NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics - Government Budget and Economy
Q1: Explain why public goods must be provided by the government.
Ans: A good that is non-rival and non-excludable is referred to as public good. Non-rival means that consumption by one individual does not affect the consumption of another individual. Whereas, non-excludable implies that no individual can be excluded from using the good. For example, parks, roads, national defence, etc.
These goods must be provided by the government because of the following reasons:
- The benefits of public goods can be easily enjoyed by anyone without affecting the consumption of other individuals. There arises market failure.
- No individual can be excluded from using public goods as it is available to all. The link between the producer and the consumer becomes non-functional, necessitating government interference through public provisions.
Q2: Distinguish between revenue expenditure and capital expenditure.
Ans: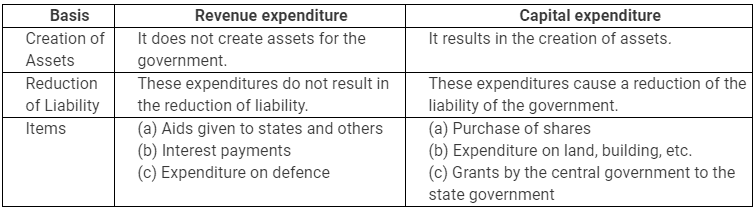
Q3:‘The fiscal deficit gives the borrowing requirement of the government’. Elucidate.
Ans: Fiscal deficit is the excess of total expenditure over total receipts.
That is, when total government expenditure is greater that total government receipts, the government faces fiscal deficit.
Fiscal deficit is estimated as:
Total Expenditure (revenue + capital) − Total Receipts (excluding borrowings).
Fiscal deficit gives an indication to the government about the total borrowing requirements from all sources. Fiscal deficit can be financed through domestic borrowings and/or borrowings from abroad. Greater fiscal deficit implies greater borrowings by the government.
Q4: Give the relationship between the revenue deficit and the fiscal deficit.
Ans: The relationship between the revenue deficit and the fiscal deficit can be explained through the following points:
- Revenue deficit is the difference between government’s revenue expenditures and government’s receipts.
Revenue deficit = Revenue expenditures − Revenue receipts
On the other hand, fiscal deficit is the difference between the total expenditure and the total receipt of the government.
Fiscal deficit = Total Expenditure − Total Receipts (excluding borrowings) - The term ‘fiscal deficit’ is used in a broader sense than the term ‘revenue deficit’.
- As revenue deficit increases, the proportion of fiscal deficit also increases.
Q5: Suppose that for a particular economy, investment is equal to 200, government purchases are 150, net taxes (that is lump-sum taxes minus transfers) is 100 and consumption is given by C = 100 + 0.75Y (a) What is the level of equilibrium income? (b) Calculate the value of the government expenditure multiplier and the tax multiplier. (c) If government expenditure increases by 200, find the change in equilibrium income.
Ans:
I = 200
G = 150
T = 100
C = 100 + 0.75 Y
So, C (Autonomous consumption) = 100
And, MPC (c) = 0.75
(a) Equilibrium level of income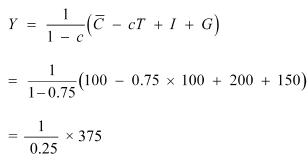
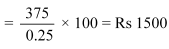
(b) Government expenditure multiplier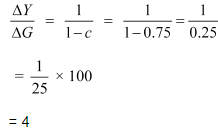
Tax multiplier 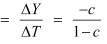
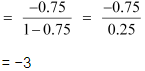
(c) ΔG = 200
New equilibrium income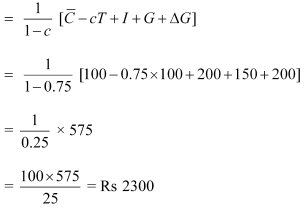
Therefore, change in equilibrium income = 2300 − 1500 = Rs 800
Q6: Consider an economy described by the following functions: C = 20 + 0.80Y, I = 30, G = 50, TR = 100 (a) Find the equilibrium level of income and the autonomous expenditure multiplier in the model. (b) If government expenditure increases by 30, what is the impact on equilibrium income? (c) If a lump-sum tax of 30 is added to pay for the increase in government purchases, how will equilibrium income change?
Ans:
(a) C = 20 + 0.80 Y 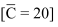
I = 30
c = 0.80
G = 50
T = 100
Equilibrium level of income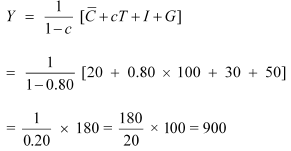
Expenditure multiplier 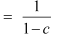
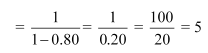
(b) Increase in government expenditure
ΔG = 30
New equilibrium expenditure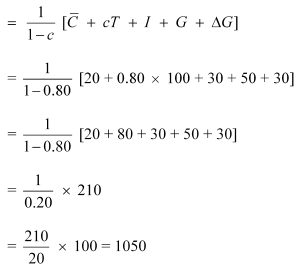
Equilibrium level of income increases by 150 (1050 − 900)
(c) Tax multiplier 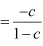
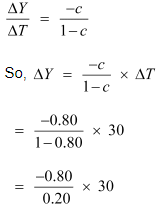
= −120
New Equilibrium level of income = Y + ΔY
= 900 + (−120)
= Rs 780
Q7: In the above question, calculate the effect on output of a 10 per cent increase in transfers, and a 10 per cent increase in lump-sum taxes. Compare the effects of the two.
Ans:
MPC = 0.80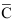 = 20
= 20
I = 30
G = 50
TR = 100
ΔTR = 10
Equilibrium level of income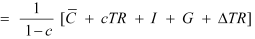
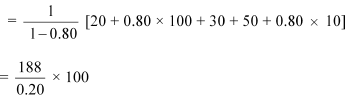
= Rs 940
Change in income = 940 − 900 = Rs 40
Increase in lump-sum tax ΔT =10
Change in Income 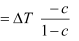
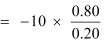
= −10 × 4
= −40
From the above results, we can conclude that increase of 10 percent in transfers will raise the income by 40%.
And, increase of 10% in tax will lead to a fall in the income by 40%.
Q8: We suppose that C = 70 + 0.70Y D, I = 90, G = 100, T = 0.10Y (a) Find the equilibrium income. (b) What are tax revenues at equilibrium Income? Does the government have a balanced budget?
Ans:
(a) C = 70 + 0.70 YD
I = 90
G = 100
T = 0.10Y
Y = C + I +G
Y = 70 + 0.70Y + 90 + 100
Y = 70 + 0.70YD + 190
Y = 70 + 0.70 (Y − T) + 190
Y = 70 + 0.70Y − 0.70 × 0.10 Y + 190
Y = 70 + 0.70Y − 0.07Y + 190
Y = 70 + 0.63Y + 190
Y = 260 + 0.63Y
Y − 0.634 = 260
0.37Y = 260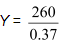
Y = 702.7
(b) T = 0.10Y
= 0.10 × 702.7
= 70.27
Government expenditure = 100
Tax revenue = 70.27
As, G > T, Government has a deficit budget, not a balanced budget.
Q9: Suppose marginal propensity to consume is 0.75 and there is a 20 per cent proportional income tax. Find the change in equilibrium income for the following (a) Government purchases increase by 20 (b) Transfers decrease by 20.
Ans: In case of proportional taxes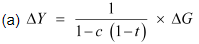
MPC = 0.75 and ΔG = 20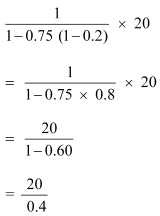
= 50
(b) Transfer decreases by 20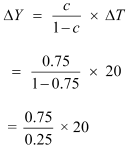
= 60
Q10: Explain why the tax multiplier is smaller in absolute value than the government expenditure multiplier.
Ans: The tax multiplier is smaller in absolute value than the government expenditure multiplier, as the government expenditure affects the total expenditure and taxes through the multiplier. Tax multiplier also influences disposable income that affects the overall consumption level.
The reason is explained through the following example.
Let’s assume MPC be to 0.80.
Then, the government expenditure multiplier 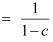
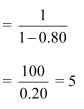
Tax multiplier 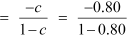
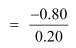
= −4
This shows that government expenditure multiplier is more than tax multiplier.
Q11: Explain the relation between government deficit and government debt.
Ans: The relation between government deficit and government debt can be explained through the following points.
- Government deficit is the excess of total expenditure over total receipt of the government; whereas, government debt is the amount of liability, owed by the government to the public, foreign and other institutions.
- The term government deficit implies increase in the debt of the government. In other words, if the government continues to borrow to finance deficit, it leads to additional debt.
Q12: Does public debt impose a burden? Explain.
Ans: Government debt or public debt refers to the amount or money that a central government owes. This amount may be borrowings of the government from banks, public financial institutions and from other external and internal sources. Public debt definitely imposes a burden on the economy as a whole, which is described through the following points.
- Adverse effect on productivity and investment: A government may impose taxes or get money printed to repay the debt. This however reduces the peoples’ ability to work, save and invest, thus hampering the development of a country.
- Burden on younger generations: The government transfers the burden of reduced consumption on future generations. Higher government borrowings in the present leads to higher taxes levied in future in order to repay the past obligations. The government imposes taxes on the younger generations, lowering their consumption, savings and investments. Hence, higher public debt has negative effect on the welfare of the younger generations.
- Lowers the private investment: The government attracts more investment by raising rates of interests on bonds and securities. As a result, a major part of savings of citizens goes in the hands of the government, thus crowding out private investments.
- Leads to the drain of National wealth: The wealth of the country is drained out at the time of repaying loans taken from foreign countries and institutions.
Q13: Are fiscal deficits inflationary?
Ans: Fiscal deficits are not necessarily inflationary; though, they are generally regarded as inflationary. When the government expenditure increases and tax reduces, there is a government deficit and there will be a corresponding increase in the aggregate demand. However, the firms might not be able to meet the growing demands, forcing the price to rise. Hence fiscal deficits are inflationary in this sense.
But on the other hand, initially if the resources are underutilised (due to insufficient demand) and output is below full employment level, then with the increase in government expenditure, more factor resources will be employed to cater to the increasing demand without exerting much pressure on price to rise. In this situation, a high fiscal deficit is accompanied by high demand, greater output level and lesser inflationary situation. Hence, whether the fiscal deficits are inflationary or not depends on how close is the original output level to the full employment level.
Q14: Discuss the issue of deficit reduction.
Ans: The ways of government budget deficit reduction are the following:
(i) Decreasing expenditure
(ii) Increasing revenue
(i) Decreasing expenditure
a) The expenditure of government should be decreased by making government activities more planned and effective.
b) The government can encourage private sector to undertake capital projects.
(ii) Increasing revenue
a) Higher taxes imply higher income earned by the government. Also, new taxes may add to the revenues of the government.
b) The government can sell shares of Public Sector Undertakings (PSU disinvestment) to increase its revenue.
Q15: What do you understand by G.S.T? How good is the system of G.S.T as compared to the old tax system? State its categories.
Ans: “Goods and services tax means any tax on supply of goods, or services or both except taxes on the supply of the alcoholic liquor for human consumption.”. It is an indirect tax which has integrated various taxes like Sales tax, excise tax, VAT, etc., into one single tax for the entire nation. By replacing the various archaic tax structures, GST is levied at every stage of the supply chain of the goods or services from production to the last retail level.
The system of G.S.T is good as compared to the old tax system in the following ways:
- Abolition of different tax structures- Service Tax, Union Excise Duty, Central Sales Tax (collected by states), Customs Duty etc. being imposed by central government and Value Added Tax, Entry Tax, Octroi, Luxury Tax etc. being imposed by state governments have been abolished with the introduction of GST. Levy of cess, resale tax, additional tax, turnover tax etc. have also been nullified.
- Widening of tax bases- GST has increased the tax bases for the governments. This has reduced the administrative cost of governments.
- The benefit of Input tax credit-Levy of GST is applicable at every stage whether it is manufacturer, intermediary or the end user. Side by side the assessee is given the advantage of input tax credit which means he needs to pay a difference of Output tax and Input tax only. So, following the lines of VAT; GST has removed the cascading effect of the tax.
- Neutralization to process, business models, structure and location-GST is supposed to boost the economic growth, efficiency and sustainability because of its neutral feature of the tax regime.
- GST may lead to the enhancement of the export because of the reduced effect of duties on many items which will provide an edge to the exporters over the competition being faced by them in the international market.
- Increased demand and production of goods and services-GST due to reduced cost of production would lead to an expansion of manufacturing units and an increase in demand for goods and services.
GST is categorized in three ways i.e. Central GST, State GST and Integrated GST.
Central GST- CGST is levied on intra-state supply of goods and services by the central government. It is collected by the central government which is 50% of the applicable tax rate. CGST is further classified into:
1. Output CGST
2. Input CGST
State GST- SGST is levied on intra-state supplies of goods and services by the state governments. It is collected by state governments being 50% of the applicable tax rate. SGST is further classified into:
1. Output SGST
2. Input SGST
Integrated GST- IGST is levied on interstate supplies of goods and services by the central government. It is collected by the central government only. IGST is further classified into:
1. Output IGST
2. Input IGST
|
108 videos|430 docs|128 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics - Government Budget and Economy
| 1. What is a government budget? |  |
| 2. Why is a government budget important for the economy? |  |
| 3. What are the components of a government budget? |  |
| 4. How does the government budget impact the economy? |  |
| 5. How is the government budget prepared in India? |  |






















