Reproduction in Organisms (Old NCERT) NCERT Solutions | Biology Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
Q.1. Why is reproduction essential for organisms?
Ans. Reproduction is a fundamental feature of all living organisms. It is a biological process through which living organisms produce offspring similar to them. Reproduction ensures the continuance of various species on the Earth. In the absence of reproduction, the species will not be able to exist for a long time and may soon get extinct.
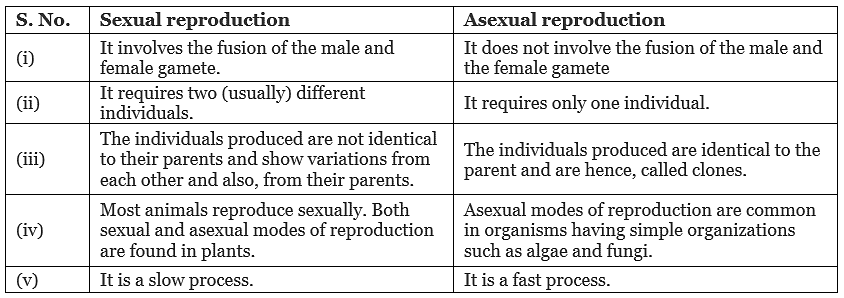
Ans. Sexual reproduction is a better mode of reproduction. It allows the formation of new variants by the combination of the DNA from two different individuals, typically one of each sex.
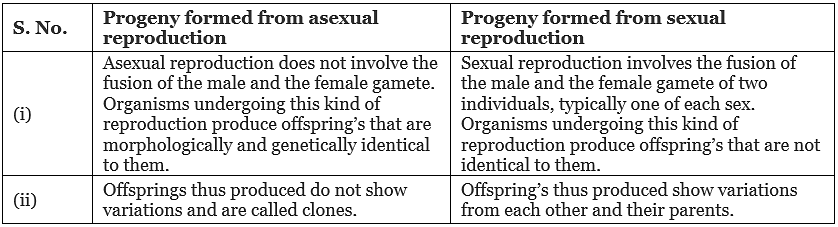
Ans. A clone is a group of morphologically and genetically identical individuals.
In the process of asexual reproduction, only one parent is involved and there is no fusion of the male and the female gamete. As a result, the offsprings so produced are morphologically and genetically similar to their parents and are thus, called clones.
Ans.
- Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of the male and the female gamete. This fusion allows the formation of new variants by the combination of the DNA from two (usually) different members of the species.
- The variations allow individuals to adapt under varied environmental conditions for better chances of survival. However, it is not always necessary that the offspring produced due to sexual reproduction has better chances of survival.
- Under some circumstances, asexual reproduction is more advantageous for certain organisms.
Example: Some individuals who do not move from one place to another and are well settled in their environment. - Also, asexual reproduction is a fast and quick mode of reproduction that does not consume much time and energy as compared to sexual reproduction.
Ans.
Ans.
Vegetative propagation is a process in which new plants are obtained without the production of seeds or spores. It involves the propagation of plants through certain vegetative parts such as the rhizome, sucker, tuber, bulb, etc.
It does not involve the fusion of the male and the female gamete and requires only one parent. Hence, vegetative reproduction is considered as a type of asexual reproduction.
Ans. Vegetative propagation is a mode of asexual reproduction in which new plants are obtained from the vegetative parts of plants. It does not involve the production of seeds or spores for the propagation of new plants.
Vegetative parts of plants such as runners, rhizomes, suckers, tubers, etc. can be used as propagules for raising new plants.
Examples of vegetative reproduction are:
- Eyes of potato: The surface of the potato has several buds called eyes. Each of these buds when buried in soil, develops into a new plant, which is identical to the parent plant.
 Eyes of Potato
Eyes of Potato- Leaf buds of Bryophyllum: The leaves of Bryophyllum plants bear several adventitious buds on their margins. These leaf buds have the ability to grow and develop into tiny plants when the leaves get detached from the plant and come in contact with moist soil.
 Bryophyllum PlantQ.8. Define:
Bryophyllum PlantQ.8. Define:(a) Juvenile Phase
(b) Reproductive Phase
(c) Senescent Phase
Ans.
(a) Juvenile phase: It is the period of growth in an individual organism after its birth and before it reaches reproductive maturity.
(b) Reproductive phase: It is the period when an individual organism reproduces sexually.
(c) Senescent phase: It is the period when an organism grows old and loses the ability to reproduce.
Ans. Although sexual reproduction involves more time and energy, higher organisms have resorted to sexual reproduction in spite of its complexity.
- This is because this mode of reproduction helps introduce new variations in progenies through the combination of the DNA from two (usually) different individuals.
- These variations allow the individual to cope with various environmental conditions and thus, make the organism better suited for the environment. Variations also lead to the evolution of better organisms and therefore, provide better chances of survival.
- On the other hand, asexual reproduction does not provide genetic differences in the individuals produced.
Ans.
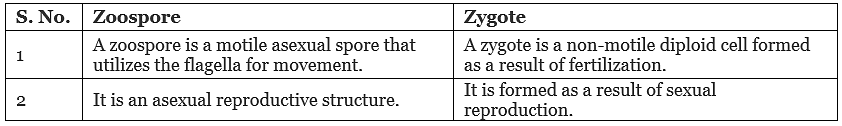
- Meiosis is a process of reductional division in which the amount of genetic material is reduced.
- Gametogenesis is the process of the formation of gametes. Gametes produced by organisms are haploids (containing only one set of chromosomes), while the body of an organism is diploid.
Therefore, for producing haploid gametes (gametogenesis), the germ cells of an organism undergo meiosis. During the process, the meiocytes of an organism undergo two successive nuclear and cell divisions with a single cycle of DNA replication to form the haploid gametes.
Ans.
Ans. External fertilization is the process in which the fusion of the male and the female gamete takes place outside the female body in an external medium, generally water. Fish, frog, starfish are some organisms that exhibit external fertilization.
Disadvantages of external fertilization:
- A large quantity of gametes is wasted and left unfertilized.
- Chances of fertilization are diminished by environmental hazards and Predators.
- Eggs and sperms, essentially, may not come in contact.
- Dessication of zygote or gametes.
Ans.
Ans.

Ans.
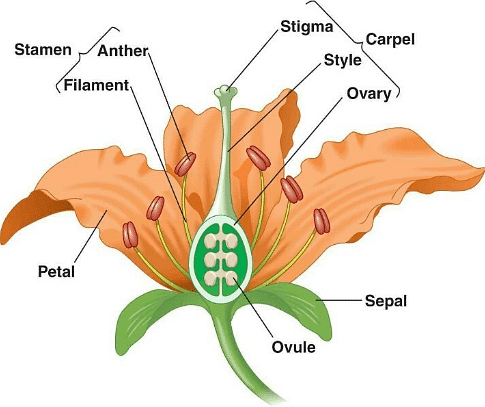
- Fertilization is the process of the fusion of the male and the female gamete to form a diploid zygote.
- After fertilization, the zygote divides several times to form an embryo. The fertilized ovule forms a seed. The seed contains an embryo, enclosed in a protective covering, called the seed coat.
- As the seed grows further, other floral parts wither and fall off. This leads to the growth of the ovary, which enlarges and ripens to become a fruit with a thick wall called the pericarp.
Ans. A flower that contains both the male and female reproductive structure (stamen and pistil) is called a bisexual flower.
Examples of plants bearing bisexual flowers are:
- Water lily (Nymphaea odorata)
- Rose (Rosa multiflora )
- Hibiscus (Hibiscus Rosa-Sinensis)
- Mustard ( Brassica nigra)
- Petunia (Petunia hybrida)
 Structure of Bisexual Flower
Structure of Bisexual Flower
Q.17. Examine a few flowers of any cucurbit plant and try to identify the staminate and pistillate flowers. Do you know any other plant that bears unisexual flowers?
Ans. Cucurbit plant bears unisexual flowers as these flowers have either the stamen or the pistil. The staminate flowers bear bright, yellow coloured petals along with stamens that represent the male reproductive structure. On the other hand, the pistillate flowers bear only the pistil that represents the female reproductive structure. Cucurbit Plant
Cucurbit Plant
Q.18. Why are the offspring of oviparous animals at a greater risk as compared to offspring of viviparous animals?
Ans.
- Oviparous animals lay eggs outside their body. As a result, the eggs of these animals are under continuous threat from various environmental factors.
- On the other hand, in viviparous animals, the development of the egg takes place inside the body of the female.
|
86 videos|294 docs|184 tests
|
FAQs on Reproduction in Organisms (Old NCERT) NCERT Solutions - Biology Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is reproduction in organisms? |  |
| 2. What are the different modes of reproduction in organisms? |  |
| 3. What is the importance of reproduction in organisms? |  |
| 4. What is the role of hormones in reproduction? |  |
| 5. How is reproduction in organisms affected by environmental factors? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|