
Q1. Mention different aspects of life in which women are discriminated or disadvantaged in India.
Ans: The different aspects of life in which women are discriminated or disadvantaged in India are:
a) Education: Education is one of the most important factors in which women are discriminated in our country. In India, the literacy rate of women is still lower than men. If we check the facts, there are only 54% of women who are literate against 76% literacy among men.
b) Proportion of women in paid jobs: The proportion of women still has small share in the highly paid jobs. Women are much harder workers than men, even though on average an Indian woman works one hour more than an average man every day, but still work of women does not get that much importance, due to which they have to work for low-paid jobs.
c) Preference for a male child: In India, the mentality of many still has not changed. They still prefer sons over daughters and find ways of aborting a girl child. This abortion has led to a decline in the child sex ratio.
d) Crime against women: Women in our country are not safe. The crime rate against women is very high. Women get exploited and harassed at the workplace and also at their homes.
Different forms of communal politics:
a) The most common expression of communalism is in everyday beliefs. Belief in the superiority of one’s religion over other religions is so common.
Example: Militant religious groups
b) A communal mind often leads to a quest for political dominance of the religious community. For those belonging to a community, it can take the form of a desire to form a separate political unit.
Example: Separatist leaders and political parties in Jammu and Kashmir
c) The most frequent form of communalism is political mobilisation on religious guidelines. It attempts to bring the people of one’s religion together.
Example: Many politicians use this technique to influence the voters from the two largest religious communities in the country.
d) Communalism can be ugliest if it takes the shape of communal violence, riots and massacres.
Example: India and Pakistan communal riots
Q3. State how caste inequalities are continuing in India.
Ans: Caste inequalities are continuing in India in the following ways:
- Most people still marry within their own caste or tribe, and inter-caste marriages are often discouraged, especially by upper castes.
- Despite being banned by the Constitution, untouchability persists, particularly in rural areas.
- Groups with historical access to education continue to excel, while those previously excluded still lag.
- Caste contributes to economic inequality, as it affects access to resources. Upper castes are best off, Dalits and Adivasis are worst off, with the backwards classes in between.
- Although every caste has some poor members, the proportion of people living in extreme poverty is much higher for the lowest castes. Lower caste people, like rural landless labourers, are generally poor and are exploited even today. The percentage of the population living below the poverty line between 1999-2000 was 45.8% (STs) 35.9%, (SCs) and 27% (OBCs) in the rural areas.

Q4. State two reasons to say that caste alone cannot determine election results in India.
Ans: Two reasons to say that caste alone cannot determine election results in India are:
(i) In our country, no parliamentary constituency has a clear majority of a single caste. So every candidate and party tries to win the confidence of more than one caste and community. If these parties and the candidate win the confidence of people belonging to various castes, then it is easy for them to win the elections.
(ii) It is also true that no party wins the votes of all the voters of a caste or community. Many political leaders and people refer to a caste as a ‘vote bank’ of one party. This simply means that people from that particular caste or community will vote in a large proportion for that party or that particular candidate.
Q5. What is the status of women’s representation in India’s legislative bodies?
Ans: The status of women’s representation in India’s legislative bodies is very less as mentioned below:
- In the Lok Sabha, the percentage of elected women members has never reached even 10% of its total strength.
- Their share in the state assemblies is less than 5%. India is among the bottom group of nations in the world in this respect.
- Thus, the proportion of women in legislative bodies has been very low. Women’s organisations and activists have been demanding reservation of at least one-third of seats in the Lok Sabha and State Assemblies for women.
Q6. Mention any two constitutional provisions that make India a secular state.
Ans: Two constitutional provisions that make India a secular state are:
- The Constitution provides all individuals and communities freedom to profess, practice and propagate any religion, or not to follow any.
Another provision that is useful in making our country secular is that our constitution prohibits discrimination on the grounds of religion under the cultural and educational rights.
 Secular India
Secular India
Q7. When we speak of gender divisions, we usually refer to:
(a) Biological difference between men and women
(b) Unequal roles assigned by society to men and women
(c) Unequal child sex ratio
(d) Absence of voting rights for women in democracies
Ans: (b) Unequal roles assigned by society to men and women
Gender division means division of rights and work on the basis of gender. It means, men always are superior than women whether in the field of job, society or home. This is the poor thinking of our society which leads in social inequalities in the society. Gender division also leads to unequal assign of roles for men and women by the society.
Q8. In India, seats are reserved for women in
(a) Lok Sabha
(b) State Legislative Assemblies
(c) Cabinets
(d) Panchayati Raj bodies
Ans: (d) Panchayati Raj bodies
In India, seats are reserved for women in Panchayati Raj bodies as there is no reservation of seats for women in the cabinets, Lok Sabha and state legislatives assemblies.
 Panchayati Raj Bodies
Panchayati Raj Bodies
Q9. Consider the following statements on the meaning of communal politics. Communal politics is based on the belief that:
Α. One religion is superior to that of others.
Β. People belonging to different religions can live together happily as equal citizens.
C. Followers of a particular religion constitute one community.
D. State power cannot be used to establish the domination of one religious group over others.
Which of the statements is/are correct?
(a) A, B, C and D
(b) A, B and D
(c) A and C
(d) B and D
Ans: (c) A and C
Communal politics is based on the belief that one religion is superior to others and followers of a particular religion form one community. Statements Β and D represent principles of secularism and equal citizenship, which are contrary to communal politics.
Q10. Which among the following statements about India’s Constitution is wrong? It
(a) prohibits discrimination on grounds of religion
(b) gives official status to one religion
(c) provides to all individuals freedom to profess any religion
(d) ensures equality of citizens within religious communities
Ans: (b) gives official status to one religion
India’s Constitution does not give official status to any religion; it promotes secularism and prohibits discrimination based on religion.
Q11. Social divisions based on ______________ are peculiar to India.
Ans: Social divisions based on caste are peculiar to India.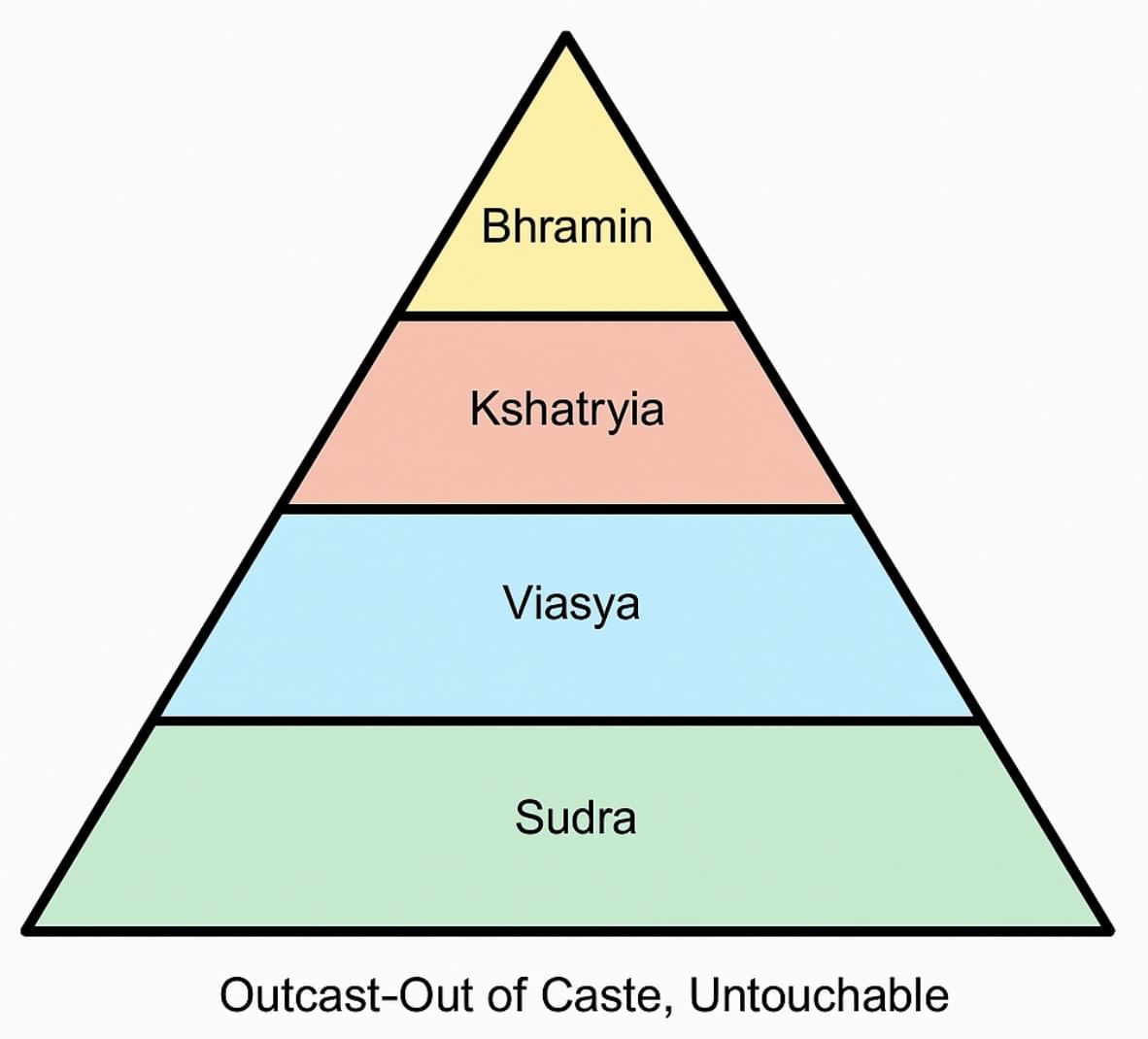
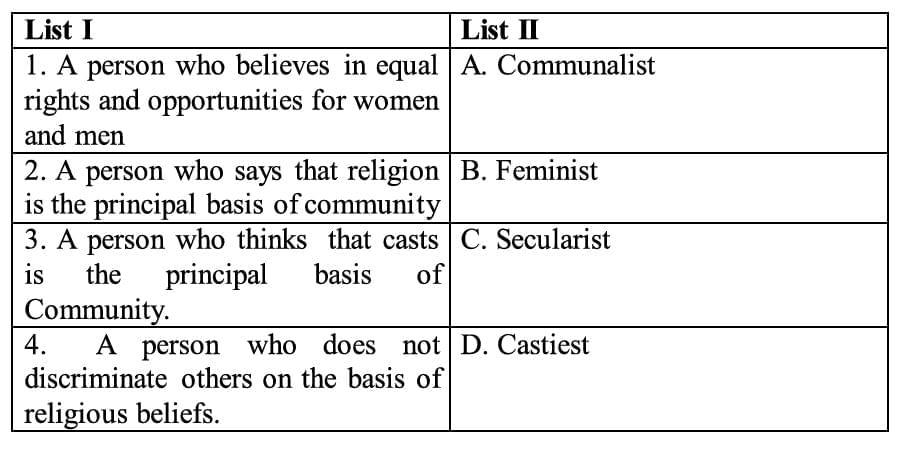
Q12. Match List I with List-II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the Lists:
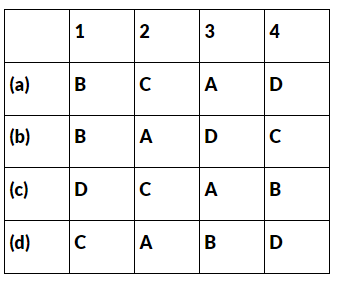
Ans: (b) B, A, D, C is the correct answer.
A person who believes in equal rights and opportunities for women and men: Feminist
A person who says that religion is the principal basis of community: Communalist
A person who thinks that castes is the principal basis of community: Castiest
A person who does not discriminate others on the basis of religious beliefs: Secularist


























