NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 - Agriculture
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1. Which one of the following describes an agriculture system where a single crop is grown on a large area?
(a) Shifting Agriculture
(b) Plantation Agriculture
(c) Horticulture
(d) Intensive Agriculture
Ans: (b) Plantation Agriculture
Plantation is a type of commercial farming where a single crop is grown over a large area. It combines agriculture and industry, using capital-intensive methods and migrant labor, with the produce serving as raw material for industries.
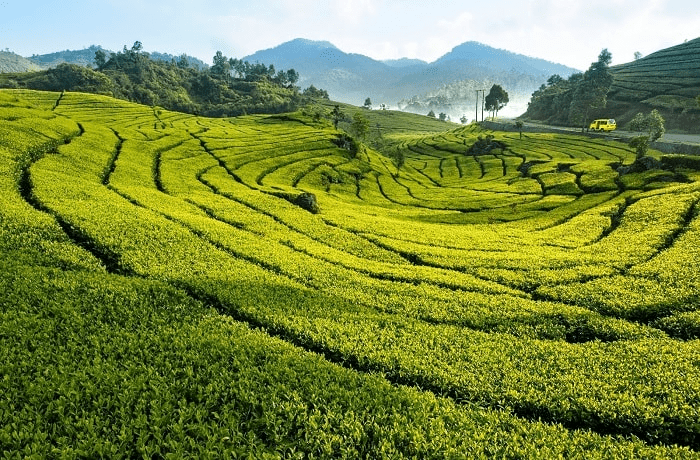 Plantation Agriculture
Plantation Agriculture
Q2. Which one of the following is a rabi crop?
(a) Rice
(b) Gram
(c) Millets
(d) Cotton
Ans: (b) Gram
Rice, millets and cotton are kharif crops, while gram is a rabi crop.
Q3. Which one of the following is a leguminous crop?
(a) Pulses
(b) Jawar
(c) Millets
(d) Sesamum
Ans: (a) Pulses
Pulses belong to the legume family, and are able to survive in dry conditions. They help in restoring soil fertility by fixing nitrogen from the air (except arhar).
 Leguminous Crops
Leguminous Crops
Answer the Following Questions in 30 words
Q1. Name one important beverage crop and specify the geographical conditions required for its growth.
Ans: Tea is an important beverage crop. Geographical conditions:
- Tropical and sub-tropical climates endowed with deep and fertile well-drained soil so rich in humus and organic matter.
- Temperature: 20°C -30°C.
- Annual rainfall: 150-300 cm.
- Frequent showers evenly distributed over the year.
Q2. Name one staple crop of India and the regions where it is produced.
Ans:
- Rice is a staple crop of India.
- Regions, where it is produced, are plains of north and north-eastern India, coastal areas and deltaic regions, i.e., West Bengal, Uttar Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Punjab and Tamil Nadu.
Q3. Enlist the various institutional reform programmes introduced by the government in the interest of farmers.
Ans: Institutional reforms:
- Minimum Support Price (MSP)
- Subsidies on fertilisers
- Crop insurance against draught, flood, etc.
- Establishment of Grameen banks, cooperative societies and banks to provide loans at lower rates of interest.
- Kissan credit cards
Answer the following questions in about 120 words
Q1. Suggest the initiative taken by the government to ensure the increase in agricultural production.
Ans:
- To ensure an increase in agricultural production, the government prioritised collectivisation, consolidation of holdings, cooperation and abolition of the zamindari system.
- 'Land reform' was the main focus of the First Five Year Plans. In the 1960s and 1970s, agricultural reforms were the order of the day.
- The Green Revolution and the White Revolution (Operation Flood) were aimed at improving Indian agricultural productivity.
- During the 1980s and 1990s, a comprehensive land development programme was initiated.
- Under this, various technical and institutional reforms were introduced by the government for the benefit of farmers.
Example: Minimum Support Price policy, provision for crop insurance, subsidy on agricultural inputs and resources, Grameen banks, Personal Accident Insurance Scheme, and special weather bulletins and agricultural programmes like 'Krishi Darshan' on national television.
Q2. Describe the geographical conditions required for the growth of rice.
Ans:
- Rice is a Kharif crop grown in the onset of monsoon and harvested in September-October.
- It is grown in plains of north and north-eastern India, coastal areas and deltaic regions.
- In India, important rice growing regions are Assam, West Bengal, coastal regions of Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Tamil Nadu, Kerala and Maharashtra, particularly the (Konkan coast) along with Uttar Pradesh and Bihar.
- It requires high temperatures (above 25°C) and high humidity with annual rainfall above 100 cm.
- In areas with less rainfall, it grows with the help of irrigation via canals and tube-wells. This has made production of rice possible in areas such as Punjab, Haryana and western Uttar Pradesh, and parts of Rajasthan.
|
94 videos|630 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 - Agriculture
| 1. कृषि क्या है और इसके महत्व क्या हैं? |  |
| 2. विभिन्न प्रकार की खेती कौन सी हैं? |  |
| 3. भारत में प्रमुख कृषि फसले कौन सी हैं? |  |
| 4. कृषि में जलवायु का क्या प्रभाव है? |  |
| 5. कृषि में आधुनिक तकनीकों का क्या योगदान है? |  |






















