NCERT Solutions Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 - Biomolecules
Q1: What are macromolecules? Give examples.
Ans: Macromolecules are large biomolecules formed by the polymerisation of many small micromolecules and have high molecular weight. They are often found in the colloidal state in the intercellular fluid due to their insolubility. Proteins, nucleic acids, and polysaccharides are examples of macromolecules.
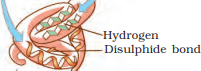
Q2: What is meant by the tertiary structure of proteins?
Ans: It is a structure that forms when the secondary coiled polypeptides are folded to produce a hollow, woollen ball-like structure. It is folded such that the functional side groups appear on the surface while the inactive side groups are found inside. This gives us a 3-dimensional view of a protein. Tertiary structure is absolutely necessary for the many biological activities of proteins.
Q3: Find and write down structures of 10 interesting small molecular-weight biomolecules. Find if there is any industry which manufactures the compounds by isolation. Find out who are the buyers.
Ans:
(a) 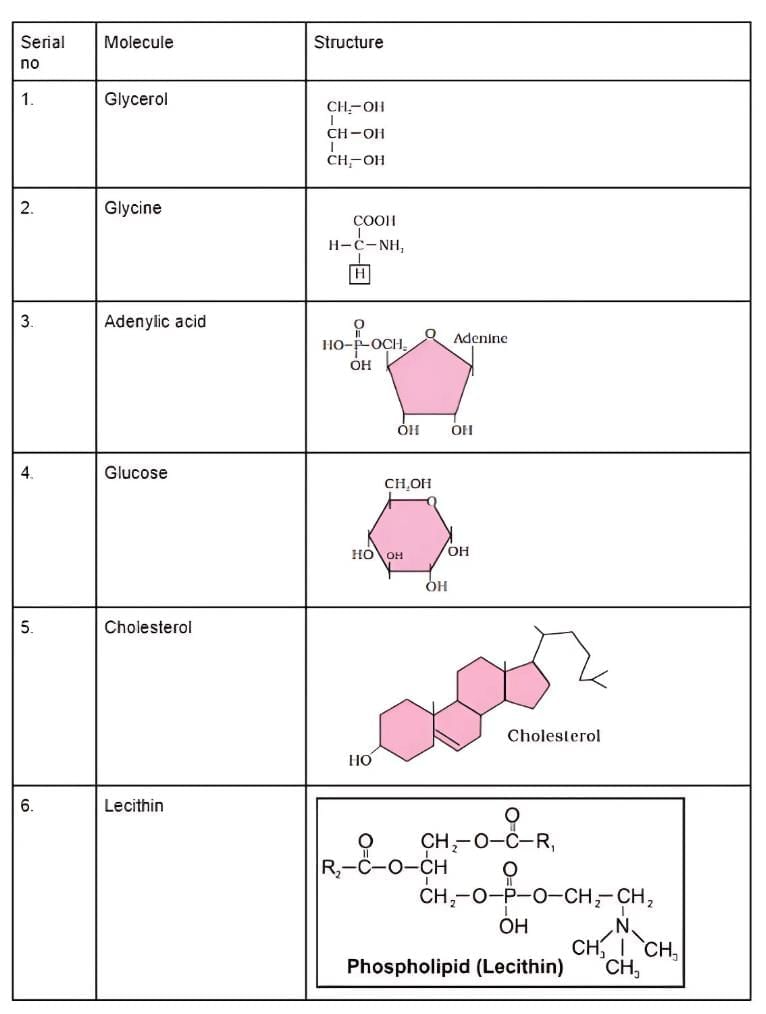
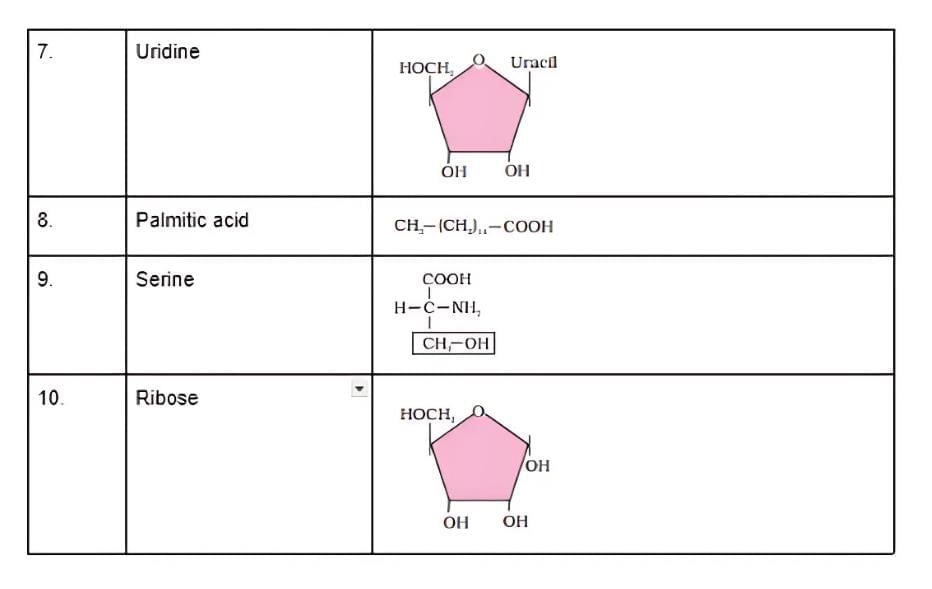
(b)
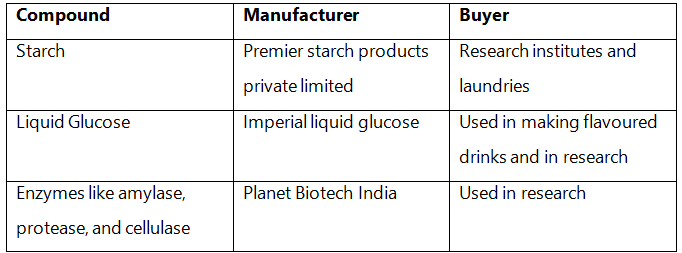
Q4: Find out and make a list of proteins used as therapeutic agents. Find other applications of proteins (e.g., Cosmetics etc.)
Ans: Examples of proteins used as therapeutic agents include insulin, antibodies, oxytocin, antidiuretic hormone (ADH), thrombin, fibrinogen, renin, and streptokinase.
Other applications of proteins include:
- They are used as artificial sweeteners. Thaumatin is a low-calorie sweetener.
- Proteins are used as dietary supplements to maintain health.
- They are used in creams and shampoos. (Caesin)
Q5: Explain the composition of triglyceride.
Ans: When glycerol combines with three fatty acids on each of the OH groups through ester bonds, it is known as a triglyceride.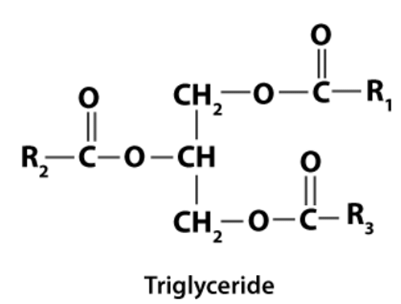 All three fatty acids of triglyceride in pure fat are similar, while in mixed fat, they are dissimilar.
All three fatty acids of triglyceride in pure fat are similar, while in mixed fat, they are dissimilar.
Q6: Can you attempt building models of biomolecules using commercially available atomic models (Ball and Stick models).
Ans: Yes, biomolecules can be modeled using commercially available ball-and-stick kits. In this representation, atoms are shown as colored balls and chemical bonds as sticks connecting them. For example, in a model of D-glucose, hydrogen atoms may be represented by green balls, oxygen by pink balls, and carbon by grey balls.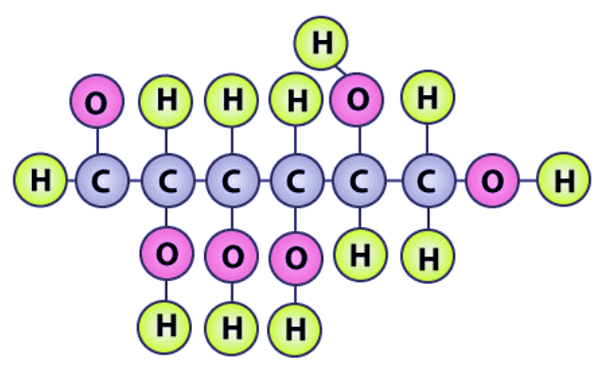
Q7: Draw the structure of the amino acid, alanine.
Ans: The structure of Alanine is as follows: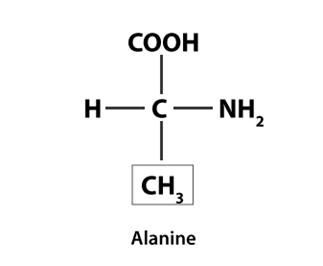
Q8: What are gums made of? Is Fevicol different?
Ans: Gums are complex carbohydrates known as heteropolysaccharides. They are made up of various monosaccharide units linked by glycosidic bonds. Fevicol, however, differs from gums. It is a synthetic adhesive composed of polymers that are artificially created, rather than derived from natural sources.
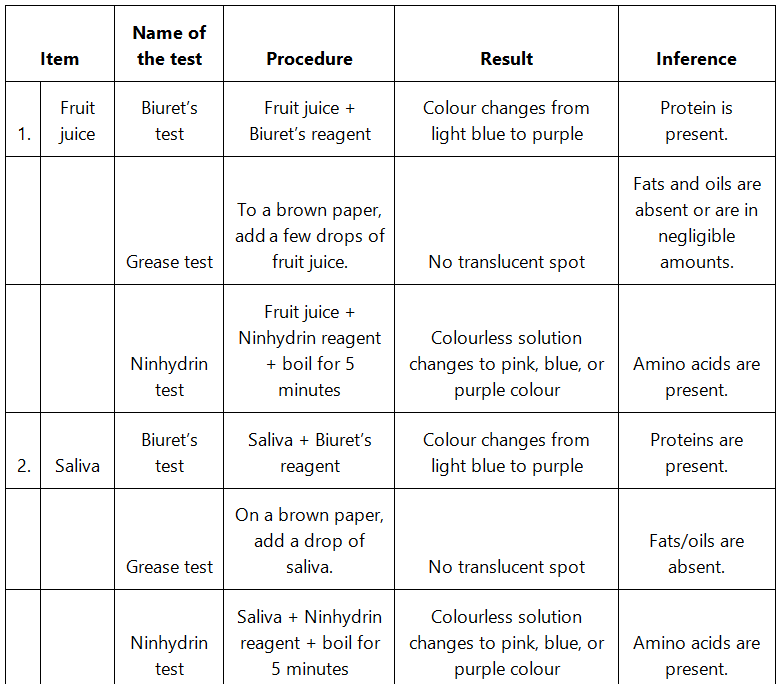
Q9: Find out a qualitative test for proteins, fats and oils, amino acids and test any fruit juice, saliva, sweat and urine for them.
Ans: Qualitative tests for proteins, amino acids and fats:
- Biuret test: The Biuret test for protein identifies the presence of protein by producing light blue to purple colour of the solution.
- Grease test for oil: Certain oils give a translucent stain on brown paper. This test can be used to show the presence of fat in vegetable oils.
- Ninhydrin test: If Ninhydrin reagent is added to the solution, then the colourless solution changes to pink, blue or purple colour depending on the type of amino acid.
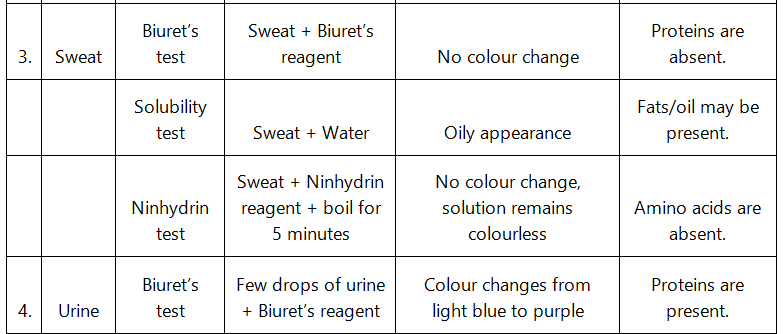
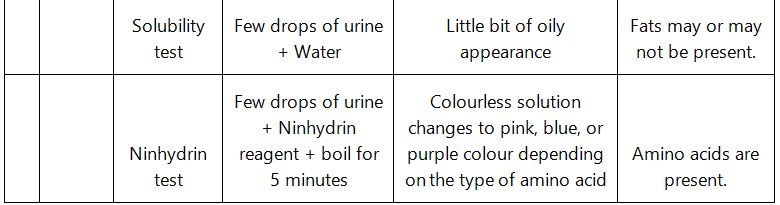
Q10: Find out how much cellulose is made by all the plants in the biosphere and compare it with how much of paper is manufactured by man and hence what is the consumption of plant material by man annually. What a loss of vegetation!
Ans: The biosphere generates approximately 100 billion tonnes of cellulose from a total of 170 billion tonnes of organic matter. In contrast, paper production consumes around 0.5 billion tonnes of wood annually. Additionally, trees are used for various other purposes, including:
- Food
- Medicines
- Timber
- Spices
It is estimated that about 1.5 billion tonnes of food is required each year, along with a wood demand of 2 billion tonnes for different uses. This makes it challenging to accurately assess the total annual consumption of plant material by humans. Consequently, the extensive use of cellulose contributes significantly to the loss of vegetation.
Q11: Describe the important properties of enzymes.
Ans: The important properties of enzymes are as follows:
- Proteins: Enzymes are typically high molecular weight, complex globular proteins. They may associate with non-protein substances to function effectively.
- Catalysts: Enzymes do not initiate chemical reactions; instead, they accelerate them. They temporarily bind to substrate molecules and remain unchanged after the reaction.
- Reversibility: Reactions catalysed by enzymes can often be reversed.
- Specificity: Each enzyme is specific to a particular reaction or substrate.
- Thermal Sensitivity: Enzymes are sensitive to heat and function best at an optimum temperature and pH.
- Inactivation: Enzymes can be inactivated by poisons and radiation.
|
150 videos|399 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 - Biomolecules
| 1. What are biomolecules? |  |
| 2. How are biomolecules classified? |  |
| 3. What is the importance of biomolecules in living organisms? |  |
| 4. How are biomolecules studied in biochemistry? |  |
| 5. Can biomolecules be used in medical treatments? |  |

















