Mnemonics: Photosynthesis in Higher Plants | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
Short lines help you remember the main ideas presented here. Learn concepts using mnemonics to boost your understanding. Enhance your knowledge with easy-to-remember techniques. Make learning fun and engaging with phrases related to concepts.
1. Key Scientists and Their Contributions
Scientists: Priestley (Oxygen Role), Ingenhousz (Light Role), Sachs (Glucose/Starch), Engelmann (Action Spectrum), Calvin (Calvin Cycle)
Mnemonic: "Priests Inspire Scientists Exploring Cycles"
Breakdown:
Priests → Priestley (Oxygen Role)
Inspire → Ingenhousz (Light Role)
Scientists → Sachs (Glucose/Starch)
Exploring → Engelmann (Action Spectrum)
Cycles → Calvin (Calvin Cycle)
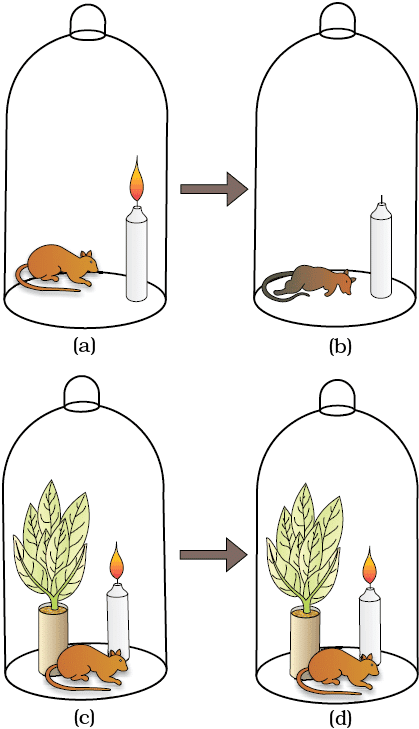 Priestley’s experiment
Priestley’s experiment
2. Major Pigments in Photosynthesis
Pigments: Chlorophyll a, Chlorophyll b, Xanthophylls, Carotenoids
Mnemonic: "Cool Cats X-ray Carrots"
Breakdown:
Cool → Chlorophyll a
Cats → Chlorophyll b
X-ray → Xanthophylls
Carrots → Carotenoids
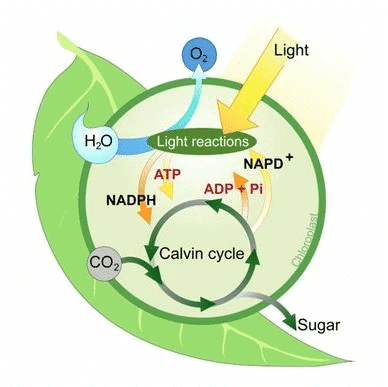
3. Products of Light Reaction
Products: ATP, NADPH, Oxygen (O₂)
Mnemonic: "Apples Nourish Oranges"
Breakdown:
Apples → ATP
Nourish → NADPH
Oranges → Oxygen (O₂)
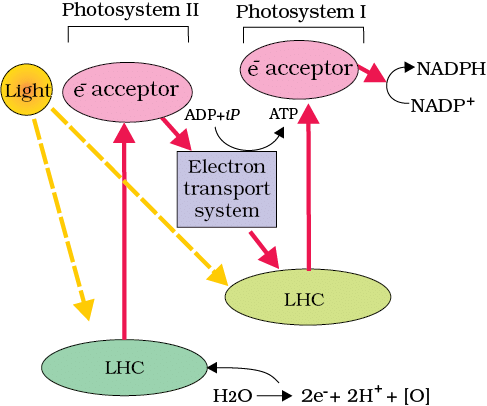 Light Reaction - Z Scheme
Light Reaction - Z Scheme
4. Photolysis (Splitting of Water)
Mnemonic Phrase: "Water Turns Energetic, Producing Oxygens and Particles."
W – Water (Splitting of H₂O during the light reaction)
T – Turns (Water molecules undergo photolysis)
E – Energetic (Light energy excites electrons)
P – Producing Oxygen (Oxygen is released from the splitting of water)
O – Oxygen (As a byproduct of photolysis)
P – Particles (Electrons and protons are released)
This mnemonic helps you understand photolysis, the process by which water is split during the light reaction to produce oxygen, electrons, and protons.
5. Cyclic and Non-Cyclic Photophosphorylation
Mnemonic Phrase: "Cyclic Paths Provide Only ATP, Non-Cyclic Powers Both."
C – Cyclic photophosphorylation (Electrons from photosystem I return to the same system, only ATP is produced)
P – Provide (Cyclic pathway only provides ATP)
O – Only (ATP is produced in cyclic photophosphorylation)
N – Non-cyclic photophosphorylation (Electrons flow from photosystem II to photosystem I and then to NADP⁺ to form NADPH)
P – Powers (ATP and NADPH are both produced in non-cyclic photophosphorylation)
B – Both (Non-cyclic photophosphorylation produces both ATP and NADPH)
This mnemonic helps you differentiate between cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation, which are the processes that generate ATP and NADPH.
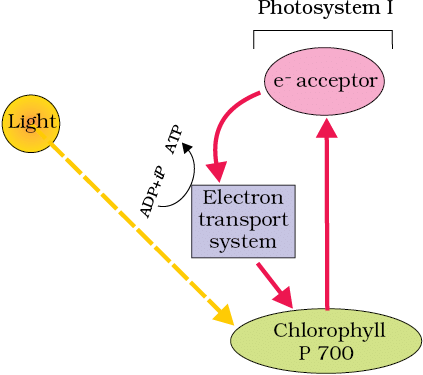 Cyclic photophosphorylation
Cyclic photophosphorylation
6. Stages of the Calvin Cycle
Stages: Carboxylation, Reduction, Regeneration
Mnemonic: "Cows Run Rapidly"
Breakdown:
Cows → Carboxylation
Run → Reduction
Rapidly → Regeneration
7. Key Components of the Calvin Cycle
Components: RuBP, CO₂, 3-PGA, Glucose
Mnemonic: "Rabbits Chew Pretty Grass"
Breakdown:
Rabbits → RuBP
Chew → CO₂
Pretty → 3-PGA
Grass → Glucose
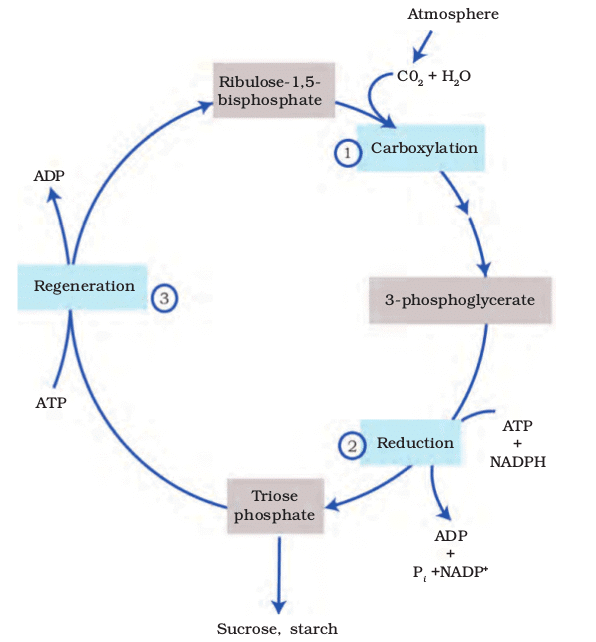 Calvin Cycle
Calvin Cycle
8. Enzymes in C₃ and C₄ Pathways
Enzymes: RuBisCO (C₃), PEPcase (C₄)
Mnemonic: "Rocks Push"
Breakdown:
Rocks → RuBisCO
Push → PEPcase
9. Cell Types in C₄ Pathway
Cells: Mesophyll Cells, Bundle Sheath Cells
Mnemonic: "Mighty Bundles"
Breakdown:
Mighty → Mesophyll Cells
Bundles → Bundle Sheath Cells
10. Steps of the C₄ (Hatch and Slack) Pathway
Steps: CO₂ Fixation (Mesophyll), Transport to Bundle Sheath, CO₂ Release, Calvin Cycle
Mnemonic: "Fix, Travel, Release, Cycle"
Breakdown:
Fix → CO₂ Fixation (Mesophyll)
Travel → Transport to Bundle Sheath
Release → CO₂ Release
Cycle → Calvin Cycle
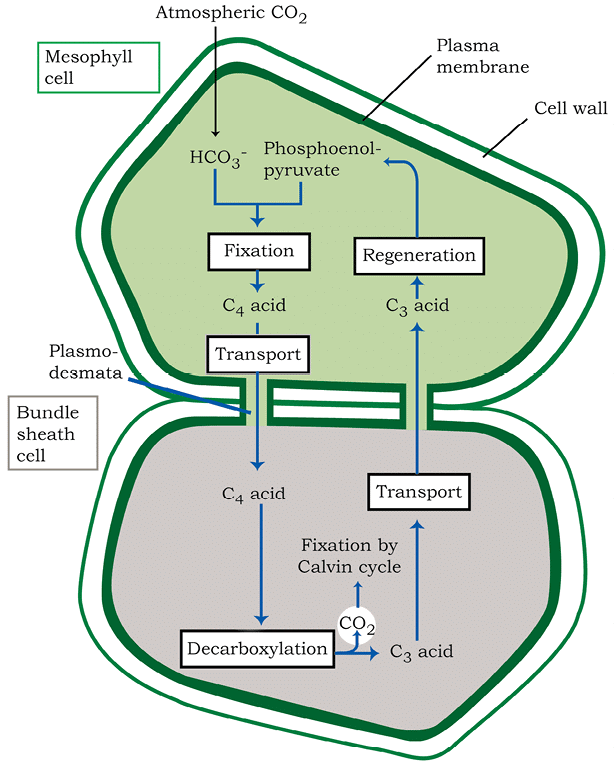 Hatch Slack Pathway
Hatch Slack Pathway
11. Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
Factors: Light, Carbon Dioxide (CO₂), Temperature, Water
Mnemonic: "Lovely Crops Thrive Well"
Breakdown:
Lovely → Light
Crops → Carbon Dioxide (CO₂)
Thrive → Temperature
Well → Water
12. Characteristics of C₄ Plants
Characteristics: Kranz Anatomy, High Productivity, No Photorespiration, High Temperature Tolerance
Mnemonic: "Kranz Helps Plants Thrive"
Breakdown:
Kranz → Kranz Anatomy
Helps → High Productivity
Plants → No Photorespiration
Thrive → High Temperature Tolerance
13. Outcomes of Photorespiration (in C₃ Plants)
Outcomes: No Sugar Synthesis, No ATP/NADPH, CO₂ Release
Mnemonic: "Nothing Sweet, Air Lost"
Breakdown:
Nothing → No Sugar Synthesis
Sweet → No ATP/NADPH
Air Lost → CO₂ Release
|
150 videos|401 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the overall equation for photosynthesis in higher plants? |  |
| 2. What are the main stages of photosynthesis? |  |
| 3. Why is chlorophyll important for photosynthesis? |  |
| 4. How do environmental factors affect photosynthesis? |  |
| 5. What role do stomata play in photosynthesis? |  |
















