NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Political Science - Federalism
Q1: From the list of following events which ones would you identify with the functioning of federalism? Why?
- The Centre on Tuesday announced Sixth Schedule status to GNLF-led Darjeeling Gorkha Hill Council, which would ensure greater autonomy to the governing body in the Hill district of West Bengal. A tripartite Memorandum of Settlement was signed in New Delhi between the Centre, West Bengal government and the Subhas Ghising-led Gorkha National Liberation Front (GNLF) after two days of hectic deliberations.
- Government for action plan for rain-hit States: Centre has asked the rain-ravaged States to submit detailed plans for reconstruction to enable it to respond to their demands for extra relief expeditiously.
- New Commissioner for Delhi: The Capital is getting a new municipal commissioner. Confirming this, present MCD Commissioner Rakesh Mehta said he has received his transfer orders and that he is likely to be replaced by IAS officer Ashok Kumar, who is serving as the Chief Secretary in Arunachal Pradesh. Mehta, a 1975 batch IAS officer, has been heading the MCD for about three-and-a-half years.
- CU Status for Manipur University: Rajya Sabha on Wednesday passed a Bill to convert the Manipur University into a Central University with the Human Resource Development Minister promising such institutions in the North Eastern States of Arunachal Pradesh, Tripura and Sikkim as well.
- Funds released: The Centre has released Rs. 553 lakh to Arunachal Pradesh under its rural water supply scheme. The first instalment was of Rs. 466.81 lakh.
- We'll teach the Biharis how to live in Mumbai: Around 100 Shiv Sainiks stormed J. J. Hospital, disrupted daily operations, raised slogans and threatened to take matters into their own hands if no action was taken against non-Maharashtrian students.
- Demand for dismissal of Government: The Congress Legislature Party (CLP) in a representation submitted to State Governor recently, has demanded dismissal of the ruling Democratic Alliance of Nagaland (DAN) government for its alleged financial mismanagement and embezzlement of public money.
- NDA government asks naxalites to surrender arms: Amid a walkout by opposition RJD and its allies Congress and CPI (M), the Bihar government today appealed to the naxalites to shun the path of violence and reaffirmed its pledge to root out unemployment to usher in a new era of development in Bihar.
Ans:
- Yes, the agreement between the centre, state government and the GNLF involves the functioning of a federal structure as it allows autonomy in governance at the state and provincial level.
- Yes, it involves the functioning of federalism because flood relief is undertaken by the states while being funded by the centre.
- No, it does not involve the functioning of federalism because this appointment reflects a centralised authority.
- No, it does not reflect a federal structure as a centralised university comes under the control of the central government.
- Yes, it involves the functioning of federalism as the centre is providing funds to the state of Arunachal Pradesh under its rural water supply scheme. The state can then make use of the funds for its own development.
- No, it does not involve the functioning of federalism because it is hampering the essence of federalism. The states have autonomy but they are tied in the bond fibered by the central power and are bound to work according to the instructions of the central government as it is superior to the state. This act of Shiv Sena is violation of citizen's rights as well as spirit of federalism.
- No, it does not involve the functioning of federalism as demand for the dismissal of a duly elected state government is an attack on the federal structure.
- Yes, it involves the functioning of federalism as the problem of naxalism is being tackled by government at state level.
Q2: Think which of the following statements would be correct. State why.
- Federalism enhances the possibility of people from different regions to interact without the fear of one's culture being imposed upon them by others.
- Federal system will hinder easier economic transaction between two different regions that have distinct types of resources.
- A federal system will ensure that the powers of those at the centre will remain limited.
Ans:
- Federalism enhances interaction: This statement is correct. It allows people from different regions to interact freely without the fear of cultural imposition.
- Federal system hinders trade: This statement is incorrect. A federal system does not obstruct economic transactions between regions with different resources.
- Central powers are limited: This statement is partially correct. While a federal system aims to limit central powers, in India, it also allows for a strong central government.

Q3: Based on the first few articles of Belgian constitution - given below - explain how federalism is visualised in that country. Try and write a similar Article for the Constitution of India.
Title I: On Federal Belgium, its components and its territory.
Article 1 : Belgium is a Federal State made up of communities and regions.
Article 2 : Belgium is made up of three communities: The French Community, the Flemish Community and the German Community.
Article 3 : Belgium is made up of three regions: The Walloon region, the Flemish region and the Brussels region.
Article 4 : Belgium has four linguistic regions: The French-speaking region, the Dutch-speaking region, the bilingual region of Brussels Capital and the German-speaking region. Each «commune» (county borough) of the Kingdom is part of one of these linguistic regions.
Article 5 : The Walloon region is made up of the following provinces: The Walloon Brabant, Hainault, Liege, Luxemburg and Namur. The Flemish region is made up of the following provinces: Antwerp, the Flemish Brabant, West Flanders, East Flanders and Limburg.
Ans:
The federal structure of Belgium is based upon communities, regions and languages. There are three communities and regions and four linguistic regions in the country.
Title I: On Federal India, its components and its territory.
Article 1 : India is a Federal State made up of communities and regions.
Article 2 : India has more than 20 major languages and several hundred minor languages.
Article 3 : India has many religions.
Article 4 : India is divided into 28 states and 7 union territories.
Article 5 : India has two separate levels of government, one at the centre and another at the state level. The power of the central government is greater than that of the state government.
Article 6: India has a judiciary that is the most powerful and independent.
Q4: Imagine that you were to rewrite the provisions regarding federalism. Write an essay of not more than 300 words making your suggestions about:
(a) division of powers among the centre and the States,
(b) distribution of financial resources,
(c) methods of resolving inter-State disputes and
(d) appointment of Governors
Ans:
Federalism is an institutional mechanism to accommodate two sets of politics one-at the national level and the other at the regional level:
(a) Division of powers:
- The powers are distributed between the central government and the state governments.
- The constitution demarcates the subjects clearly in the lists.
- The disputes are settled by the judiciary.
- The economic and the financial powers have been centralised to the central government.
(b) Distribution of financial resources:
- Some certain taxes are levelled by the center but are collected by the states, i.e. stamp duty and the taxes on production of medicines and cosmetic preparations.
- Some certain taxes are levied and collected by the center and are distributed among the states, i.e. succession of property other than agricultural land, terminal taxes on goods and passengers carried by railway, sea and air, taxes on railways freights and fare, taxes on newspaper, etc.
- The taxes which are levied and collected by the center but are distributed between the center and the states, i.e. income tax on the income other than agricultural land on the recommendation of the finance commission.
- Bihar, Odisha, West Bengal and Assam have been given grants in lieu of export duty on jute and jute products.
(c) Methods of resolving inter-state dispute:
- An inter-state committee can be established by the Parliament if it thinks it to be fit.
- This committee enquirers into the dispute and submits its report and recommendations to the Parliament.
Example:
- Haryana and Punjab dispute on Chandigarh
- Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat have dispute over sharing of water of Narmada river.
(d) Appointment of Governors:
- The Governors of the states are appointed by the President of India on the advice of Council of Ministers at center.
- He enjoys the power to remove them also.
- Hence, the Governors work as the representatives of the central Government in the state who inform the center about the condition of the states if required.
Q5: Which of the following should be the basis for formation of a State? Why?
(a) Common Language
(b) Common economic interests
(c) Common religion
(d) Administrative convenience
Ans: (d)
Administrative convenience should be the basis for forming a state because it enhances the administration and welfare of the citizens in that area. This approach can lead to:
- Economic development and the growth of a common economy.
- Better management of resources and services for the population.
Forming a state based on factors like language, economic interests, or religion is not advisable because:
- People with similar economic or religious backgrounds are often dispersed across different regions, making administration challenging.
- Language has previously been used as a basis for state formation, but cases like Andhra Pradesh and Telangana show that it does not guarantee stability.
- Conflicts can arise when states are formed on insufficient grounds.
Q6: Majority of people from the States of north India-Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar - speak Hindi. If all these States are combined to form one State, would it be in tune with the idea of federalism? Give arguments.
Ans: Federalism is a system that allows for two levels of government: one at the national level and another at the regional level. If the Hindi-speaking states of Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, and Bihar were merged into a single state, it could challenge the principles of federalism. Here are some key points to consider:
- The merger would create a unitary system rather than a federal one.
- It would centralise power, reducing the autonomy of regional governments.
- Federalism thrives on diversity and local governance, which would be compromised.
- Such a change could lead to conflicts over cultural and linguistic identities.
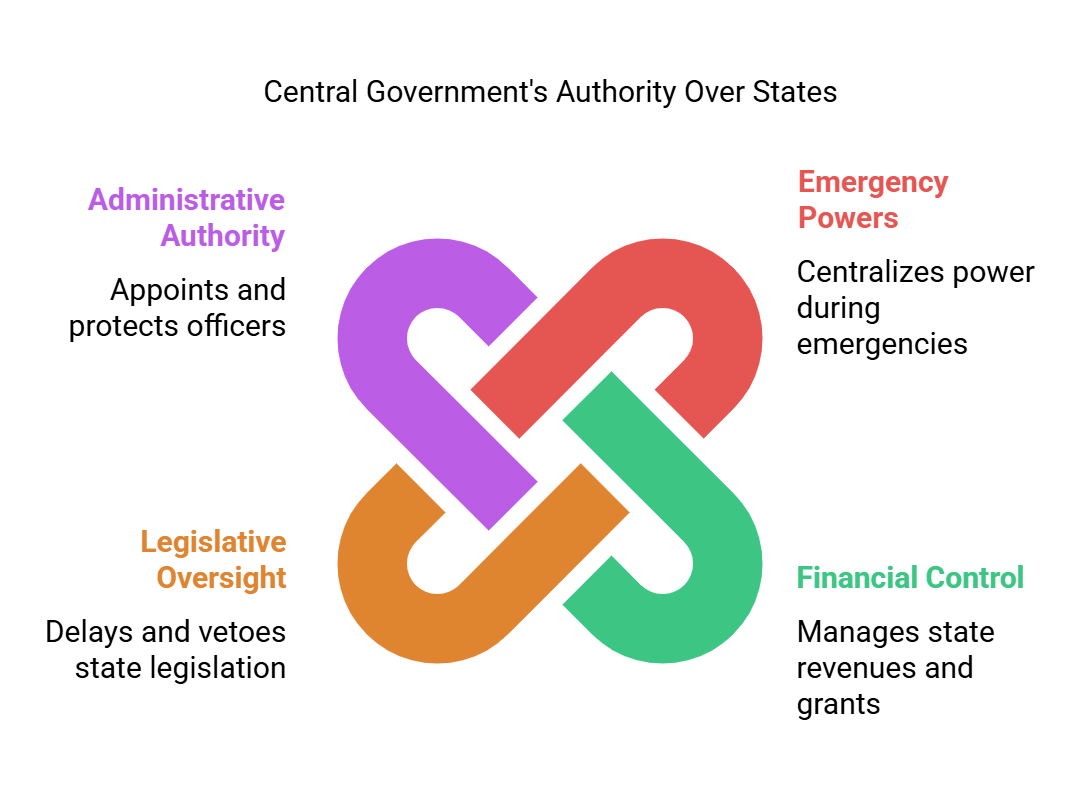
Q7: List four features of the Indian Constitution that give greater power to the central government than the State government.
Ans: The Indian Constitution contains several features that grant greater power to the central government compared to state governments. Here are four key features:
- Emergency Powers: During an emergency, power is lawfully centralised, allowing the central government to legislate on state matters.
- Financial Control: The central government controls revenue-generating items, making states reliant on grants and financial assistance.
- Legislative Oversight: The central government can delay state legislation and veto bills passed by state legislatures.
- Administrative Authority: The central government appoints administrative officers, and states cannot take disciplinary action against them.
Q8: Why are many States unhappy about the role of the Governor?
Ans: Many states are unhappy about the role of the Governor for several reasons:
- The Governor is appointed by the central government, not elected by the people.
- This appointment can lead to the Governor being seen as a tool for controlling or removing the state government.
- The Governor has the authority to suspend the elected state government and dissolve the legislative assembly.
- They can also reserve bills passed by the state for the President's assent, which can delay or block state legislation.
- When different parties govern at the central and state levels, the Governor's role can become even more contentious.
Q9: President's rule can be imposed in a State if the government is not being run according to the provisions of the Constitution. State whether any of the following conditions are a fit case for imposition of President's rule in the State. Give reasons.
- Two members of the State legislative assembly belonging to the main opposition party have been killed by criminals and the opposition is demanding dismissal of the State government.
- Kidnapping of young children for ransom is on rise. The number of crimes against women are increasing.
- No political party has secured majority in the recent elections of the State Legislative Assembly. It is feared that some MLAs from the other parties may be lured to support a political party in return for money.
- Different political parties are ruling in the State and at the centre and they are bitter opponents of each other.
- More than 2000 people have been killed in the communal riots.
- In the water dispute between the two States, one State government refused to follow the decision of the Supreme Court.
Ans:
- No. Killing of two members of the State legislative assembly belonging to the main opposition party by the criminals is not the basis for removal of the state government as it is a law and order problem.
- No. Rise in kidnapping of young children for ransom and the number of crimes against women is a law and order problem but does not represent a breakdown of the Constitution.
- No. President's rule cannot be imposed in a state without giving the largest political party or alliance a chance to prove their majority on the floor of legislative assembly.
- No. Ruling of two opponent and different political parties at the State and at the centre is not a criterion for implementing President's rule.
- Yes. If the state is inefficient to control the riots then President's Rule needs to be implemented as it represents a complete failure of the administration.
- Yes. If one state has refused to follow the decision of Supreme Court then it is a case of breakdown of constitutional order and fit for imposition of President's rule.
Q10: What are the demands raised by States in their quest for greater autonomy?
Ans: There are four demands raised by States in their quest for greater autonomy that are as follows:
- Separation of Powers: States like Tamil Nadu, West Bengal, and Punjab seek more significant powers to be assigned to them, reducing central control.
- Financial Autonomy: States demand independent revenue sources and greater control over their resources.
- Administrative Autonomy: There is a call for the central government to relinquish control over state administrative machinery.
- Cultural and Linguistic Rights: Some states advocate for autonomy based on their unique languages and cultures, resisting the dominance of Hindi.
Q11: Should some states be governed by special provisions? Does this create resentment among other States? Does this help in forging greater unity among the regions of the country?
Ans: It is essential that some states should be governed by the special provisions on the basis of historical, cultural and social circumstances and administrative requirements. The north-eastern states, Jammu & Kashmir, the hilly state of Himachal Pradesh and some other states like Andhra Pradesh, Goa, Gujarat, Maharashtra and Sikkim are governed by special provisions. The special provisions are made according to the special requirements. For example, the north-eastern states of India have a unique history and tribal culture that needs to be protected.
This has created resentment among other states as there is a fear that these provisions would lead to separation in those areas.
Many people oppose these provisions because they believe that there should be equal division of powers in federal state.
No, this does not forge greater unity among the regions of the country as it leads to a feeling of bias.
|
142 videos|779 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Political Science - Federalism
| 1. What is federalism and how does it function in India? |  |
| 2. What are the key features of federalism? |  |
| 3. How does the division of powers work in Indian federalism? |  |
| 4. What challenges does federalism face in India? |  |
| 5. How does federalism promote unity in diversity in India? |  |

















