NCERT Solutions Class 11 Biology Chapter 10 - Cell Cycle and Cell Division
Q1: What is the average cell cycle span for a mammalian cell?
Ans: The average cell cycle span for a mammalian cell is approximately 24 hours. The cells remains in the G1 phase for about 10 hours. The duration of S phase or the Synthetic phase varies with respect to the total DNA present in a cell.
 Mitotic
Mitotic
Q2: Distinguish cytokinesis from karyokinesis.
Ans: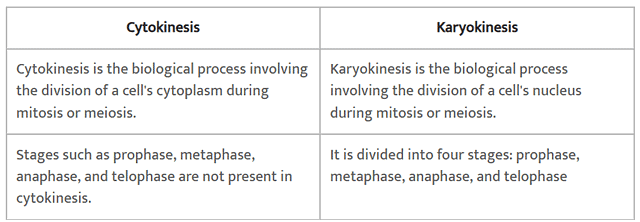
Q3: Describe the events taking place during interphase.
Ans: Interphase involves a series of changes that prepare a cell for division. It is the period during which the cell experiences growth and DNA replication in an orderly manner. Interphase is divided into three phases.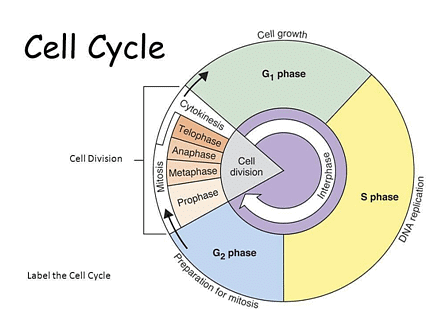 Interphase
Interphase
- G1 phase: It is the stage during which the cell grows and prepares its DNA for replication. In this phase, the cell is metabolically active.
- S phase: It is the stage during which DNA synthesis occurs. In this phase, the amount of DNA (per cell) doubles, but the chromosome number remains the same.
- G2 phase: In this phase, the cell continues to grow and prepares itself for division.The proteins and RNA required for mitosis are synthesised during this stage.
G2 Phase
Q4: What is G0 (quiescent phase) of cell cycle?
Ans: In adult animals, some cells will not exhibit cell division, and many other cells occasionally divide when there is a need to replace cells that have been lost because of injury or cell death. These cells exit the G1 phase to enter an inactive stage of the cell cycle called the G0 phase. Cells in the G0 phase do not proliferate unless called on to do so. Hence, the cells in this phase tend to become inactive, stop dividing and become specialized through the differentiation process.
Q5: Why is mitosis called equational division?
Ans: Mitosis is the process of cell division wherein the chromosomes replicate and get equally distributed into two daughter cells. The chromosome number in each daughter cell is equal to that in the parent cell, i.e., diploid. Hence, mitosis is known as equational division.
Q6: Name the stage of cell cycle at which one of the following events occur:
(i) Chromosomes are moved to spindle equator.
(ii) Centromere splits and chromatids separate.
(iii) Pairing between homologous chromosomes takes place.
(iv) Crossing over between homologous chromosomes takes place.
Ans:
(i) In Metaphase, chromosomes are transported to the spindle equator.
(ii) In Anaphase, centrosomes split and chromatids separate.
(iii) In meiosis, the pairing of homologous chromosomes occurs in the Zygotene stage of prophase 1.
(iv) In meiosis, crossing across between homologous chromosomes occurs in the Pachytene stage of prophase 1.
Q7: Describe the following:
(a) Synapsis
(b) Bivalent
(c) Chiasmata
Draw a diagram to illustrate your answer.
Ans:
(a) Synapsis: The pairing of homologous chromosomes is called synapsis. This occurs during the second stage of prophase I or zygotene.
(b) Bivalent: Bivalent or tetrad is a pair of synapsed homologous chromosomes. They are formed during the zygotene stage of prophase I of meiosis.
(c) Chiasmata: Chiasmata is the site where two sister chromatids have crossed over. It represents the site of cross-over. It is formed during the diplotene stage of prophase I of meiosis.
Q8: How does cytokinesis in plant cells differ from that in animal cells?
Ans: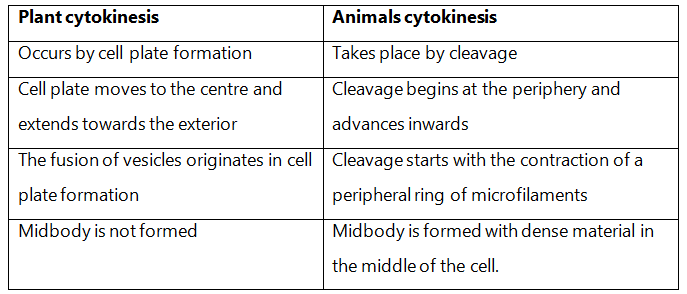
Q9: Find examples where the four daughter cells from meiosis are equal in size and where they are found unequal in size.
Ans: During the formation of male gametes in human beings (sperms), the four daughter cells formed during meiosis are equal in size. The formation of the female gamete (ovum) during meiosis results in the formation of four daughter cells, unequal in size. The unequal daughter cells are – one big mature ovum and 3 small polar bodies.
Q10: Distinguish anaphase of mitosis from anaphase I of meiosis.
Ans: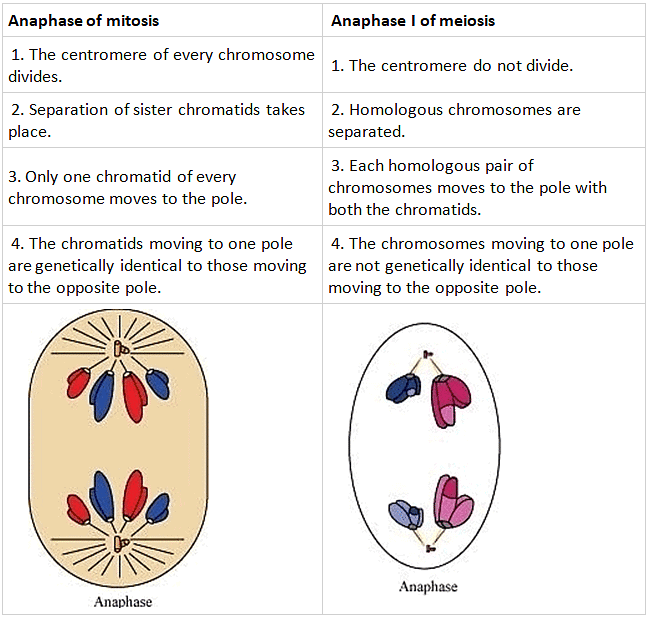
Q11: List the main differences between mitosis and meiosis.
Ans: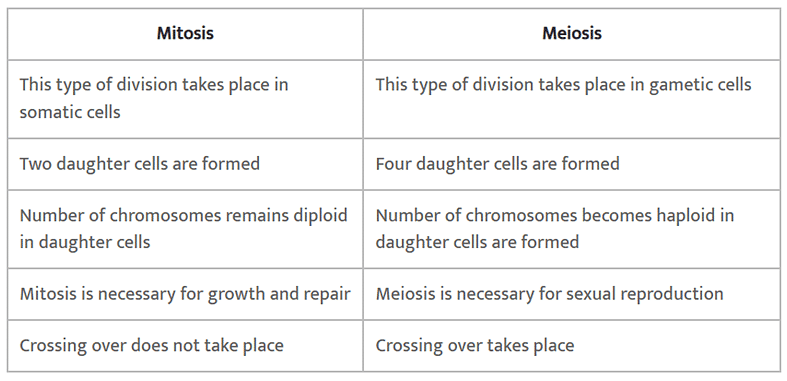
Q12: What is the significance of meiosis?
Ans: Meiosis is the process involving the reduction in the amount of genetic material. It comprises two successive nuclear and cell divisions, with a single cycle of DNA replication. As a result, at the end of meiosis II, four haploid cells are formed.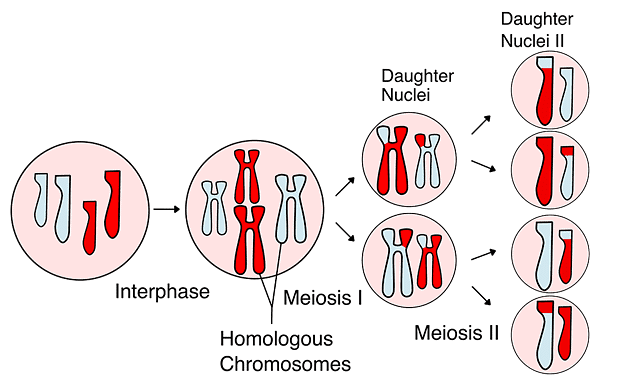 Meiosis
Meiosis
Significance of meiosis
- Meiosis maintains the chromosome number from generation to generation. It reduces the chromosome number to half so that the process of fertilization restores the original number in the zygote.
- Variations are caused by the cross-over and the random distribution of homologous chromosomes between daughter cells. Variations play an important role in evolution.
- Chromosomal mutations are brought about by the introduction of certain abnormalities. These chromosomal mutations may be advantageous for an individual.
Q13: Discuss with your teacher about
(i) haploid insects and lower plants where cell-division occurs, and
(ii) some haploid cells in higher plants where cell-division does not occur.
Ans: (i) In some insects and lower plants, fertilization is immediately followed by zygotic meiosis, which leads to the production of haploid organisms. This type of life cycle is known as haplontic life cycle.
(ii) The phenomenon of polyploidy can be observed in some haploid cells in higher plants in which cell division does not occur. Polyploidy is a state in which cells contain multiple pairs of chromosomes than the basic set. Polyploidy can be artificially induced in plants by applying colchicine to cell culture.
Q14: Can there be mitosis without DNA replication in ‘S’ phase?
Ans. No, there cannot be mitosis without DNA replication in S phase because additional DNAs are required for the formation of new cells. DNA duplication is important as it maintains the chromosome number in the daughter cells and hence Mitosis is an equational division. Therefore, the duplication of DNA is an essential step and without it, no mitosis can take place.
Q15: Can there be DNA replication without cell division?
Ans: DNA replication can take place without cells division as in case of formation of new mitochondria and chloroplasts. During cell division, the parent cell gets divided into two daughter cells. However, if there is a repeated replication of DNA without any cell division, then this DNA will keep accumulating inside the cell. This would increase the volume of the cell nucleus, thereby causing cell expansion.
Q16: Analyse the events during every stage of cell cycle and notice how the following two parameters change
(i) Number of chromosomes (N) per cell
(ii) Amount of DNA content (C) per cell
Ans: During meiosis, the number of chromosomes and the amount of DNA in a cell change.
(i) Number of chromosomes (N) per cell: During anaphase I of the meiotic cycle, the homologous chromosomes separate and start moving toward their respective poles. As a result, the bivalents get divided into two sister chromatids and receive half the chromosomes present in the parent cell. Therefore, the number of chromosomes reduces in anaphase I.
 Number of chromosomes
Number of chromosomes
(ii) Amount of DNA content (C) per cell: During anaphase II of the meiotic cycle, the chromatids separate as a result of the splitting of the centromere. It is the centromere that holds together the sister chromatids of each chromosome. As a result, the chromatids move toward their respective poles. Therefore, at each pole, a haploid number of chromosomes and a haploid amount of DNA are present. During mitosis, the number of chromosomes remains the same. The DNA duplicated in the S phase gets separated in the two daughter cells during anaphase. As a result, the DNA content (C) of the two newly-formed daughter cells remains the same.
|
150 videos|399 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions Class 11 Biology Chapter 10 - Cell Cycle and Cell Division
| 1. What is the significance of the cell cycle in the growth and development of organisms? |  |
| 2. How is the cell cycle regulated to prevent uncontrolled cell division? |  |
| 3. What are the different phases of the cell cycle and what happens in each phase? |  |
| 4. How does cell division contribute to the maintenance of genetic stability in organisms? |  |
| 5. Can you explain the process of cell division and its significance in the regeneration of tissues in multicellular organisms? |  |

















