): Probability of decay → λ = ln2 / T₁/₂
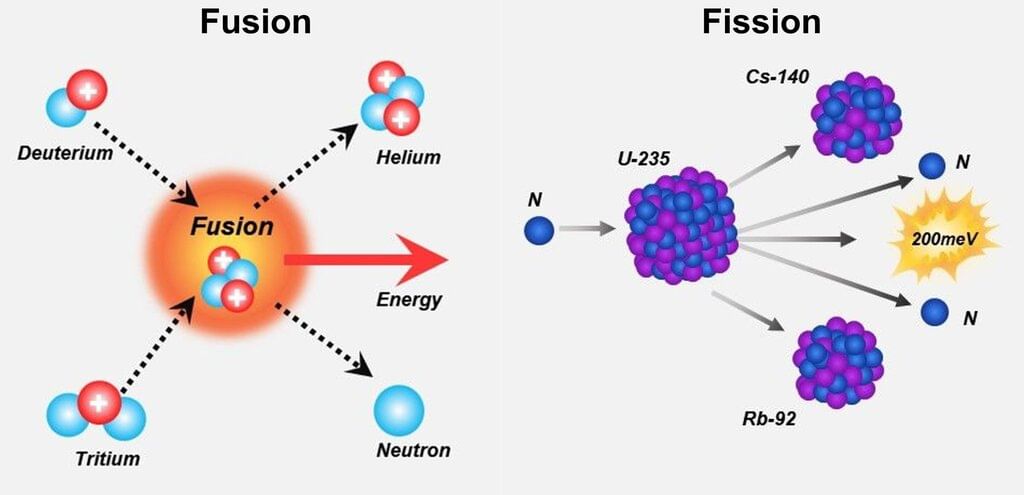
Nuclear Reactions
Types: Fission, Fusion
Mnemonic: "Farah Fuses Fireworks"
Breakdown:
- Farah - Fission
- Fuses Fireworks - Fusion
Fission:
Heavy nucleus splits → smaller nuclei + neutrons + energy
Example: U-235 + neutron → splits + energy
Used in: Reactors, bombsFusion:
Light nuclei combine → heavier nucleus + more energy
Example: H + H → He + energy (in the Sun)
Releases more energy than fission
Particles in Nuclear Physics
Types: Alpha Particle, Beta Particle, Neutrino
Mnemonic: "Always Be Neat"
Breakdown:
- Always - Alpha Particle
- Be - Beta Particle
- Neat - Neutrino
Alpha Particles (α):
2 protons + 2 neutrons (He nucleus), + charge, low penetration.
Stopped by paper/skin
Example: U-238 → Th-234 + αBeta Particles (β⁻/β⁺):
High-speed electrons or positrons, – or + charge, moderate penetration.
Example: C-14 → N-14 + β⁻Neutrinos (ν):
Neutral, tiny mass, weakly interacting, very hard to detect.
Emitted with beta particles
Example: Neutron → Proton + Electron + Neutrino (β⁻ decay)
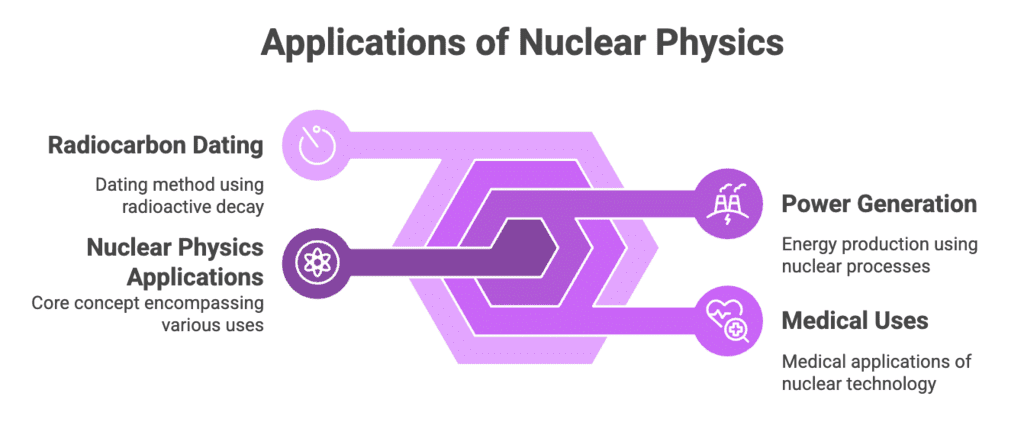
Applications of Nuclear Physics
Types: Power Generation, Medical Uses, Radiocarbon Dating
Mnemonic: "Power Makes Radiations Durable"
Breakdown:
- Power - Power Generation
- Makes - Medical Uses
- Radiations Durable - Radiocarbon Dating
Power Generation:
Nuclear reactors use fission (e.g., U-235) to produce heat and generate electricity.
Example: Nuclear power plants.Medical Uses:
Radioactive isotopes for imaging (PET, CT scans) and cancer treatment (radiation therapy).
Example: Tc-99m for scans, Co-60 for cancer therapy.Radiocarbon Dating:
Uses C-14 decay to date ancient organic materials.
Example: Dating fossils and archaeological artifacts.
|
74 videos|314 docs|88 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Nuclei - Physics Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What are some effective mnemonics to remember the structure of a nucleus for NEET preparation? |  |
| 2. How important is understanding nuclear chemistry concepts for the NEET exam? |  |
| 3. What strategies can I use to memorize the properties of different types of nuclei? |  |
| 4. Can you explain the significance of isotopes in the context of the nucleus for NEET? |  |
| 5. What resources are recommended for mastering nuclear concepts for NEET? |  |
















