NCERT Exemplar: Biological Classification - 2 | NCERT Exemplar & Revision Notes for NEET PDF Download
Short Answer Type Questions
Q.1. Diatoms are also called as ‘pearls of ocean’, why? What is diatomaceous earth?
Ans. The diatoms are unique organisms because of their distinctive cell walls. The walls are embedded with silica and thus the walls are indestructible. They show sculpturing and ornamentation that why Diatoms are also called as ‘Pearls of Ocean’. DiatomsDiatoms have left behind large amount of cell wall deposits in their habitat; this accumulation over billions of years is referred to as ‘diatomaceous earth’. Being gritty this soil is used in polishing, filtration of oils and syrups. Diatoms are the chief ‘producers’ in the oceans.
DiatomsDiatoms have left behind large amount of cell wall deposits in their habitat; this accumulation over billions of years is referred to as ‘diatomaceous earth’. Being gritty this soil is used in polishing, filtration of oils and syrups. Diatoms are the chief ‘producers’ in the oceans.
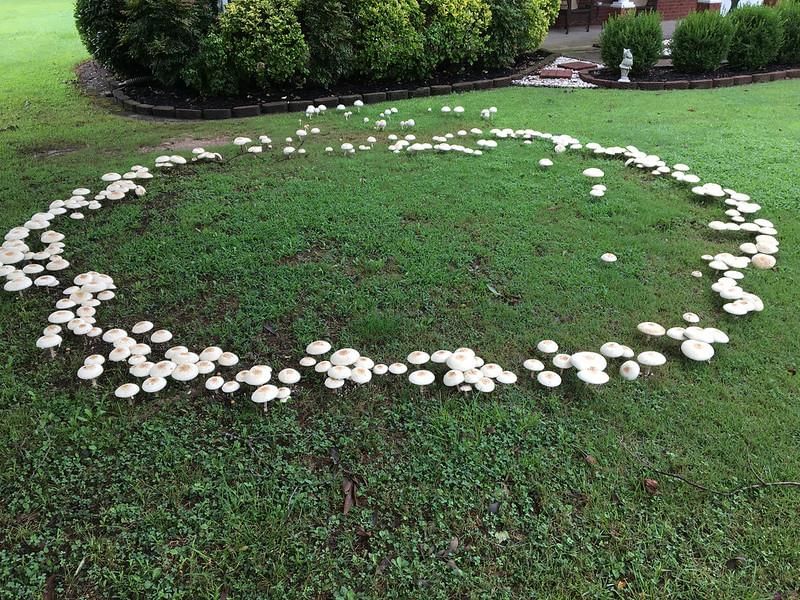
Q.2. There is a myth that immediately after heavy rains in forest, mushrooms appear in large number and make a very large ring or circle, which may be several metres in diameter. These are called ‘Fairy rings’. Can you explain this myth of fairy rings in biological terms?
Ans.
- After heavy rains in forest, moisture and nutrients pass down in the soil and activates the growth of mushroom mycelium.
- The basidiocarps of Agaricus (mushroom) arise from the mycelium present in the soil. They appear in a circle like a ring.
 Fairy Rings
Fairy Rings - As these basidiocarps resemble buttons and grow in rings, they are known as fairy rings.
Q.3. Neurospora—an ascomycetes fungus has been used as a biological tool to understand the mechanism of plant genetics much in the same way as Drosophila has been used to study animal genetics. What makes Neurospora so important as a genetic tool?
Ans.
- Neurospora is used as a genetic tool because it is easy to grow and has a haploid life cycle that makes genetic analysis simple since recessive traits will show up in the offspring. Neurospora
- Beadle and Tatum exposed Neurospora crassa to X-rays, causing mutations. This led them to propose the “one gene, one enzyme” hypothesis that specific genes code for specific proteins.
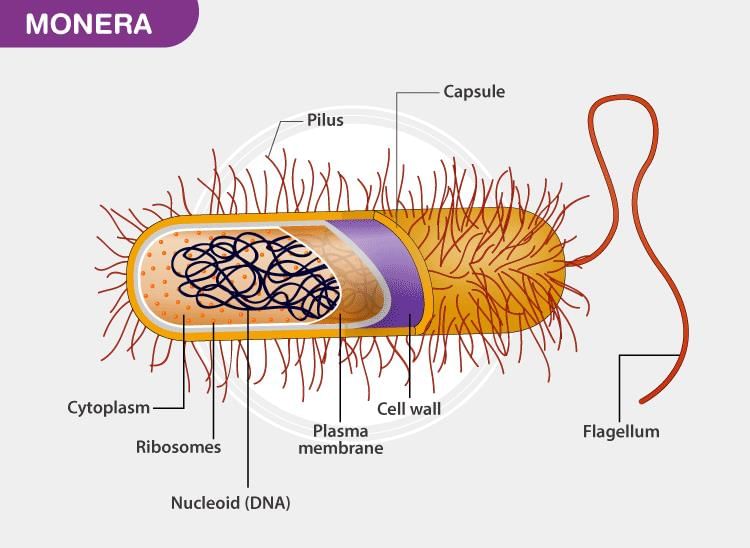
Q.4. Cyanobacteria and heterotrophic bacteria have been clubbed together in Eubacteria of kingdom Monera as per the “Five Kingdom Classification” even though the two are vastly different from each other. Is this grouping of the two types of taxa in the same kingdom justified? If so, why?
Ans.
- Cyanobacteria and heterotrophic bacteria have been clubbed together in Eubacteria of Kingdom Monera as per the “Five Kingdom Classification” because they do not have the nuclear envelope and membrane-bound organelles. Their genetic material is naked.
- They have 70S type of ribosomes. So, cyanobacteria and heterotrophic bacteria are prokaryotes and belong, to Kingdom Monera.
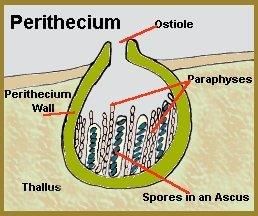
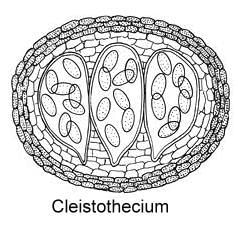
Q.5. At a stage of their cycle, ascomycetes fungi produce the fruiting bodies like apothecium, perithecium or cleistothecium. How are these three types of fruiting bodies different from each other?
Ans.
- An apothecium is a wide, open, saucer-shaped or cup-shaped fruit body. It is sessile and fleshy.
- A cleistothecium is a globose, completely closed fruit body with no special opening to the outside.
- Perithecium are flask-shaped structures opening by a pore or ostiole (short papilla opening by a circular pore).
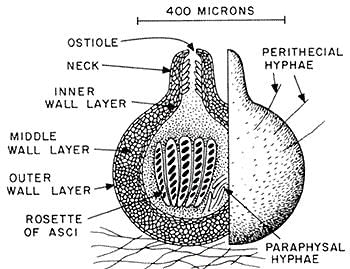 Perithecium
Perithecium
Q.6. What would observable features in Trypanosoma make you classify it under Kingdom Protista?
Ans.
Trypanosoma is classified under the Kingdom Protista because it is unicellular eukaryotes. It has a well-defined nucleus with the nuclear envelope, membrane-bound organelles, 80S ribosomes and flagella with 9 + 2 organisation.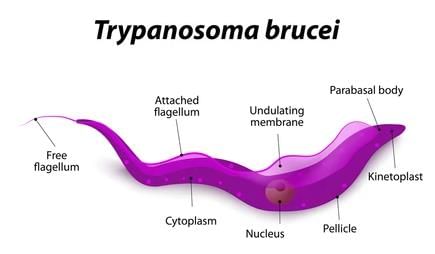
Q.7. Fungi are cosmopolitan. Write the role of fungi in your daily life.
Ans.
- Dough which is used for making bread, is fermented by fungi Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Baker’s yeast).
- Roquefort cheese are ripened by growing a specific fungi on them, which gives them a particular flavor.
- Microbes mainly yeasts used for the production of beverages like wine, beer, whisky, brandy or rum. For this purpose the yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) used for fermenting malted cereals and juices to produce ethanol and commonly called Brewer’s yeast.
Antibiotics Produced by Fungi:
- Cyclosporin A is produced by Trichoderma polysporum (Fungus). Cyclosporin A is used as an immunosuppressive agent in organ transplant patients.
- Statins produced by Monascus purpureus (Yeast). Statins used as blood- cholesterol-lowering agent.
- Mushrooms, morels (Morchella) and truffles are edible fungi.
- Fungi causes several diseases in plants and animals including human beings.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q.1. Algae are known to reproduce asexually by variety of spores under different environmental conditions. Name these spores and the conditions under which they are produced.
Ans. Asexual reproduction is by the production of different types of spores, the most common being the zoospores. They are flagellated (motile) and on germination gives rise to new plants.
Types of asexual reproduction:
(i) Zoospores: Motile and formed in favourable condition.
(ii) Aplanospores: Thin-walled, non-motile and formed in unfavourable condition.
(iii) Hypnospore: Thick-walled, non-motile and formed in unfavorable condition.
(iv) Akinete: Under unfavorable condition, entire cell becomes thick.
(v) Palmella stage: In condition of drought, protoplast is surrounded by gelatinous covering.
Q.2. Apart from chlorophyll, algae have several other pigments in their chloroplast. What pigments are found in blue-green, red and brown algae that are responsible for their characteristic colors?
Ans. Apart from chlorophyll, algae have several other pigments in their chloroplast like carotenoids, xanthophylls (fucoxanthin) and r-phycoerythrin.
(a) In blue-green algae, phycocyanin and r-phycoerythrin pigments are present beside chlorophyll a.
(b) Brown algae possess chlorophyll a, c, carotenoids and xanthophylls. They vary in colour from olive green to various shades of brown depending upon the amount of the xanthophyll pigment, fucoxanthin present in them.
(c) Red algae possess chlorophyll a, d and phycoerythrin in their body. Rhodophyceae members are commonly called red algae because of the predominance of the red pigment, r-phycoerythrin in their body.
Q.3. Make a list of algae and fungi that have commercial value as source of food, chemicals, medicines and fodder.
Ans.
(a) Economic Importance of Algae
- Many species of Porphyra, Laminaria and Sargassum, are among the 70 species of marine, algae used as food. Chlorella and Spirulina are unicellular algae, rich in proteins and are used as food supplements even by space travellers.
- Certain marine brown and red algae produce large amounts of hydrocolloids (water holding substances) or phycocolloids.
Example: Algin (brown algae) and Carrageen (red algae) are used commercially. Agar, one of the commercial products obtained from Gelidium and Gracilaria are used to grow microbes and in preparations of ice-creams and jellies. - Bromine is obtained from red algae Polysiphonia. Macrocystis is the source of Potash. Laminaria and Fucus are the sources of Iodine.
(b) Economic Importance of Fungi
- Mushrooms, morels (Morchella) and truffles are edible fungi.
- Microbes mainly yeasts used to produce beverages like wine, beer, whiskey, brandy or rum. For this purpose the yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) is used to ferment malted cereals and juices to produce ethanol and commonly called Brewer’s yeast.
(i) Cyclosporin A is produced by Trichoderma polysporum (Fungus). Cyclosporin A is used as an immunosuppressive agent in organ transplant patients.
(ii) Statins produced by Monascus purpureus (Yeast). Statins used as the blood-cholesterol lowering agent.
Antibiotics Produced by Fungi:
Q.4. ‘Peat’ is an important source of domestic fuel in several countries. How is ‘peat’ formed in nature?
Ans.
- Species of Sphagnum, a moss, provide peat that have long been used as fuel and because of their capacity to hold water as packing material for trans-shipment of living material.
- Peat forms when plant material decaying fully by acidic and anaerobic conditions.
- Peat is soft and easily compressed. Under pressure, water in the peat is forced out. Upon drying, peat can be used as fuel.
Q.5. Biological classification is a dynamic and ever-evolving phenomenon which keeps changing with our understanding of life forms. Justify the statement taking any two examples.
Ans.
- Kingdom Protista brought together Chlamydomonas, Chlorella (earlier placed in algae within plants and both having cell walls) with Amoeba and Paramoecium (earlier placed in the animal kingdom and both lacking cell walls).
- Five kingdom classification has put together organisms (like Chlamydomonas and Amoeba) which were placed in different kingdoms in earlier classifications.
- This change happened because the criteria for classification changed. This kind of changes will take place in future too depending on the improvement in our understanding of characteristics and evolutionary relationships.
- So, biological classification is a dynamic and ever-evolving phenomenon which keeps changing with our understanding of life forms.
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar: Biological Classification - 2 - NCERT Exemplar & Revision Notes for NEET
| 1. What is biological classification? |  |
| 2. Why is biological classification important? |  |
| 3. How are organisms classified into different kingdoms? |  |
| 4. What is the basis of classification in the Linnaean system? |  |
| 5. How does biological classification help in understanding evolutionary relationships? |  |
















