NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Geography - Composition and Structure of Atmosphere
Q1: Multiple choice questions.
(i) Which one of the following gases constitutes the major portion of the atmosphere?
(a) Oxygen
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Argon
(d) Carbon dioxide
Ans: (b)
(ii) Atmospheric layer important for human beings is:
(a) Stratosphere
(b) Mesosphere
(c) Troposphere
(d) Ionosphere
Ans: (c)
(iii) Sea salt, pollen, ash, smoke soot, fine soil — these are associated with:
(a) Gases
(b) Dust particles
(c) Water vapour
(d) Meteors
Ans: (b)
(iv) Oxygen gas is in negligible quantity at the height of atmosphere:
(a) 90 km
(b) 120 km
(c) 100 km
(d) 150 km
Ans: (b)
(v) Which one of the following gases is transparent to incoming solar radiation and opaque to outgoing terrestrial radiation?
(a) Oxygen
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Helium
(d) Carbon dioxide
Ans: (d)
Q2: Answer the following questions in about 30 words.
(i) What do you understand by atmosphere?
Ans: Atmosphere is a mixture of different gases and it envelopes the earth all round. It contains life-giving gases like oxygen for humans and animals and carbon dioxide for plants.
(ii) What are the elements of weather and climate?
Ans: The elements of weather and climate are temperature, pressure, winds, humidity, clouds and precipitation. These elements are subject to change and which influence human life on earth.
(iii) Describe the composition of atmosphere.
Ans: The atmosphere is composed of gases, water vapour and dust particles. Nitrogen constitutes 78.8%, oxygen constitutes 20.94% and argon constitutes 0.93%. Both gases together constitute 99% of the atmosphere. Other gases include are Carbon dioxide, Neon, Helium, Krypto, Xenon and Hydrogen.
(iv) Why is troposphere the most important of all the layers of the atmosphere?
Ans: Troposphere is the most important of all the layers of the atmosphere:
- All changes in climate and weather take place in this layer.
- This layer contains dust particles and water vapour
- All biological activities take place in this layer.
Q3: Answer the following questions in about 150 words.
(i) Describe the composition of the atmosphere.
Ans: The atmosphere is a mixture of gases, water vapour, and dust particles. Its main components include:
- Nitrogen: 78.8%
- Oxygen: 20.94%
- Argon: 0.93%
Other gases present are carbon dioxide, helium, ozone, methane, hydrogen, krypton, xenon, and neon. Notably:
- Nitrogen and oxygen together make up 99% of the atmosphere.
- Scarce gases include neon, krypton, and xenon.
As altitude increases, the composition changes:
- At 120 km, oxygen is nearly absent.
- Carbon dioxide and water vapour are found only up to 90 km above the Earth's surface.
Carbon dioxide is crucial for the greenhouse effect as it absorbs and reflects heat. Its levels have risen due to human activities, primarily the burning of fossil fuels.
(ii) Draw a suitable diagram for the structure of the atmosphere and label it and describe it.
Ans: The atmosphere consists of different layers with varying density and temperature. The column of atmosphere is divided into five different layers depending upon the temperature condition.
They are troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, and exosphere.
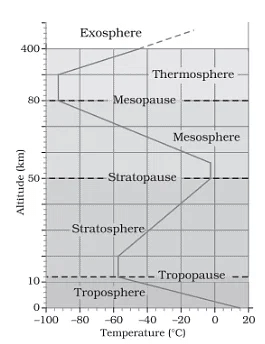
- Troposphere: The troposphere is the lowermost layer of the atmosphere. Its average height is 13 km and extends roughly to a height of 8 km near the poles and about 18 km at the equator. The thickness of the troposphere is greatest at the equator because heat is transported to great heights by strong convectional currents. This layer contains dust particles and water vapour. All changes in climate and weather take place in this layer. The temperature in this layer decreases at the rate of 1°C for every 165 m of height.
- Stratosphere: The stratosphere is found above the tropopause and extends up to a height of 50 km. One important feature of the stratosphere is that it contains the ozone layer. This layer absorbs ultra-violet radiation and shields life on the earth from an intense, harmful form of energy.
- Mesosphere: The mesosphere lies above the stratosphere, which extends up to a height of 80 km. In this layer, the temperature starts decreasing with the increase in altitude and reaches up to minus 100°C at the height of 80 km.
- Ionosphere: The ionosphere is located between 80 and 400 km above the mesopause. It contains electrically charged particles known as ions, and hence, it is known as the ionosphere. Radio waves transmitted from the earth are reflected back to the earth by this layer. Temperature here starts increasing with height.
- Exosphere: The uppermost layer of the atmosphere above the thermosphere is known as the exosphere. This is the highest layer but very little is known about it.
|
175 videos|624 docs|192 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Geography - Composition and Structure of Atmosphere
| 1. What are the main layers of the atmosphere and their characteristics? |  |
| 2. How does the composition of the atmosphere affect weather and climate? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the ozone layer in the stratosphere? |  |
| 4. What are the main greenhouse gases in the atmosphere? |  |
| 5. How does altitude affect temperature in different layers of the atmosphere? |  |






















