NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Political Science - Executive
Q1 Parliamentary executive means:
(a) Executive where there is a parliament
(b) The executive elected by the parliament
(c) Where the parliament functions as the Executive
(d) An executive that is dependent on the support of the majority in the parliament
Ans:
(d) An executive that is dependent on the support of the majority in the parliament.
Q2: Read this dialogue. Which argument do you agree with? Why?
Amit: Looking at the constitutional provisions, it seems that the President is only a rubber stamp.
Shama: The President appoints the Prime Minister. So, he must have the power to remove the Prime Minister as well.
Rajesh: We don't need a President. After the election, the Parliament can meet and elect a leader to be the Prime Minister.
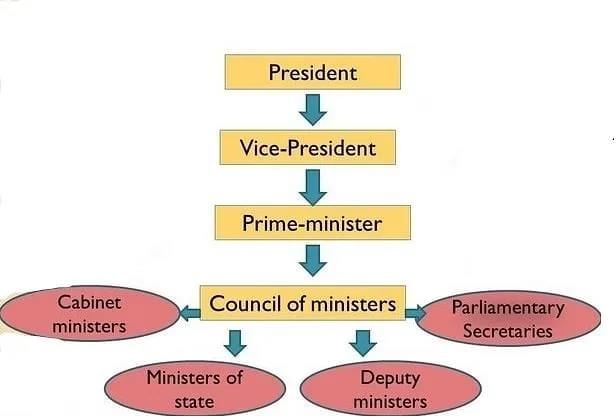
Ans: Sample answers for all arguments: Council of Ministers
Council of Ministers
Amit: I partly agree with Amit’s argument, but with clarifications.
While the President often acts on the aid and advice of the Council of Ministers, led by the Prime Minister, as per Article 74 of the Constitution, the President is not merely a rubber stamp.
The President has some discretionary powers, such as:
- Appointing the Prime Minister when no party has a clear majority.
- Returning a bill once for reconsideration (except in the case of a money bill).
- Exercising judgment during constitutional crises.
Thus, the President functions as a constitutional head and ensures that the government operates within constitutional limits.
Shama: Shama’s argument is valid because the office of the President of India carries respect and nominal supremacy.
- The President is not a mere rubber stamp and can exercise discretionary powers, especially while appointing the Prime Minister when no clear majority exists.
- The Council of Ministers is collectively responsible to the Lok Sabha; if it loses the House’s confidence, it must resign.
- The Prime Minister holds office only as long as supported by the majority in the Lok Sabha, so removal is effectively controlled by Parliament, not directly by the President.
Rajesh: The argument by Rajesh is incorrect. The President is essential to the Indian parliamentary system, not redundant.
- The President is the constitutional head who ensures compliance with the Constitution.
- He appoints the Prime Minister, summons and dissolves Parliament, and gives assent to bills before they become law.
- The President acts as a stabilising authority during political uncertainty or constitutional crises.
Therefore, the President’s office is vital for stability and constitutional balance in a parliamentary democracy.
Q3: Match the following
Ans:
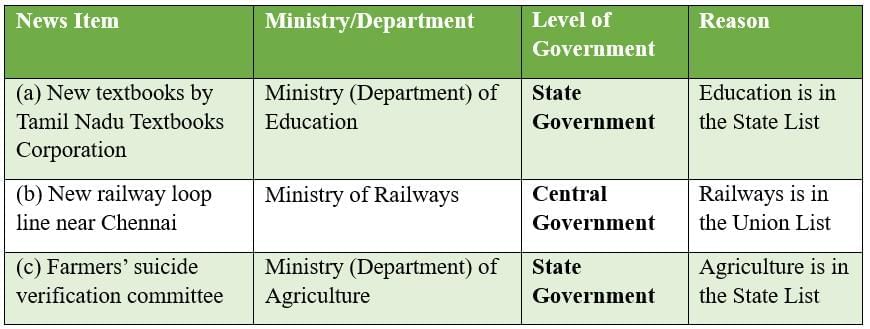
Q4: Identify the ministry which may have released the following news items. Would this be a ministry of the central government or the State government? Why?
(a) An official release said that in 2004-05, the Tamil Nadu Textbooks Corporation would release new versions for standards VII, X and XI.
Ans: Ministry/Department: Ministry (Department) of Education
Level of Government: State Government
Reason: Education is a subject under the State List; thus, each State Government has the authority to legislate and implement education policies. Hence, the release is from the State Education Department.
(b) A new railway loop line bypassing the crowded Tiruvallur-Chennai section to help iron ore exporters. The new line, likely to be about 80 km long, will branch off at Puttur and then reach Athipattu near the port.
Ans: Ministry/Department: Ministry of Railways
Level of Government: Central Government
Reason: Railways is a subject included in the Union List and is managed exclusively by the Central Government. Hence, the Ministry of Railways has issued the news.
(c) The three-member sub-divisional committee formed to verify suicide by farmers in Ramayampet mandal has found that the two farmers who committed suicide this month have had economic problems due to the failure of crops.
Ans:
Ministry/Department: Ministry (Department) of Agriculture
Level of Government: State Government
Reason: Agriculture is listed in the State List and falls under the jurisdiction of the State Government. Therefore, the news concerns the State Agriculture Department.
 Q5: While appointing the Prime Minister, the President selects
Q5: While appointing the Prime Minister, the President selects
(a) Leader of the largest party in the Lok Sabha
(b) Leader of the largest party in the alliance, which secures a majority in the Lok Sabha
(c) The leader of the largest party in the Rajya Sabha
(d) Leader of the alliance or party that has the support of the majority in the Lok Sabha
Ans: (d)
Leader of the alliance or party that has the support of the majority in the Lok Sabha.
Q6: Read this discussion and say which of these statements applies most to India.
Alok: The Prime Minister is like a king; he decides everything in our country.
Shekhar: The Prime Minister is only 'first among equals', he does not have any special powers. All ministers and the PM have similar powers.
Bobby: The Prime Minister has to consider the expectations of the party members and other supporters of the government. But after all, the Prime Minister has a greater say in policy-making and in choosing the ministers.
Ans:
The statement of Bobby applies most to India.
- In India, the Prime Minister is the head of the government but functions within a parliamentary system, making him “first among equals” in the Council of Ministers.
- The Prime Minister leads policy-making, coordinates government work, and advises the President on ministerial appointments, giving him more influence than other ministers.
- At the same time, the Prime Minister must consider the views of party members, allies, and Parliament, thereby not acting as an absolute ruler.
Q7: Why do you think the advice of the Council of Ministers is binding on the President? Give your answer in not more than 100 words.
Ans:
The advice of the Council of Ministers is binding on the President because:
- The President is the formal head of state in a parliamentary democracy.
- Article 74(1) mandates a Council of Ministers headed by the Prime Minister to aid and advise the President.
- The President is constitutionally required to act according to the aid and advice of the Council.
- This ensures that the elected government governs, while the President acts as a constitutional head, safeguarding democratic governance.
Q8: The parliamentary system of executive vests many powers in the legislature for controlling the executive. Why, do you think, is it so necessary to control the executive?
Ans:
- In a parliamentary system, the Prime Minister is the head of the government, while the President is the nominal head.
- The executive is accountable to Parliament and continues to hold office only as long as it enjoys its confidence.
- Control over the executive is necessary to ensure it remains sensitive to public expectations and accountable to democratic needs and aspirations.
Q9: It is said that there is too much political interference in the working of the administrative machinery. It is suggested that there should be more and more autonomous agencies which do not have to answer to the ministers.
(a) Do you think this will make the administration more people-friendly?
Ans: No. Removing political accountability can make administration arbitrary and less responsive to the people, as it may lack proper checks and citizen oversight.
(b) Do you think this will make administration more efficient?
Ans: No. Autonomous agencies may not align with elected government policies, creating conflicts that compromise efficiency and social welfare goals.
(c) Does democracy mean full control of elected representatives over the administration?
Ans: No. Democracy requires elected representatives to oversee and hold administration accountable, but administration needs a degree of autonomy to perform specialised functions effectively.
Q10: Write an essay of two hundred words on the proposal to have an elected administration instead of an appointed administration.
Ans:
Essay: Proposal for an Elected Administration
The idea of having an elected administration instead of an appointed one suggests that officials should be directly chosen by the people. Proponents argue this would increase accountability and responsiveness to public needs, enabling citizens to influence decisions more directly and ensuring policies better reflect public opinion.
However, administration requires specialised skills, training, and experience to implement laws and policies efficiently. Elected officials may lack this expertise and could prioritise short-term popularity over long-term planning, risking inefficiency and poor governance.
Currently, India has an appointed administration where trained bureaucrats manage daily affairs impartially. Elected representatives guide and oversee the administration, ensuring accountability while allowing professionals to perform the specialised functions.
In conclusion, while an elected administration may seem more democratic, India requires a balance between elected leaders and a professionally appointed administration to ensure both effective governance and accountability.
|
151 videos|780 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Political Science - Executive
| 1. What is NCERT? |  |
| 2. What are NCERT solutions? |  |
| 3. Are NCERT solutions enough for exam preparation? |  |
| 4. Are NCERT solutions available for all classes and subjects? |  |
| 5. How can I get NCERT solutions for free? |  |

















