NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 - Carbon and its Compounds
Page No: 61
Q1: What would be the electron dot structure of carbon dioxide, which has the formula CO2?
Ans:
- A molecule of CO2 consists of one atom of carbon and two atoms of oxygen.
- The electronic configuration of carbon is 2,4 while that of oxygen is 2, 6. Each of the two atoms of oxygen shares two electrons with the carbon atom to complete the octet of both the elements, thereby forming a double covalent bond.
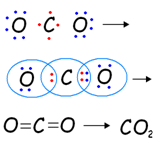 Electron Dot Structure of CO2
Electron Dot Structure of CO2
Q2: What would be the electron dot structure of a molecule of sulphur, which is made up of eight atoms of sulphur? (Hint - the eight atoms of sulphur are joined together in the form of a ring.)
Ans: In S8, the atoms are joined together in the form of a ring.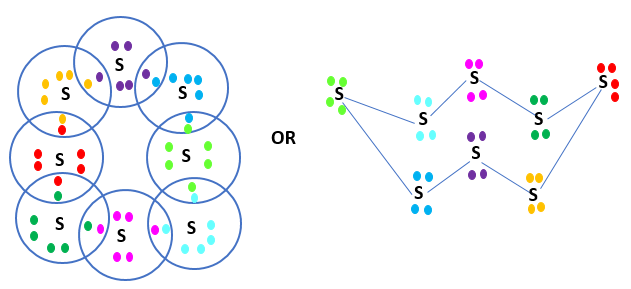 Electron Dot Structure of S8
Electron Dot Structure of S8
Page No. 68
Q1: How many structural isomers can you draw for pentane?
Ans: We can draw three structural isomers of pentane (C5H12).
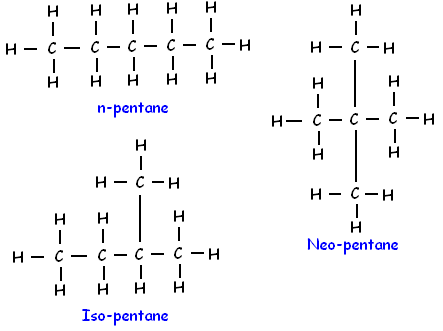
Q2: What are the two properties of carbon which lead to the huge number of carbon compounds we see around us?
Ans: The two features of carbon that give rise to a large number of compounds are as follows:
- Catenation: The self linking ability of carbon to form a long straight-chain, branched-chain, and closed ring structures.
- Tetravalency: With the valency of four, carbon is capable of bonding with four other atoms.
Q3: What will be the formula and electron dot structure of cyclopentane?
Ans: The formula of cyclopentane is C5H10.
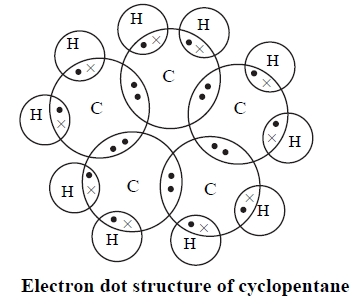
Page No. 69
Q4: Draw the structures for the following compounds.
(a) Ethanoic acid
(b) Bromopentane
(c) Butanone
(d) Hexanal
Are structural isomers possible for bromopentane?
Ans:
(a) 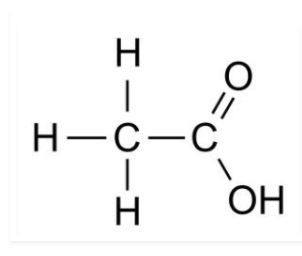
(b)

(c)
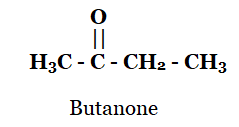
(d)
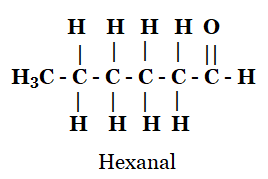
Yes, the structural isomers of bromopentane are possible by changing the bromine position and branching in the parent carbon chain.
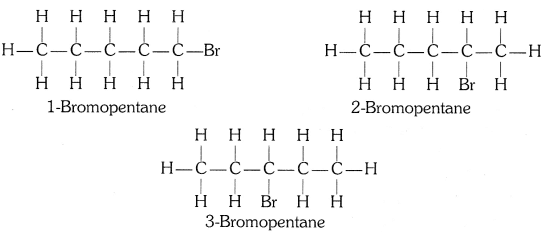 Structural Isomers of Bromopentane
Structural Isomers of Bromopentane
Q5: How would you name the following compounds?
(i) CH3—CH2—Br
(ii)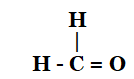
(iii) 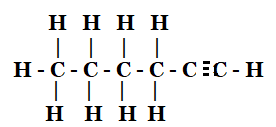
Ans:
(i) Bromoethane
(ii) Methanal (formaldehyde)
(iii) Hex-1-yne
Page No. 71
Q1: Why is the conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid an oxidation reaction?
Ans:
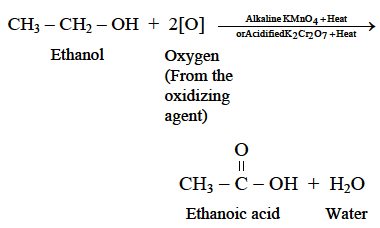 Since the conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid involves the addition of oxygen to ethanol, therefore it is an oxidation reaction.
Since the conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid involves the addition of oxygen to ethanol, therefore it is an oxidation reaction.
Q2: A mixture of oxygen and ethyne is burnt for welding. Can you tell why a mixture of ethyne and air is not used?
Ans:
- 2HC ≡ CH + 5O2 → 4CO2 + 2H2O + Heat
- When ethyne is burnt in air, it gives a sooty flame.
- This is due to incomplete combustion caused by a limited supply of air.
- However, if ethyne is burnt with oxygen, it gives a clean flame with a temperature of 3000°C because of complete combustion.
- This oxy-acetylene flame is used for welding. It is not possible to attain such a high temperature without mixing oxygen.
- This is the reason why a mixture of ethyne and air is not used.
Page No. 74
Ans:
Q2: What are oxidising agents? Give an example.
Ans: Those substances that give oxygen or replace hydrogen on reaction with other compounds are known as oxidising agents, such as potassium permanganate (KMnO4).
Page No. 76
Ans:
- Detergents are ammonium or sulphonate salts of long-chain carboxylic acids. Unlike soap, they do not react with calcium and magnesium ions present in hard water to form scum.
- They give a good amount of lather irrespective of whether the water is hard or soft.
- This means that detergents can be used in both soft and hard water. Therefore, it cannot be used to check whether the water is hard or not.
Q2: People use a variety of methods to wash clothes. Usually, after adding the soap, they 'beat' the clothes on a stone, or beat it with a paddle, scrub with a brush, or the mixture is agitated in a washing machine. Why is agitation necessary to get clean clothes?
Ans:
- A soap molecule has two parts, namely hydrophobic and hydrophilic. With the help of these, it attaches to the grease or dirt particles and forms a cluster called a micelle.
- These micelles remain suspended in solution as a colloid.
- When water is agitated, the oily dirt tends to lift off from the dirty surface and dissociates into fragments.
- This gives an opportunity to other tails to stick to oil. This results in the formation of an emulsion in water.
- This emulsion now contains small globules of oil surrounded by soap or detergent molecules.
- The negatively charged heads present in water prevent the small globules from coming together and form clusters.
- Thus, the oily dirt is removed from the object.
Exercise (Page 77)
Q1: Ethane, with the molecular formula C2H6, has
(a) 6 covalent bonds
(b) 7 covalent bonds
(c) 8 covalent bonds
(d) 9 covalent bonds
Ans: (b)
Sol:
The structural formula for ethane is:
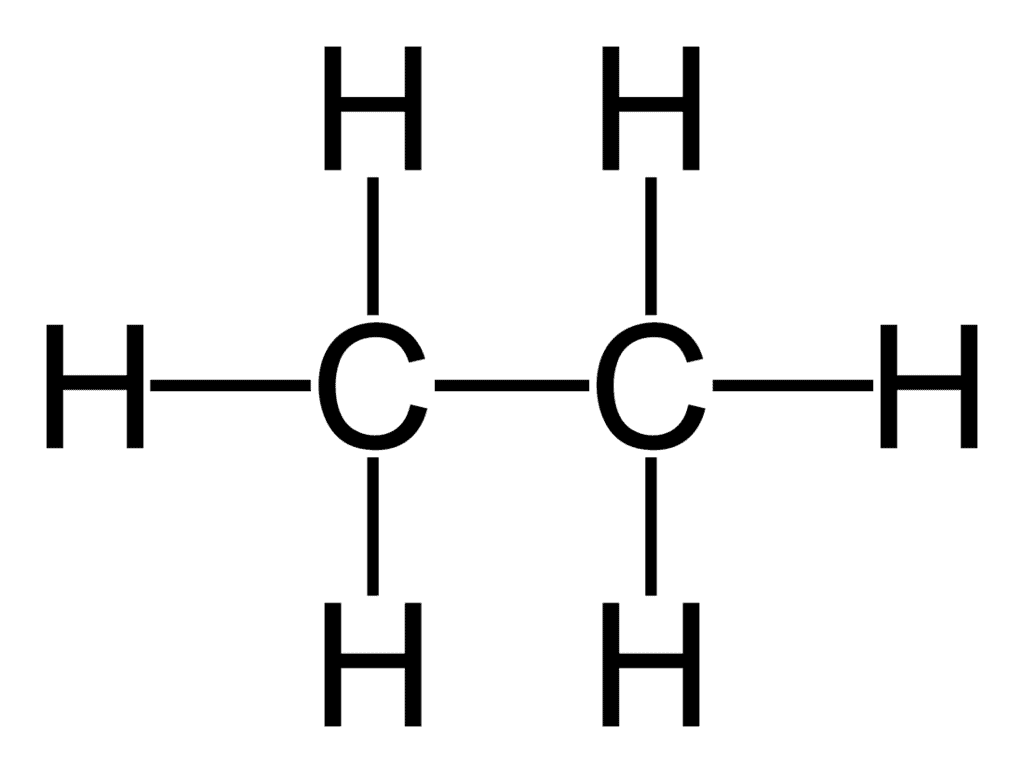 So, it has 7 covalent bonds.
So, it has 7 covalent bonds.
Q2: Butanone is a four-carbon compound with the functional group
(a) Carboxylic acid
(b) Aldehyde
(c) Ketone
(d) Alcohol
Ans: (c)
Sol: Butanone has the formula CH3COCH2CH3. Thus, it has ketone as a functional group. Option (c) is correct.
Q3: While cooking, if the bottom of the vessel is getting blackened on the outside, it means that
(a) The food is not cooked completely.
(b) The fuel is not burning completely.
(c) The fuel is wet.
(d) The fuel is burning completely.
Ans: (b)
Sol: This means that the fuel is not burning completely, and unburnt carbon particles get deposited on the bottom of the vessel, making it black.
Q4: Explain the nature of the covalent bond using the bond formation in CH3Cl.
Ans: Carbon can neither lose 4 electrons nor do gain four electrons as these process make the system unstable due to requirement of extra energy. Therefore CH3Cl completes its octet configuration by sharing its 4 electrons with carbon atoms or with atoms of other elements. Hence the bonding that exists in CH3Cl is a covalent bonding.
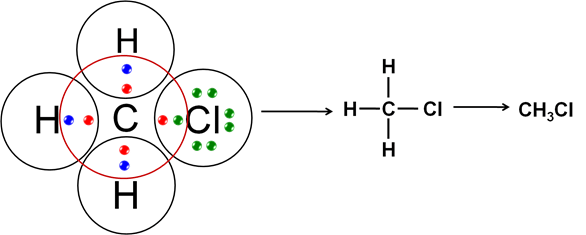
Here, carbon requires 4 electrons to complete its octet, while each hydrogen atom requires one electron to complete its duplet. Also, chlorine requires an electron to complete the octet. Therefore, all of these share the electrons and as a result, carbon forms 3 bonds with hydrogen and one with chlorine.
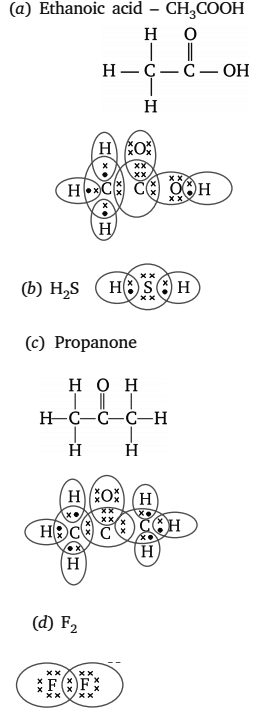
Q5: Draw the electron dot structures for
(i) Ethanoic acid
(ii) H2S
(iii) Propanone
(iv) F2
Ans:
Q6: What is a homologous series? Explain with an example.
Ans:
- It is a series of organic compounds having the same general formula, same functional group, same general methods of preparation, similar chemical properties, and gradation in physical properties where the adjacent members differ by a CH2 group.
Example: The general formula for the homologous series of alkanes is CnH2n+2. CH4 (Methane), C2H6 (Ethane), C3H8 (Propane), and C4H10 (Butane). - Every homologous series have a general formula.
- In alkane, a single bond is a functional group, an alkene double bond, and in alkyne triple bond.
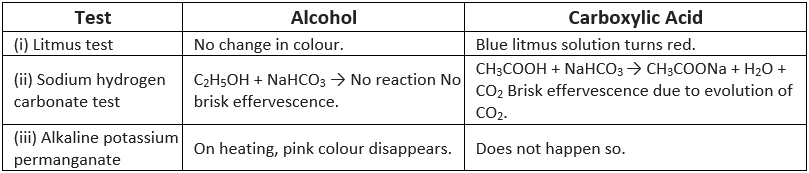
Q7: How can ethanol and ethanoic acid be differentiated on the basis of their physical and chemical properties?
Ans:
(i) Difference on the physical basis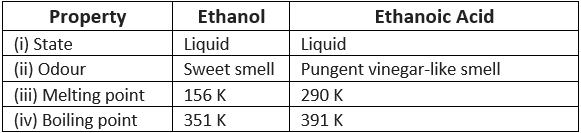
(ii) Difference on the chemical basis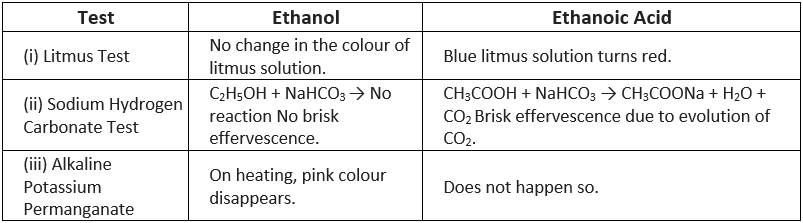
Q8: Why does micelle formation take place when soap is added to water? Will a micelle be formed in other solvents such as ethanol also?
Ans:
- A soap molecule has both a hydrophilic and a hydrophobic end. The hydrophilic end is soluble in water, whereas the hydrophobic end is insoluble in water.
- When soap is added to water, the hydrophilic part gets dissolved in water, but the hydrocarbon tail being the hydrophobic part, forms clusters called micelles.
- As soap is soluble in ethanol, micelle formation will not take place in it.
Q9: Why are carbon and its compounds used as fuels for most applications?
Ans: During the process of combustion of carbon and its compounds, a large amount of heat and light is released, i.e., They have high calorific value, and because of this, carbon and its compounds are used as fuels.
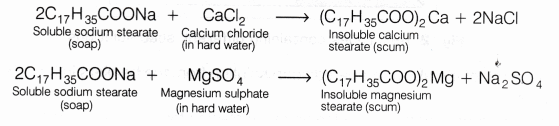
Q10: Explain the formation of scum when hard water is treated with soap.
Ans:
- Soaps are sodium or potassium salts of fatty acids having cleansing action in the water.
- Hard water contains Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions, which react with soap to form calcium and magnesium salts of fatty acids, which are insoluble and are called scum.
Q11: What change will you observe if you test soap with litmus paper (red and blue)?
Ans: As a soap solution is basic in nature, it will turn red litmus paper into blue, but it will not affect blue litmus paper.
Q12: What is hydrogenation? What is its industrial application?
Ans:
- Hydrogenation is a process in which Hydrogen is added in the presence of nickel or palladium as a catalyst.
- Industrial application: The process of hydrogenation is used to prepare vegetable ghee from vegetable oil.
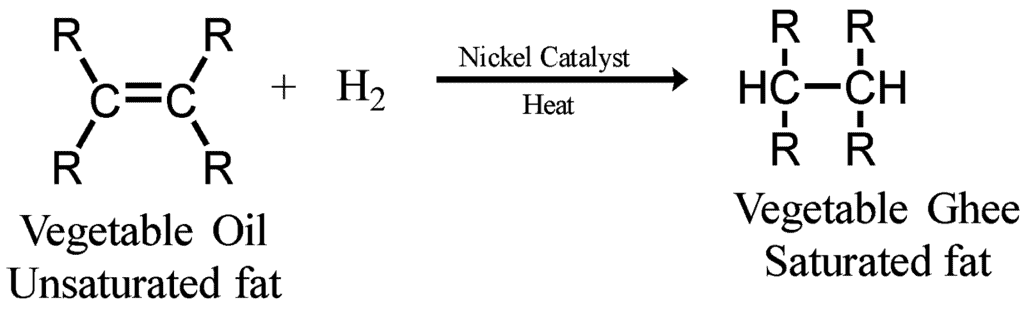
Q13: Which of the following hydrocarbons undergo addition reactions:
C2, H6, C3H8, C3H6, C2H2, and CH4.
Ans: Unsaturated hydrocarbons undergo addition reactions. Being unsaturated hydrocarbons, C3H6, and C2H2 will undergo addition reactions.
Q14: Give a test that can be used to differentiate chemically between butter and cooking oil.
Ans:
- Add bromine water to each of them.
- Cooking oil will decolourize bromine water showing that it is unsaturated, whereas butter will not decolourize bromine water showing that it is saturated.
Q15: Explain the mechanism of the cleaning action of soaps.
Ans:
- A soap molecule has hydrophobic and hydrophilic ends. In water, hydrophobic ends of soap, which consists of hydrocarbon chains, cluster together to form micelles.
- The oily dirt collects in the centre of the micelle.
- These micelles stay in solution as a colloid and will not come together to form precipitate because of ion-ion repulsion.
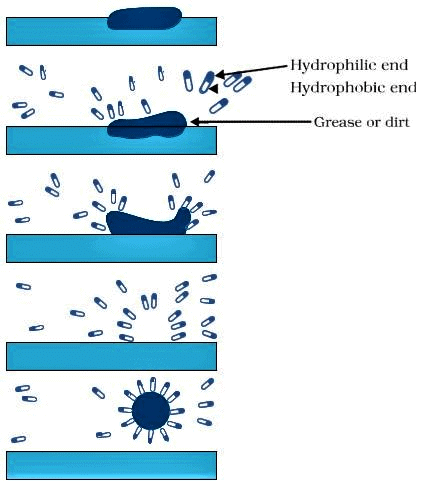 Formation of Micelle
Formation of Micelle
- Thus the dirt suspended in the micelles can be easily rinsed away, and hence, soaps are effective in cleaning.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 - Carbon and its Compounds
| 1. What are the main allotropes of carbon and their properties? |  |
| 2. How do carbon compounds differ from inorganic compounds? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of carbon in biological systems? |  |
| 4. What are some common uses of carbon compounds in everyday life? |  |
| 5. What are the environmental impacts of carbon compounds? |  |






















