NCERT Exemplar: Human Reproduction | Biology Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple-Choice Questions |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Questions |

|
Multiple-Choice Questions
Q.1. Choose the incorrect statement from the following:
(a) In birds and mammals, internal fertilisation takes place.
(b) Colostrum contains antibodies and nutrients.
(c) Polyspermy in mammals is prevented by the chemical changes in the egg surface.
(d) In the human female, implantation occurs almost seven days after fertilisation.
Ans. (c)
Solution: Internal fertilisation is a type of fertilisation in which there is a union of an egg and sperm inside a parent's body. Examples include reptiles, mammals, and birds. Colostrum is the first form of milk that is produced by the mammary glands of mammals. It contains large numbers of IgA antibodies and lymphocytes that help protect the mucous membranes of the infant.
- Polyspermy is a condition in which the egg has been fertilised by more than one sperm.
- It is prevented by depolarisation of the egg plasma membrane after the entry of the first sperm.
- This depolarisation prevents the entry of additional sperm.
- The fertilised ovum enters the uterine cavity 3-4 days later.
- Implantation occurs almost 7 to 10 days after fertilisation and 5 to 6 days after it has entered the uterine cavity.
Q.2. Identify the correct statement from the following:
(a) High levels of estrogen trigger the ovulatory surge.
(b) Oogonial cells start to proliferate and give rise to functional ova in regular cycles from puberty onwards.
(c) Sperms released from the seminiferous tubules are highly motile.
(d) Progesterone level is high during the post-ovulatory phase of the menstrual cycle.
Ans. (d)
Solution:
Option a) High levels of estrogen trigger the ovulatory surge - INCORRECT Ovulatory surge is triggered by luteinizing hormone.
Option b) Oogonial cells start to proliferate and give rise to functional ova in regular cycles from puberty onwards - INCORRECT It is not formed from puberty onwards.
Option c) Sperms released from seminiferous tubules are highly motile - INCORRECT They are not highly motile in seminiferous tubules rather they undergo maturation in the epididymis and acquire motility during the epididymal transition. Final maturation (capacitation) is completed in the female reproductive tract.
Option d) Progesterone level is high during the post-ovulatory phase of the menstrual cycle - CORRECT During the post-ovulatory phase, the progesterone is high to make the uterus ready for implanting and supporting a fertilized egg during pregnancy.
Hence, the correct answer is Option 4.
Q.3. Spot the odd one out from the following structures with reference to the male reproductive system:
(a) Rete testis
(b) Epididymis
(c) Vasa efferentia
(d) Isthmus
Ans. (d)
Solution:
- The male reproductive system contains rete testis, vasa efferentia, Epididymis and vas deferens etc.
- The female reproductive system contains isthmus, ampulla, infundibulum and uterus etc.
Q.4. Seminal plasma, the fluid part of semen, is contributed by.
i. Seminal vesicle
ii. Prostate gland
iii. Urethra
iv. Bulbourethral gland
(a) i and ii
(b) i, ii and iv
(c) ii, iii and iv
(d) i and iv
Ans. (b)
Solution: Secretion of the seminal vesicle (paired), prostate gland (unpaired) and bulbourethral glands or Cowper’s glands (paired) constitute the seminal plasma which is rich in fructose, calcium and certain enzymes.
Q.5. Spermiation is the process of the release of sperms from:
(a) Seminiferous tubules
(b) Vas deferens
(c) Epididymis
(d) Prostate gland
Ans. (a)
Solution: 
Q.6. Mature Graafian follicle is generally present in the ovary of a healthy human female around:
(a) 5 – 8 day of the menstrual cycle
(b) 11 – 17 day of the menstrual cycle
(c) 18 – 23 day of the menstrual cycle
(d) 24 – 28 day of the menstrual cycle
Ans. (b)
Solution: Mature Graafian follicle is generally present in a healthy human female's ovary around 11-17 day of the menstrual cycle.
Q.7. Acrosomal reaction of the sperm occurs due to:
(a) Its contact with zona pellucida of the ova
(b) Reactions within the uterine environment of the female
(c) Reactions within the epididymal environment of the male
(d) Androgens produced in the uterus
Ans. (a)
Solution:
Acrosome reaction in sperm is triggered by the release of fertilizin. The acrosome's secretions help the sperm enter into the cytoplasm of the ovum through the zona pellucida and the plasma membrane.
Q.8. Which one of the following is not a male accessory gland?
(a) Seminal vesicle
(b) Ampulla
(c) Prostate
(d) Bulbourethral gland
Ans. (b)
Solution:
- A male accessory gland is a seminal vesicle, prostate gland and bulbourethral gland.
- The ampulla is a part of the female reproductive system.
Q.9. The spermatogonia undergo division to produce sperms by the process of spermatogenesis. Choose the correct one with reference to above.
(a) Spermatogonia have 46 chromosomes and always undergo meiotic cell division.
(b) Primary spermatocytes divide by mitotic cell division.
(c) Secondary spermatocytes have 23 chromosomes and undergo second meiotic division.
(d) Spermatozoa are transformed into spermatids.
Ans. (c)
Solution:
- Spermatogonia are diploid cells on the inside wall of seminiferous tubules that multiply by mitotic divisions. Some of the spermatogonia called primary spermatocyte undergo meiosis-I to give rise to secondary spermatocytes (haploid).
- Each secondary spermatocyte undergoes meiosis-II to give rise to two haploid spermatids which are transformed to spermatozoa by spermiogenesis.
Q.10. Match between the following representing parts of the sperm and their functions and choose the correct option.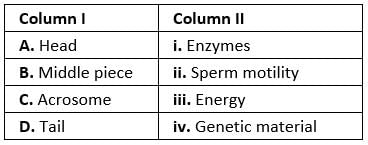
Options:
(a) A-ii, B-iv, C-i, D-iii
(b) A-iv, B-iii, C-i, D-ii
(c) A-iv, B-i, C-ii, D-iii
(d) A-ii, B-i, C-iii, D-iv
Ans. (b)
Solution: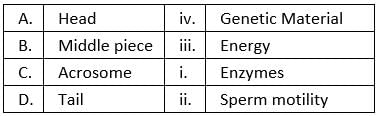
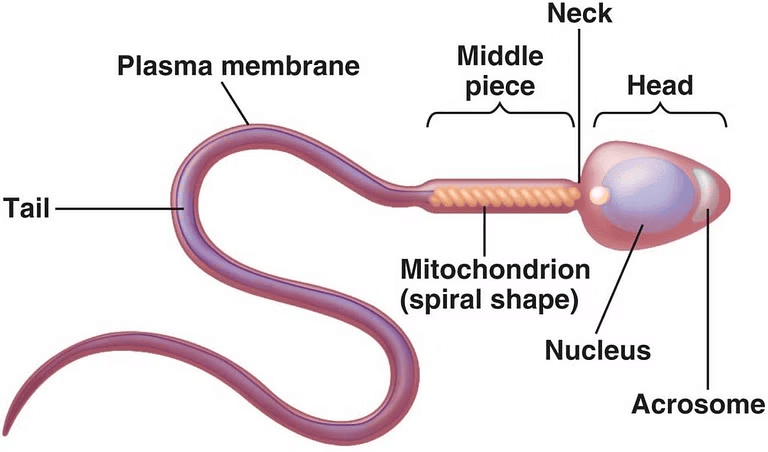 Sperm
Sperm
Q.11. Which among the following has 23 chromosomes?
(a) Spermatogonia
(b) Zygote
(c) Secondary oocyte
(d) Oogonia
Ans. (c)
Solution: Secondary oocyte (n = 23)
Q.12. Match the following and choose the correct options: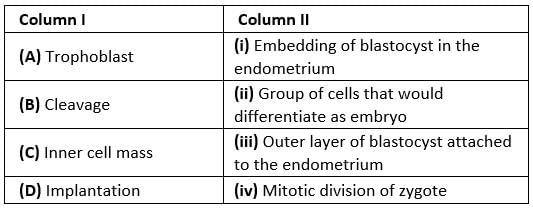
Options:
(a) A-ii, B-i, C-iii, D-iv
(b) A-iii, B-iv, C-ii, D-i
(c) A-iii, B-i, C-ii, D-iv
(d) A-ii, B-iv, C-iii, D-i
Ans. (b)
Solution: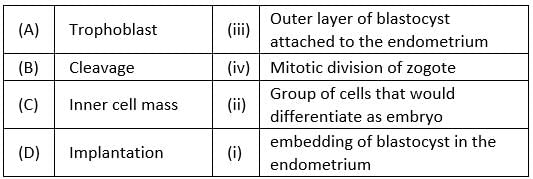
Q.13. Which of the following hormones is not secreted by human placenta?
(a) hCG
(b) Estrogens
(c) Progesterone
(d) LH
Ans. (d)
Solution:
- The placenta acts as an endocrine tissue and produces several hormones like human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), human placental lactogen (hPL), estrogens, progestogens, etc.
- The pituitary gland secretes LH.
Q.14. The vas deferens receives duct from the seminal vesicle and opens into the urethra as:
(a) Epididymis
(b) Ejaculatory duct
(c) Efferent ductule
(d) Ureter
Ans. (b)
Solution: The vas deferens receives duct from the seminal vesicle and opens into the urethra as ejaculatory duct.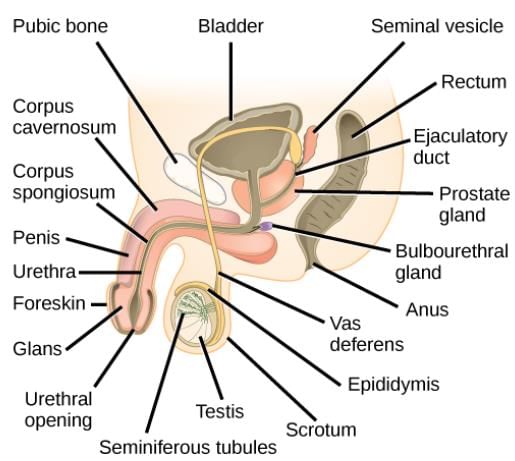 Male Reproductive System
Male Reproductive System
Q.15. Urethral meatus refers to the following:
(a) Urinogenital duct
(b) Opening of vas deferens into the urethra
(c) External opening of the urinogenital duct
(d) Muscles surrounding the urinogenital duct
Ans. (c)
Solution: The urethra originates from the urinary bladder and extends through the penis to its external opening called urethral meatus (external opening of the urinogenital duct).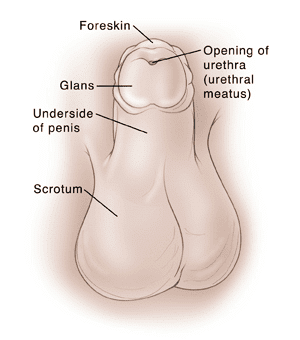 Urethral MeatusQ.16. Morula is a developmental stage:
Urethral MeatusQ.16. Morula is a developmental stage:
(a) Between the zygote and blastocyst
(b) Between the blastocyst and gastrula
(c) After the implantation
(d) Between implantation and parturition
Ans. (a)
Solution: The embryo with 8 to 16 blastomeres is called a morula. Morula is the solid mass of cells and is mulberry like. Morula is a developmental stage between the zygote and blastocyst.
Q.17. The membranous cover of the ovum at ovulation is:
(a) Corona radiata
(b) Zona radiata
(c) Zona pellucida
(d) Chorion
Ans. (a)
Solution: The membranous cover of the ovum at ovulation is corona radiata.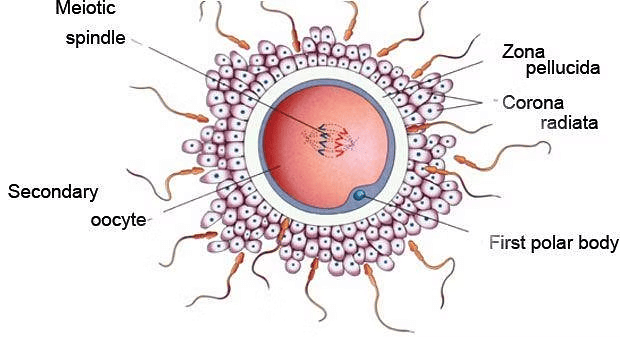 Ovum
Ovum
Q.18. Identify the odd one from the following:
(a) Labia minora
(b) Fimbriae
(c) Infundibulum
(d) Isthmus
Ans. (a)
Solution: Fimbriae, infundibulum isthmus and ampulla are the part of the fallopian duct while labia minora is female external genitalia.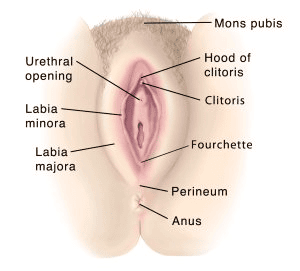
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q.1. Given below are the events in human reproduction. Write them in correct sequential order:
Insemination, gametogenesis, fertilisation, parturition, gestation, implantation
Ans. Gametogenesis → Insemination → Fertilisation → Implantation → Gestation → Parturition
Q.2. The path of sperm transport is given below. Provide the missing steps in blank boxes.
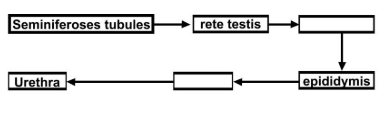
Ans.
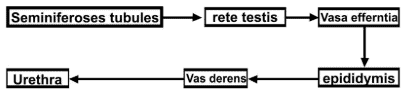
Q.3. What is the role of cervix in the human female reproductive system?
Ans. Cervix helps in regulating the passage of sperms into the uterus and forms the birth canal to facilitate parturition.
Q.4. Why are menstrual cycles absent during pregnancy.
Ans. The high levels of progesterone and estrogens during pregnancy suppress the gonadotropins which are required for the development of new follicles. Therefore, a new cycle cannot be initiated.
Q.5. Female reproductive organs and associated functions are given below in column A and B. Fill the blank boxes.
| Column A | Column B |
| Ovaries | Ovulation |
| Oviduct | .......a........ |
| ........b........ | Pregnancy |
| Vagina | Birth |
Ans.
| Column A | Column B |
| Ovaries | Ovulation |
| Oviduct | Fertilization |
| Uterus | Pregnancy |
| Vagina | Birth |
Q.6. From where the parturition signals arise-mother or foetus? Mention the main hormone involved in parturition.
Ans.
- The signals for parturition originate from the fully developed foetus and the placenta which induce mild uterine contractions called foetal ejection reflex.
- This triggers the release of oxytocin from the maternal pituitary.
- The main hormone involved in parturition is oxytocin.
Q.7. What is the significance of epididymis in male fertility?
Ans. In the epididymis sperms undergo physiological maturation, acquiring increased motility and fertilizing capacity.
Q.8. Give the names and functions of the hormones involved in the process of spermatogenesis. Write the names of the endocrine glands from where they are released.
Ans. Spermatogenesis starts at the age of puberty due to the significant increase in the secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). This is a hypothalamic hormone.
- The increased levels of GnRH then act at the anterior pituitary gland and stimulate the secretion of two gonadotropins luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
- LH acts at the Leydig cells and stimulates the synthesis and secretion of androgens. Androgens, in turn, stimulate the process of spermatogenesis.
- FSH acts on the Sertoli cells and stimulates the secretion of some factors that help in spermiogenesis.
Q.9. The mother germ cells are transformed into a mature follicle through a series of steps. Provide the missing steps in the blank boxes.
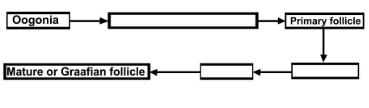
Ans.
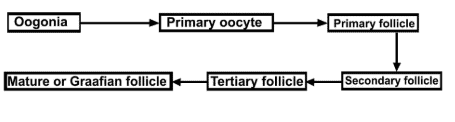
Q.10. During reproduction, the chromosome number (2n) reduces to half (n) in the gametes, and again the original number (2n) is restored in the offspring, What are the processes through which these events take place?
Ans. The halving of chromosomal number takes place during gametogenesis and regaining the 2n number occur as a result of fertilisation.
Q.11. What is the difference between a primary oöcyte and a secondary oöcyte?
Ans.
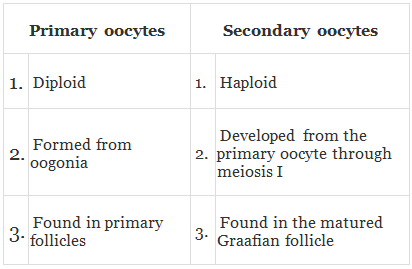
Q.12. What is the significance of the ampullary–isthmic junction in the female reproductive tract?
Ans. In mammals, fertilisation takes place in the ampullary-isthmic junction.
Q.13. How does zona pellucida of ovum help in preventing polyspermy?
Ans.
- Polyspermy means more than one sperm has fertilised an egg. Proteases modify the zona pellucida.
- The proteases destroy the protein link between the cell membrane and the vitelline membrane, remove any receptors that other sperm have bound to, and help to form the fertilisation membrane that prevents polyspermy.
Q.14. Mention the importance of the LH surge during the menstrual cycle.
Ans. LH surge is essential for the events leading to ovulation.
Q.15. Which type of cell division forms spermatids from the secondary spermatocytes?
Ans. Second meiotic division.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q.1. A human female experiences two major changes, menarche and menopause during her life. Mention the significance of both events.
Ans.
- Menarche represents the beginning of the menstrual cycle, which is an indication of the attainment of sexual maturity.
- Menopause, on the other hand, refers to the cessation of menstruation, which in turn means stoppage of gamete production, i.e., it marks the end of reproductive/ fertile life of the female.
Q.2. (a) How many spermatozoa are formed from one secondary spermatocyte?
(b) Where does the first cleavage division of the zygote take place?
Ans.
(a) Two spermatozoa are formed from one secondary spermatocyte.
(b) First cleavage division of the zygote takes place in fallopian tube or oviduct.
Q.3. The Corpus luteum in pregnancy has a long life. However, if fertilisation does not take place, it remains active only for 10-12 days. Explain.
Ans. During pregnancy, there is no menstruation. The corpus luteum secretes a large amount of progesterone in case fertilisation occurs. This is to maintain the corpus luteum as long as the embryo remains there. In the absence of fertilisation, the corpus luteum cannot be maintained for more than 10-12 days and hence, it degenerates.
Q.4. What is the foetal ejection reflex? Explain how it leads to parturition.
Ans. Vigorous contraction of the uterus at the end of the pregnancy causes expulsion/delivery of the foetus. This process of delivery of the foetus (childbirth) is called parturition.
- A complex neuroendocrine mechanism induces parturition. The signals for parturition originate from the fully developed foetus and the placenta, which induce mild uterine contractions called foetal ejection reflex. This triggers the release of oxytocin from the maternal pituitary. Oxytocin acts on the uterine muscle and causes stronger uterine contractions, which in turn stimulate the further secretion of oxytocin.
- The stimulatory reflex between the uterine contraction and oxytocin secretion continues, resulting in stronger and stronger contractions. This leads to the expulsion of the baby out of the uterus through the birth canal- parturition. Soon after the infant is delivered, the placenta is also expelled from the uterus.
Q.5. Except for endocrine function, what are the other functions of the placenta?
Ans. The placenta facilitates the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the embryo. It also removes CO2 and excretory wastes produced by the embryo.
Q.6. Why do doctors recommend breastfeeding during the initial period of infant growth?
Ans.
- The female's mammary glands undergo differentiation during pregnancy and start producing milk towards the end of pregnancy by a process called lactation.
- During the initial few days of lactation, the milk produced is called colostrum, which contains several antibodies absolutely essential to develop resistance for the newborn babies. Doctors recommend breastfeeding during the initial period of infant growth to bring up a healthy baby.
Q.7. What are the events that take place in the ovary and uterus during the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle?
Ans.
- During this phase, the primary follicles in the ovary grow to become a fully mature Graafian follicle, and simultaneously the endometrium of the uterus regenerates through proliferation.
- These changes in the ovary and the uterus are induced by changes in the levels of pituitary and ovarian hormones.
- The secretion of gonadotropins (LH and FSH) increases gradually during the follicular phase and stimulates follicular development as well as the secretion of estrogens by the growing follicles.
Q.8. Given below is a flow chart showing ovarian changes during the menstrual cycle. Fill in the spaces giving the name of the hormones responsible for the events shown.
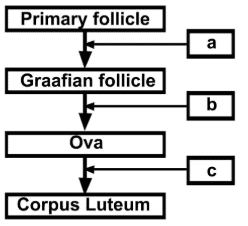
Ans.
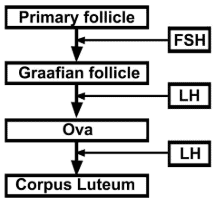
Q.9. Give a schematic labelled diagram to represent Oögenesis (without descriptions).
Ans.
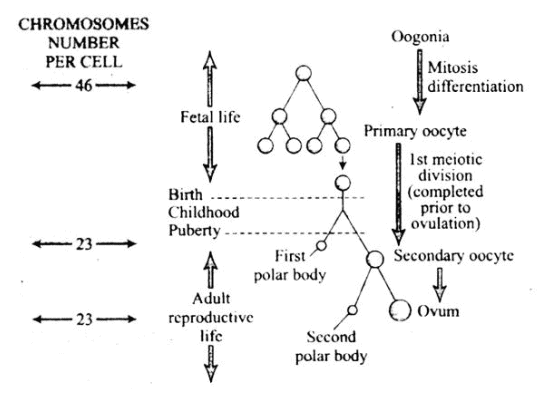 Schematic representation of OogenesisQ.10. What are the changes in the oogonia during the transition of a primary follicle to a Graafian follicle?
Schematic representation of OogenesisQ.10. What are the changes in the oogonia during the transition of a primary follicle to a Graafian follicle?
Ans.
- Oogenesis is initiated during the embryonic development stage when a couple of million gamete mother cells (oogonia) are formed within each fetal ovary (about the third month of the foetal ovary), no more oogonia are formed and added after birth.
- These cells start division and enter into prophase-I of the meiotic division and get temporarily arrested at that stage, called primary oocytes. Each primary oocyte then gets surrounded by a layer of granulosa cells and then called the primary follicle. 1° follicle contains 1° oocyte. A large number of these follicles degenerate during the phase from birth to puberty.
- The primary follicles are surrounded by more layers of granulosa cells and a new theca called secondary follicles. The theca layer is organised into an inner theca interna and an outer theca externa. Theca interna secretes estrogen hormone. The secondary follicle soon transforms into a tertiary follicle which is characterised by a fluid-filled cavity called the antrum.
- It is important to draw your attention that it is at this stage that the primary oocyte within the tertiary follicle grows in size and completes its first meiotic division. It is an unequal division resulting in the formation of a large haploid secondary oocyte and a tiny first polar body. The tertiary follicle further changes into the mature follicle or Graafian follicle.
Long Answer Questions
Q.1. What role do pituitary gonadotropins play during the follicular and ovulatory phases of the menstrual cycle? Explain the shifts in steroidal secretions.
Ans.
- The hypothalamus regulates the menstrual cycle through the pituitary gland. At the end of the menstrual phase, the pituitary FSH gradually increases, resulting in follicular development within the ovaries.
- As the follicles mature, Estrogen secretion increases, resulting in a surge in FSH and LH. The surge of LH is responsible for ovulation. LH also induces luteinisation. This leads to the formation of the corpus luteum.
- The corpus luteum secretes progesterone and some estrogen, which help in maintaining the uterine endometrium for implantation.
Q.2. Meiotic division during oogenesis is different from that in spermatogenesis. Explain how and why?
Ans. It is true that the meiotic division during oogenesis is different from that in spermatogenesis.
The following are the details about significant differences between them:
- In the case of spermatogenesis, meiotic division begins at the time of puberty. This is the time when spermatogenesis begins in a male. On the other hand, oogenesis begins in the female when the female is still in the womb. Thus. It can be said that the meiotic division during oogenesis begins when the girl child is still in the womb.
- Formation of primary oocytes stops by the 20th week of gestation of the female child. On the contrary, the production of spermatocytes continues throughout the reproductive phase of a male.
- In the case of spermatogenesis, all the stages of meiosis take place quickly after one another, and there is no time lag between them. In the case of oogenesis, meiosis is suspended at the Prophase I state.
- Meiosis resumes only once puberty begins.
Following are some possible reasons for this difference in patterns of oogenesis and spermatogenesis:
- Male gametes need to be formed in a very large number to ensure fertilisation.
- Female gametes are not exposed to external hazards, and hence a smaller number of them would be enough. Limiting the production of female gametes helps In the conservation of resources from the female body. The resources can then be properly utilised during the development of the foetus.
Q.3. The zygote passes through several developmental stages till implantation. Describe each stage briefly with suitable diagrams.
Ans.
- The mitotic division starts as the zygote moves through the isthmus of the oviduct, called cleavage, towards the uterus and forms 2, 4, 8, 16 daughter cells called blastomeres.
- The embryo with 8 to 16 blastomeres is called a morula. The morula continues to divide and transforms into blastocysts; it moves further into the uterus.
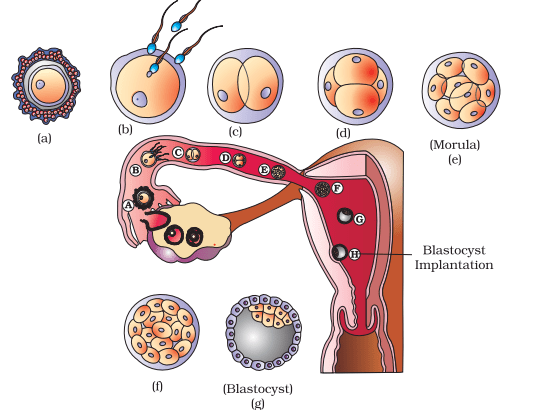
- The blastomeres in the blastocyst are arranged into an outer layer called trophoblast and an inner group of cells attached to the trophoblast called the inner cell mass. The trophoblast layer then gets attached to the endometrium, and the inner cell mass gets differentiated as the embryo.
- After attachment, the uterine cells divide rapidly and cover the blastocyst. As a result, the blastocyst becomes embedded in the endometrium of the uterus. This is called implantation, and it leads to pregnancy.
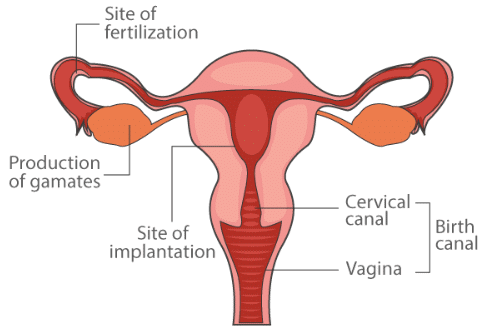
Q.4. Draw a neat diagram of the female reproductive system and label the parts associated with the following:
(a) Production of gamete
(b) Site of fertilisation
(c) Site of implantation
(d) Birth canal
Ans.
 Female Reproductive SystemQ.5. With a suitable diagram, describe the organisation of the mammary gland.
Female Reproductive SystemQ.5. With a suitable diagram, describe the organisation of the mammary gland.
Ans.
- A functional mammary gland is characteristic of all female mammals. The mammary glands are paired structures (breasts) that contain glandular tissue and a variable amount of fat.
- Each breast's glandular tissue is divided into 15—20 mammary lobes containing clusters of cells called alveoli.
- The cells of alveoli secrete milk, which is stored in the cavities (lumens) of alveoli.
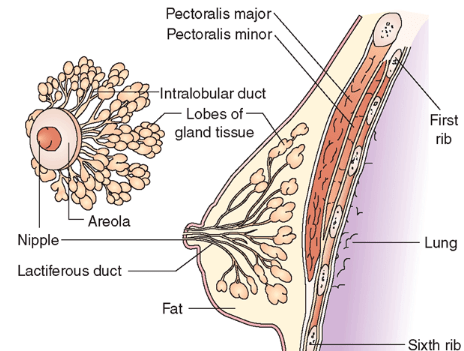
- The alveoli open into mammary tubules.
- The tubules of each lobe join to form a mammary duct.
- Several mammary ducts join to form a wider mammary ampulla, which is connected to lactiferous ducts through which milk is sucked out.
|
59 videos|290 docs|168 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar: Human Reproduction - Biology Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What are the main stages of human reproduction? |  |
| 2. How does the menstrual cycle relate to human reproduction? |  |
| 3. What role do hormones play in human reproduction? |  |
| 4. What are assisted reproductive technologies (ART)? |  |
| 5. What are common issues that can affect human reproduction? |  |
















