NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics Chapter 4 - Globalisation and the Indian Economy
| Table of contents |

|
| Page - 57 |

|
| Page - 59 |

|
| Page - 61 |

|
| Page - 62 |

|
| Page - 64 |

|
| Page - 66 |

|
| Page - 67 |

|
| Page - 68 |

|
| Page - 70 |

|
| Page - 72 |

|
| Page - 73 |

|
Page - 57
Q1: Complete the following statement to show how the production process in the garment industry is spread across countries:
The brand tag says ‘Made in Thailand’ but they are not Thai products. We dissect the manufacturing process and look for the best solution at each step. We are doing it globally. In making garments, the company may, for example, get cotton fibre from Korea, ........
Ans: The tag says ‘Made in Thailand,’ but the products are made from parts and services sourced worldwide. For example, cotton might come from Korea, dyeing from India, design from Italy, sewing from Bangladesh, and final assembly in Thailand. This global approach helps the company save costs and use the best skills from each country, creating high-quality, affordable garments by combining different inputs from around the world. dability. Cotton fiber
Cotton fiber
Page - 59
Q1: Would you say Ford Motors is a MNC? Why?
Ans: Yes, Ford Motors is a multinational corporation (MNC) because it operates in 26 countries worldwide, including India. It engages in significant international trade and investment, indicating its multinational presence.
Q2: What is foreign investment? How much did Ford Motors invest in India?
Ans: Foreign investment refers to investments made by companies or individuals from one country in businesses or assets located in another country. Ford Motors invested Rs. 1700 crore in India to establish a large production plant near Chennai in collaboration with Mahindra and Mahindra.
Q3: By setting up their production plants in India, MNCs such as Ford Motors tap the advantage not only of the large markets that countries such as India provide, but also the lower costs of production. Explain the statement.
Ans: Setting up production plants in countries like India allows MNCs to access large domestic markets with growing consumer demand. Moreover, these countries often offer lower production costs due to factors such as lower labor costs, favorable government policies, and availability of raw materials. This combination of market access and cost advantages helps MNCs like Ford Motors enhance their global competitiveness and profitability.
Q4: Why do you think the company wants to develop India as a base for manufacturing car components for its global operations? Discuss the following factors:
(a) cost of labour and other resources in India
(b) the presence of several local manufacturers who supply auto parts to Ford Motors
(c) closeness to a large number of buyers in India and China
Ans: (a) India offers relatively lower labor costs compared to developed countries, which reduces overall production costs for Ford Motors.
(b) India has a well-established network of suppliers for auto parts, ensuring a stable and efficient supply chain for Ford Motors' manufacturing operations.
(c) Establishing manufacturing in India allows Ford Motors to be closer to two of the world's largest automotive markets, facilitating faster delivery and response times to market demands.
Q5: In what ways will the production of cars by Ford Motors in India lead to interlinking of production?
Ans: The production of cars by Ford Motors in India will lead to interlinking of production by creating demand for local suppliers to provide various components and materials, integrating with Ford Motors' global supply chain, and fostering technology transfer and knowledge exchange between its global operations and Indian facilities.
Q6: In what ways is an MNC different from other companies?
Ans: A multinational corporation (MNC) operates in multiple countries and manages production or service facilities outside its home country. It engages in significant international trade, investment, and has a global presence compared to domestic companies that operate within a single country or region.
Q7: Nearly all major multinationals are American, Japanese or European, such as Nike, Coca-Cola, Pepsi, Honda, Nokia. Can you guess why?
Ans: Big companies from the United States, Japan, and Europe have an advantage because they have a long history of being large and globally ambitious. They also have access to advanced technology, strong research capabilities, skilled workers, supportive government policies, and established international networks that help them expand and operate around the world.
 Multinational Company
Multinational Company
Page - 61
Q1: What was the main channel connecting countries in the past? How is it different now?
Ans: In the past, the main channel connecting countries for trade was primarily through maritime routes and overland trade routes such as the Silk Road. These routes facilitated the exchange of goods and ideas between different civilizations.
Today, the main channels connecting countries include not only maritime and overland routes but also air transport, digital communication networks, and sophisticated logistics systems. Globalization and advancements in technology have significantly increased the speed, volume, and complexity of international trade and communication compared to historical methods.
Q2: Distinguish between foreign trade and foreign investment.
Ans:
- Foreign trade refers to the exchange of goods and services across international borders. It involves importing and exporting products between countries to meet consumer demands or access resources not locally available.
- Foreign investment involves investments made by individuals, businesses, or governments from one country into assets or businesses located in another country. This can include investments in physical assets (like factories or real estate), financial assets (like stocks or bonds), or the establishment of new businesses or subsidiaries abroad.
Q3: In recent years China has been importing steel from India. Explain how the import of steel by China will affect:
(a) steel companies in China.
(b) steel companies in India.
(c) industries buying steel for production of other industrial goods in China.
Ans: (a) Steel companies in China may face reduced domestic demand or competition from cheaper imports, potentially leading to lower prices and profit margins. They may need to adjust their production levels or focus on higher value-added products to remain competitive.
(b) Steel companies in India will benefit from increased export opportunities, leading to higher production levels and potentially better economies of scale. This could improve profitability and investment in modernizing production facilities.
(c) Industries in China that buy steel for producing other industrial goods may benefit from lower input costs if imported steel from India is cheaper or of better quality. This can enhance their competitiveness in both domestic and international markets.
Q4: How will the import of steel from India into the Chinese markets lead to integration of markets for steel in the two countries? Explain.
Ans: The import of steel from India into China will lead to integration of steel markets in both countries in several ways:
- It will create a direct link between Indian steel producers and Chinese consumers, fostering ongoing trade relationships and market interactions.
- Indian steel exporters will need to meet Chinese quality standards and market demands, leading to mutual adaptation and cooperation between industries in both countries.
- This integration can lead to price harmonization and information exchange between steel markets in India and China, enhancing market efficiency and transparency.
Over time, it may encourage joint ventures, partnerships, or even investments by Indian companies in China's steel sector, further solidifying the interdependence of the two markets. Steel
Steel
Page - 62
Q1: What is the role of MNCs in the globalization process?
Ans: Multinational corporations (MNCs) play a significant role in globalization by:
- Facilitating the movement of goods, services, technology, and capital across borders.
- Creating employment opportunities and transferring skills and knowledge to local economies.
- Introducing advanced technologies and management practices that enhance productivity.
- Connecting markets globally, thereby increasing trade and economic interdependence among countries.
Q2: What are the various ways in which countries can be linked?
Ans: Countries can be linked through various means including:
- Trade linkages: Exchanging goods and services through imports and exports.
- Financial linkages: Investments, loans, and financial flows between countries.
- Technological linkages: Sharing and adopting technologies, research, and development.
- Cultural linkages: Exchanging cultural practices, values, and ideas.
- Political linkages: Diplomatic relations, treaties, and international organizations.
Q3: Choose the correct option.
Globalization, by connecting countries, shall result in
(a) lesser competition among producers.
(b) greater competition among producers.
(c) no change in competition among producers.
Ans: (b) greater competition among producers.
Globalization connects countries and markets, leading to increased competition among producers as they face competition not only from domestic firms but also from international ones.
Page - 64
Q1: What do you understand by liberalisation of foreign trade?
Ans: Liberalization of foreign trade means reducing or eliminating barriers like tariffs and quotas to promote free exchange of goods and services between countries, aiming to boost economic growth and efficiency.
Q2: Tax on imports is one type of trade barrier. The government could also place a limit on the number of goods that can be imported. This is known as quotas. Can you explain, using the example of Chinese toys, how quotas can be used as trade barriers? Do you think this should be used? Discuss.
Ans: Quotas restrict the quantity of imported goods, like Chinese toys, into a country. They protect domestic industries but can raise prices for consumers and reduce choice. Their use depends on balancing domestic industry protection with consumer interests and international relations.
Page - 66
Q1: Fill in the blanks.
WTO was started at the initiative of developed countries. The aim of the WTO is to facilitate international trade and resolve trade disputes. WTO establishes rules regarding trade tariffs, quotas, and trade-related policies for all countries, and sees that member countries follow these rules and engage in fair trade practices. In practice, trade between countries is not always fair due to varying levels of protectionism and subsidies. Developing countries like India have been pressured to liberalize their economies, whereas developed countries, in many cases, have continued to provide protection to their producers.
Q2: What do you think can be done so that trade between countries is more fair?
Ans: To make trade fairer between countries, we should work on reducing trade barriers like tariffs and quotas that put some countries at a disadvantage. Also, having clear and enforceable rules through international agreements, like those from the WTO, can help promote fair competition and prevent unfair trade practices.
Q3: In the above example, we saw that the US government gives massive sums of money to farmers for production. At times, governments also give support to promote production of certain types of goods, such as those which are environmentally friendly. Discuss whether these are fair or not.
Ans: Government subsidies can disrupt international trade by giving local producers an unfair edge over foreign competitors, often leading to dumping of cheap, subsidized goods in global markets, which hurts producers in other countries. While this is generally seen as unfair, subsidies that support environmentally friendly production can be justified, as they help address global goals like sustainability and climate protection. Finding the right balance between these factors is key to ensuring fairness in international trade.  US Government
US Government
Page - 67
Q1: How has competition benefited people in India?
Ans: Competition has helped people in India by boosting innovation, improving product quality, and lowering prices. It has increased consumer choices, leading to better goods and services. Competition also pushes businesses to be more efficient, which can result in higher wages and better working conditions for workers.
Q2: Should more Indian companies emerge as MNCs? How would it benefit the people in the country?
Ans: Yes, more Indian companies becoming MNCs can benefit the country in several ways. It can lead to increased employment opportunities, technology transfer, and skill development. MNCs can also contribute to the economy through foreign exchange earnings and infrastructure development. Moreover, Indian MNCs can enhance the country's global influence and competitiveness.
Q3: Why do governments try to attract more foreign investment?
Ans: Governments try to attract foreign investment to boost economic growth, create jobs, and improve infrastructure. Foreign investment brings in money, technology, and management skills that can help local industries grow and become more productive. It also strengthens trade relations with other countries and increases foreign exchange reserves.
Q4: In Chapter 1, we saw what may be development for one may be destructive for others. The setting of SEZs has been opposed by some people in India. Find out who are these people and why are they opposing it.
Ans: Opposition to Special Economic Zones (SEZs) in India often comes from local communities, environmental activists, and farmers. They are concerned about land acquisition, displacement, environmental damage, and loss of farmland. Critics argue that SEZs focus on industrial and commercial interests over social and environmental needs, leading to inequalities and negative effects on marginalized groups.
Page - 68
Q1: What are the ways in which Ravi’s small production unit was affected by rising competition?
Ans: Ravi's unit faced lower sales and profits due to cheaper imports, forcing him to improve quality and efficiency to stay competitive.
Q2: Should producers such as Ravi stop production because their cost of production is higher compared to producers in other countries? What do you think?
Ans: No, Ravi should focus on improving efficiency and quality to compete effectively rather than stopping production.
Q3: Recent studies point out that small producers in India need three things to compete better in the market:
(a) better roads, power, water, raw materials, marketing and information network
(b) improvements and modernisation of technology
(c) timely availability of credit at reasonable interest rates.
Ans:
(a) Can you explain how these three things would help Indian producers?
Ans: These improvements would lower costs, enhance quality, and expand market reach for Indian producers, making them more competitive.
(b) Do you think MNCs will be interested in investing in these? Why?
Ans: Yes, MNCs may invest in these areas to reduce costs, improve efficiencies, and access skilled labor, aligning with their expansion strategies in emerging markets like India.
(c) Do you think the government has a role in making these facilities available? Why?
Ans: Yes, the government's role is crucial in providing infrastructure, technology support, and affordable credit to create a conducive business environment and attract investments.
(d) Can you think of any other step that the government could take? Discuss.
Ans: The government could focus on skills development, promote research and development, simplify regulations, and reduce bureaucratic hurdles to further support small producers and enhance their competitiveness.
Page - 70
Q1: In what ways has competition affected workers, Indian exporters, and foreign MNCs in the garment industry?
Ans: Workers face job insecurity and wage pressure. Indian exporters must meet higher standards at lower costs. Foreign MNCs streamline operations for profitability.
Q2: What can be done so that workers get a fair share of globalization's benefits?
Ans:
- Government: Enforce labor laws, ensure fair wages, and safe conditions.
- Employers: Pay fair wages, improve working conditions, and provide training.
- MNCs: Uphold ethical labor practices, offer career growth opportunities.
- Workers: Join unions, seek skill development, advocate for rights.
Q3: One of the present debates in India is whether companies should have flexible policies for employment. Based on what you have read in the chapter, summarise the point of view of the employers and workers.
Ans: Employers view flexibility as enhancing productivity and adaptability. Workers fear job insecurity and prefer stable employment with benefits.
Page - 72
Q1: What do you understand by globalisation? Explain in your own words.
Ans: Globalisation is the process where economies, cultures, societies, and communication become more connected and integrated worldwide. It involves the flow of goods, services, ideas, information, and people across borders, making national boundaries less important in how the world functions.
Globalisation is like when your favorite food or music from another part of the world becomes popular in your own country. It's when people, ideas, products, and information from one place easily travel and connect with people in other places around the world.
Imagine you have a smartphone. The parts for it may come from different countries, it might be designed in one country, and then you can use apps from all over the world. That's globalization in action.
Q2: What were the reasons for putting barriers to foreign trade and foreign investment by the Indian government? Why did it wish to remove these barriers?
Ans:
(A) Foreign Trade
- The government had put restrictions on the import of goods to protect domestic producers from foreign competition.
- The government allowed imports of only essential items such as machinery, fertilisers and petroleum. These restrictions helped to attain technological capability within the country.
(B) Foreign Investment
- Starting around 1991, the government wished to remove the barriers because India had attained technological capability.
- The government decided that the time had come for Indian producers to compete with producers around the globe.
- It felt that competition would improve the performance of producers within the country.
- There would be an unrestricted exchange of capital, technology and experience between India and other countries of the world.
Q3: How would flexibility in labour laws help companies?
Ans:
- Instead of hiring workers on a regular basis, companies can hire workers, ‘flexibly’ for short periods during the period of intense work.
- This will reduce the cost of labour.
- The company can negotiate wages and terminate workers depending on market conditions.
Q4: What are the various ways in which MNCs set up, or control, production in other countries?
Ans: The factories or production units of Multinational Companies are set up mainly close to the markets where they can get the desired skilled or unskilled labour at low cost along with other factors of production. After the company has been set up, they set production units in the following ways:
Form a company jointly with some local companies of the existing country.
• Buy the local companies and then expand its production with the help of modern technology.
• The order is placed by them for small producers to sell these products under their own brand name to the customers worldwide.
Q5: Why do developed countries want developing countries to liberalise their trade and investment? What do you think should the developing countries demand in return?
Ans:
(a) The developed countries want developing countries to liberalise their trade and investment so that they may sell their products in those countries to earn profit. Generally, developed countries produce goods/products at a very low cost and sell at a very higher price.
(b)
- The developed countries are biased against the developing countries. They have been following wrong practices as is the case in the agriculture sector in the USA.
- In view of the above facts, the developing countries should demand fair trade practices to be followed by the developed countries.
- They should stop giving subsidies to their agricultural sector.
- Trade barriers put unfairly should be removed.
- Only then there would be a free and fair trade in the world and the interest of the developing countries would be protected.
Q6: “The impact of globalisation has not been uniform.” Explain this statement.
Ans: 
(a) Positive impact:
- It has resulted in more choice for the consumers to get various products of better quality and at lower prices.
- It has improved the standard of living.
- With the investments by the MNCs new jobs have been created in the developing countries.
- New technology has been introduced.
- Large companies have become multi-national companies such as Infosys.
(b) Negative impact:
- The creation of special economic zones has disrupted the lives of the people who have been displaced.
- Flexibility in labour laws has worsened the condition of workers who may be appointed on a temporary basis.
- Small producers are unable to compete with MNCs. Thus, several units have been shut down rendering many workers jobless.
Q7: How has the liberalisation of trade and investment policies helped the globalisation process?
Ans:
- Goods can now be imported and exported easily.
- Companies can set up factories and offices in other countries. For example, Ford Motors, a U.S. company set up a plant in India in 1995 in Chennai.
- Activities of many MNCs have increased foreign investment and foreign trade which has led to greater integration of production and markets across countries or globalisation process.
- Thus, more and more countries are coming closer contacts and liberalisation of trade and investment policies have helped in the globalisation process.
Q8: How does foreign trade lead to the integration of markets across countries? Explain with an example other than those given here.
Ans:

- It creates an opportunity for producers to reach beyond the domestic market, i.e., markets of their own countries.
- Producers can sell their products in the markets of their own country as well as in other countries of all over the world.
- The buyers too have a choice between the goods produced in different parts of the world. It enables the consumer to buy according to his requirement.
- The competition among the producers brings them closer to each other.
- Producers in two countries closely compete against each other even though they are separated by thousands of miles.
Q9: Globalisation will continue in the future. Can you imagine what the world would be like twenty years from now? Give reasons for your answer.
Ans: After twenty years, the world would undergo a positive change and enhanced human resource efficiency which will possess the following features- healthy competition, improved production efficiency, increased volume of output, income and employment better living standards, greater availability of information and modern technology. The reasons for this view include:
- With the development of human resources as well as technological advancements, the small producers will be in a better position to compete with the foreign competition.
- Growing entrepreneurship worldwide, especially in developing countries, acts as an incentive for producers to collaborate and take advantage of global networks.
- Growing domestic market means higher demand for domestic goods as well as imports.
Q10: Supposing you find two people arguing: One is saying globalisation has hurt our country’s development. The other is telling, globalisation is helping India develop. How would you respond to these organisations?
Ans: Following are the benefits of globalisation in India:
• There is an increase in the volume of trade in goods and services.
• It has led to the rise of a quality product.
• There is an inflow of private foreign capital and export orientation of the economy.
• There is an increase in the volume of output, income and employment.
Though there are also some negative impacts of globalisation. They are as follows:
• It might not help in achieving sustainable growth.
• It might not lead to a lessening of income inequalities among various countries.
• It might lead to aggravation of income inequalities within countries.
Q11: Fill in the blanks.
Indian buyers have a greater choice of goods than they did two decades back. This is closely associated with the process of ______________. Markets in India are selling goods produced in many other countries. This means there is increasing ______________ with other countries. Moreover, the rising number of brands that we see in the markets might be produced by MNCs in India. MNCs are investing in India because _____________. While consumers have more choices in the market, the effect of rising _______________ and ______________has meant greater ________________among the producers.
Ans: Indian buyers have a greater choice of goods than they did two decades back. This is closely associated with the process of globalisation. Markets in India are selling goods produced in many other countries. This means there is increasing trade with other countries.
Moreover, the rising number of brands that we see in the markets might be produced by MNCs in India. MNCs are investing in India because of cheaper production costs. While consumers have more choices in the market, the effect of rising demand and purchasing power has meant greater competition among the producers.
Q12: Match the following.
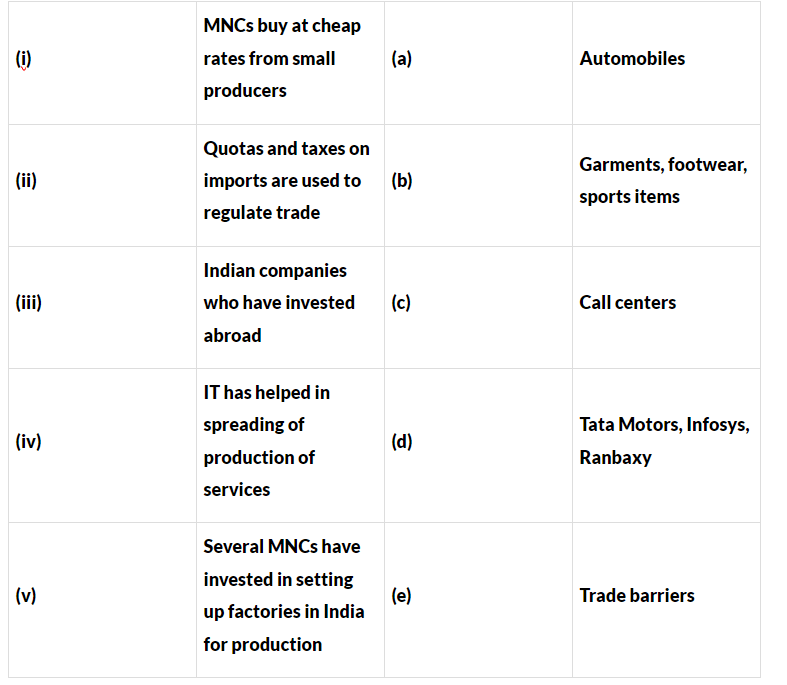
Ans: 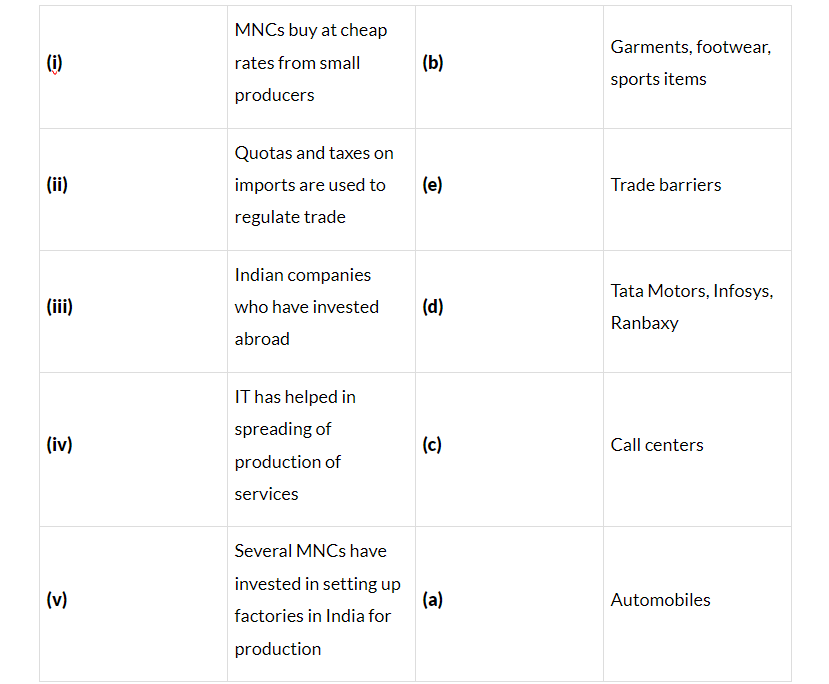
Page - 73
Q13: Choose the most appropriate option.
(i) The past two decades of globalisation has seen rapid movements in
(a) goods, services and people between countries.
(b) goods, services and investments between countries.
(c) goods, investments and people between countries.
Ans: (i) (b)
In the past two decades, globalization has led to increased movement of goods, services, and investments across countries. This has expanded international trade, enhanced access to various services, and allowed for greater foreign investment, driving economic growth and global interconnectedness.
(ii) The most common route for investments by MNCs in countries around the world is to
(a) set up new factories.
(b) buy existing local companies.
(c) form partnerships with local companies.
Ans: (ii) (b)
The most common route for investments by multinational corporations (MNCs) is to buy existing local companies. This approach allows MNCs to quickly gain access to established markets, resources, and local expertise.
(iii) Globalisation has led to improvement in living conditions
(a) of all the people
(b) of people in the developed countries
(c) of workers in the developing countries
(d) none of the above
Ans: (iii) (d)
While globalisation has improved living standards in some developed countries through increased access to goods and economic growth, its effects in developing countries are more complex. Some individuals benefit from new opportunities, while others face job insecurity and inequality. The uneven distribution of globalization's benefits means that its impact on living conditions is not uniformly positive for all groups or regions.
|
66 videos|614 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics Chapter 4 - Globalisation and the Indian Economy
| 1. What is globalization and how does it affect the Indian economy? |  |
| 2. What are the positive impacts of globalization on India? |  |
| 3. What are the negative consequences of globalization for the Indian economy? |  |
| 4. How has globalization influenced employment patterns in India? |  |
| 5. What role does the government play in managing globalization in the Indian economy? |  |





















