Muscles: Skeletal, Cardiac & Smooth Muscles | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
What is a Muscle?
A muscle is a group of muscle tissues which contract together to produce a force. A muscle consists of fibers of muscle cells surrounded by protective tissue, bundled together many more fibers, all surrounded in a thick protective tissue.
- Muscle is a soft tissue found in both animals and humans.
- The cells of the muscles comprise protein filaments of actin and myosin that slide past one another, which produces contraction and changes both the length and the shape of the cell.
- In humans, muscles function by producing force and motion.
- The term muscle is derived from the Latin word “musculus” which refers to a little mouse, which is due to the shape of certain muscles or the contraction of muscles that look like a moving mouse.
Muscles are primarily responsible for:
- Locomotion
- Maintaining and changing body posture
- Circulation of blood cells throughout the body
- Movement of internal organs, such as the contraction of the heart and the movement of food through the digestive system via peristalsis
Important Facts about Muscles
- The human muscular system includes more than 600 muscles, which makes up about 40 to 50 per cent of the total body weight.
- These muscles are attached to bones, blood vessels and other internal organs of our body and are mainly composed of skeletal muscles, tissue, tendons, and nerves.
- The muscles of the human muscular system are composed of a kind of elastic tissue.
- Every movement in our body is the result of muscle contraction and is found in every organ, including the blood vessels, heart, digestive organs, etc. In these organs, muscles function by transferring substances throughout the body.
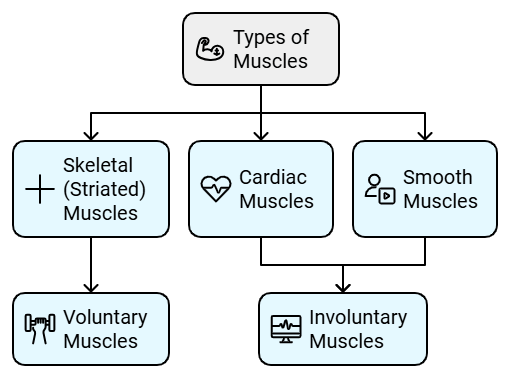
- There are three types of muscle and are mainly classified based on their movements and structures.
- The energy required for the functioning of muscles is predominantly powered by the oxidation of fats, carbohydrates particularly and from the stored energy molecules adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
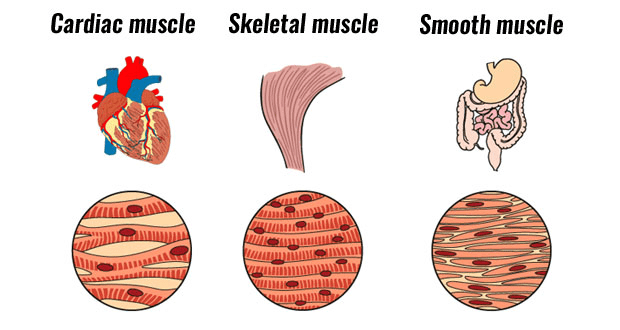
Types of Muscles
1. Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal muscle is a muscle tissue that is attached to the bones and is involved in the functioning of different parts of the body. These muscles are also called voluntary muscles as they come under the control of the central nervous system in the body.
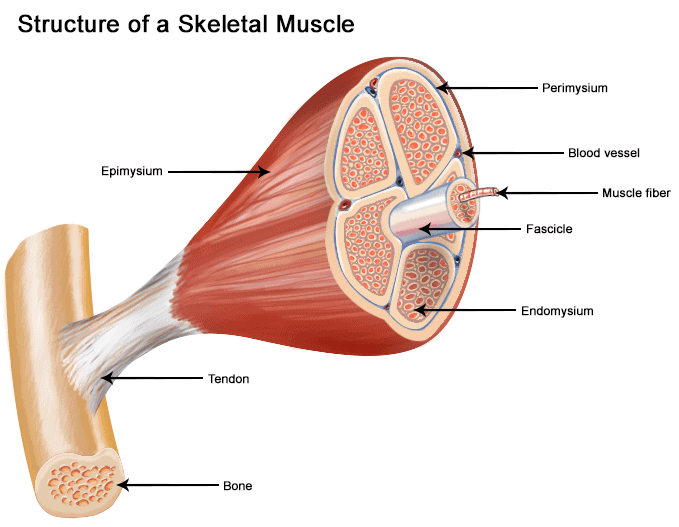
Structure of Skeletal Muscle
- Skeletal muscle is a series of muscle fibres composed of muscle cells, which are long and multinucleated.
- Skeletal muscles are cylindrically shaped with branched cells attached to the bones by an elastic tissue or collagen fibres called tendons, which are composed of connective tissues.
- The end of each skeletal muscle has a tendon, which connects the muscle to bone and connects directly to the collagenous, the outer covering of skeletal muscle.
- There is a group of muscle fibres, present below the epimysium, which are collectively called the fascicles. These muscle fibres are surrounded by another protective shield formed from collagen.
- The perimysium, a sheath of connective tissue surrounding the muscle fibres allows nerve and blood vessels to make their way through the muscle.
Functions of Skeletal Muscle
- It maintains body posture.
- It regulates body temperature.
- It connects to and controls the motions of the skeleton.
- It is responsible for performing muscular involuntary movements.
- It is responsible for body movements such as breathing, extending the arm, typing, writing, etc.
- It is responsible for the erect posture of the body. The sartorius muscles in thighs are responsible for body movement.
- The skeletal muscles protect the internal organs and tissues from any injury and also provide support to these delicate organs and tissues.
- These also support the entry and exit points of the body.
Example:
The sphincter muscles present
- Around the mouth – These muscles reduces the size of the openings by the contraction of the muscles and facilitates the swallowing of food.
- Around the urinary tract - These muscles control urination by the contraction of the muscles in the urethra.
- Around the anus - These muscles reduces the size of the openings by the contraction of the muscles and facilitates defecation.
2. Cardiac Muscle
- Cardiac muscles are found only in the heart and are self-stimulating, which has an intermediate speed of contraction and energy requirement. This muscle is not part of the musculoskeletal system.
- Cardiac muscles are striated muscles, which are responsible for keeping our heart functioning by pumping and circulating blood throughout the body and performing muscular involuntary movements. They are involved in continuous rhythmic contraction and relaxation. The interconnected muscle cells or fibres provide strength and flexibility to the cardiac muscle tissue.
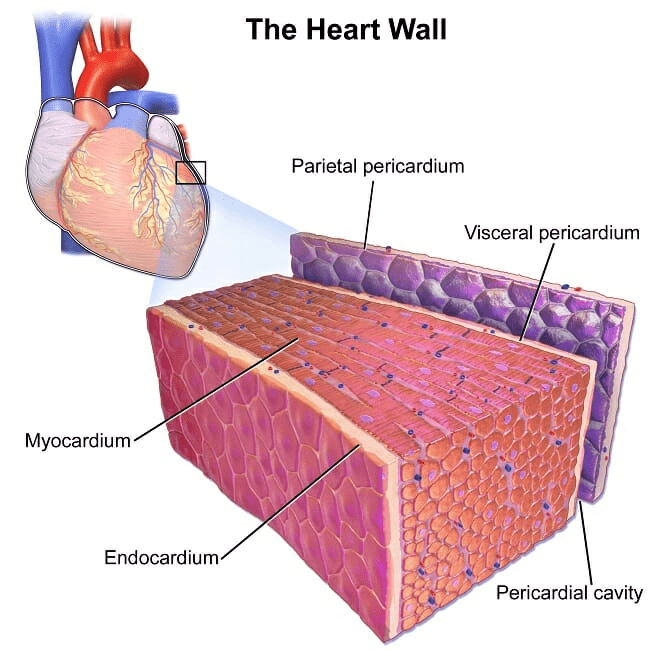
Structure of a Cardiac Muscle
- Cardiac muscle exists only within the human heart. It is a specialized form of muscle evolved to continuously and repeatedly contract, providing circulation of blood throughout the body.
- Cardiac muscle has a regular pattern of fibres similar to that of smooth muscles. These muscles comprise cylindrical, branched fibres and a centrally located nucleus.
- The T-tubules or transverse tubules are rich in ion channels and are found in the atrial muscle cells. These muscles are striated muscles with cylindrical-shaped cells, which includes intercalated discs and joins neighbouring fibres.
Functions of a Cardiac Muscle
The primary function of the cardiac muscle is to regulate the functioning of the heart by the relaxation and contraction of the heart muscles. Other functions of cardiac muscles include:
- The cardiac muscles function as involuntary muscle.
- The cardiac muscles are also involved in the movement or locomotion.
- The cardiac muscles work without stopping, day and night. They work automatically and make the heart contract so that the heart can squeeze the blood vessels and release them so that the heart can fill up with blood again.
- The heart comprises a specialized type of cardiac tissue, which consists of “pacemaker” cells. These contract and expand in response to electrical impulses from the nervous system.
3. Smooth Muscle
- Smooth muscles are non-striated, involuntary muscles, which are controlled by the Autonomous Nervous System (ANS). These muscles are found almost in all organ systems such as the stomach, bladder, vessels, bile ducts, in the eye, in sphincters, in the uterus, etc.
- The smooth muscles function by stimulating the contractility of the digestive, urinary, reproductive systems, blood vessels, and airways. The cells of the smooth muscles are spindle-shaped with a single nucleus. These muscles are activated automatically and do not depend on conscious thought.
Structure of Smooth Muscle
The smooth muscles of the human muscular system are spindle-shaped muscle fibres with a single nucleus. The thickness of the smooth muscles ranges between 3-10 µm and its length ranges between 20 to 200 μm, which are shorter compared to the skeletal muscle. These muscles lack filaments, special protein, actin and myosin and produce their own connective tissue.
Functions of a Smooth Muscle
Like all other types of muscles, smooth muscles are also involved in contraction and relaxation. Other functions of smooth muscles include:
- It is involved in the sealing of orifices.
- It produces connective tissue proteins such as collagen and elastin.
- Transports chyme (a pulpy acidic fluid) for the contractions of the intestinal tube.
- Smooth muscle plays a vital role in the circulatory system by maintaining and controlling the blood pressure and flow of oxygen throughout the body.
- Smooth muscles are also responsible for:
(i) Contracting the irises.
(ii) Raising the small hairs on your arm.
(iii) Contracting the sphincters in our body.
(iv) In the movement of the fluids through organs.
(v) It is much more useful for providing consistent and elastic tension.
Classification on the basis of Muscle Action:
Voluntary muscles
Voluntary muscles are long, multinucleated cells, containing sarcomeres arranged into bundles. These muscles are composed of cylindrical fibres and are usually attached to bones and the skin. They play an important role in allowing the body to move by contracting and relaxing and their actions are mainly under the control of the somatosensory nervous system. These voluntary muscles include skeletal muscles.Involuntary muscles
Involuntary muscles are striated and branched in the case of cardiac muscle. The actions of involuntary muscles are mainly controlled by the autonomic nervous system in the body. These involuntary muscles include smooth muscles and cardiac muscles.
Summary of Muscles
The human muscular system is composed of the muscles and the tendons that connect them to the skeleton. All muscle types are capable of receiving and responding to stimulation from nerves and are capable of contracting. Each type of muscle also has its own special role that it performs within our bodies
Summary of roles of three muscle types:
Skeletal Muscles
These muscles are located beneath the layers of skin and are connected to tendons and bones. They are responsible for creating movement and are under voluntary control.Cardiac Muscles
This muscle is only found in the heart. It is responsible for contracting and relaxing the pumping of the blood around your body. Cardiac muscle is an involuntary muscle.Smooth Muscles
This muscle forms the walls of the organs, glands and blood vessels within the body. It is responsible for expanding and contracting the passage of blood and other fluids through the vessels and organs. A smooth muscle is an involuntary muscle. This article concludes the introduction to muscles, their types and functions.
|
150 videos|401 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Muscles: Skeletal, Cardiac & Smooth Muscles - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What are the main functions of muscles in the human body? |  |
| 2. How do skeletal muscles differ from cardiac and smooth muscles? |  |
| 3. What is the role of cardiac muscle in the circulatory system? |  |
| 4. What are the characteristics of smooth muscle? |  |
| 5. How can regular exercise affect skeletal muscles? |  |

















