NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Political Science - Social Justice
Q1: What does it mean to give each person his/her due? How has the meaning of “giving each his due” changed over time?
Ans: Giving each person his/her due means ensuring that everyone receives what they deserve in terms of justice and well-being. Over time, this concept has evolved to focus on the inherent rights of individuals as human beings. Key points regarding this evolution include:
- The idea now emphasises dignity for all individuals.
- Philosopher Immanuel Kant argued that everyone should have the chance to develop their talents and pursue their goals.
- Justice requires equal consideration for all individuals.
Today, the principle of giving each person his/her due involves:
- Recognising equal rights, such as life, liberty, and property.
- Ensuring political rights, like the right to vote, to enable participation in governance.
- Providing social rights for equal opportunities.
Additionally, it is essential to avoid discrimination based on class, caste, race, or gender, and to judge individuals based on their actions and contributions.
Q2: Briefly discuss the three principles of justice outlined in the chapter. Explain each with examples.
Ans:
- Principle of treating equals equally: This principle asserts that individuals who share certain characteristics deserve equal rights and treatment. For example, everyone should have the right to life, liberty, and property, as well as political rights like the right to vote. This ensures that all individuals can participate in political processes.
- Principle against discrimination: No individual should be treated unfairly based on characteristics such as caste, race, or gender. For instance, if male teachers receive higher salaries than female teachers for performing the same tasks, this is unjust. Individuals should be evaluated based on their capabilities and contributions.
- Proportional justice: Equal treatment is not always just. In some cases, treating everyone the same can lead to unfair outcomes. For example, if all students receive the same marks for an exam regardless of their performance, it may be more equitable to award marks based on the quality of their answers and their effort. This principle suggests that justice involves rewarding individuals in proportion to their efforts and achievements.
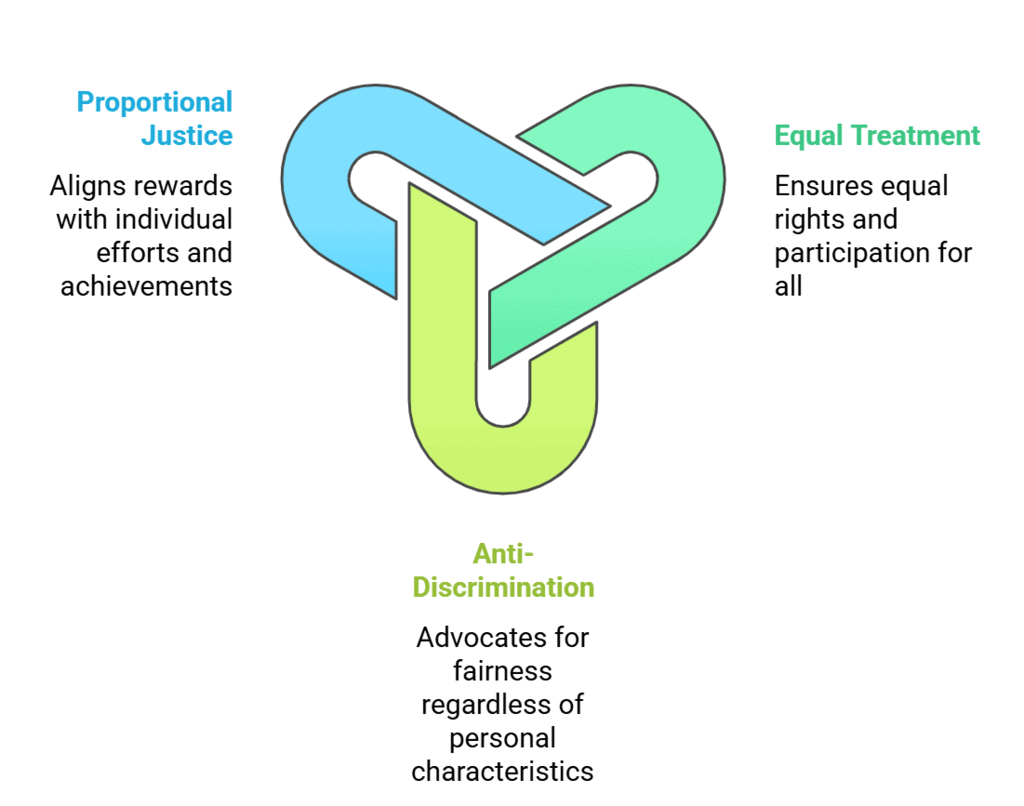
Q3 : Does the principle of considering the special needs of people conflict with the principle of equal treatment for all?
Ans:
- The principle of considering the special needs of people does not raise a conflict with the principle of equal treatment for all.
- People with special needs are given special treatment to facilitate their participation in the running of the society.
- People with special needs also require special treatment for integration with society and for securing opportunities and basic needs that would be otherwise denied to them.
- The senior citizens, women and socially backward people are given special treatment due to their special needs.
Q4: How does Rawls use the idea of a veil of ignorance to argue that fair and just distribution can be defended on rational grounds?
Ans:
- Rawls uses the idea of a veil of ignorance to argue that fair and just distribution can be defended on rational grounds.
- He says that if a person keeps herself/himself under the 'veil of ignorance' then s/he would come up with the just distribution, fair laws and policies that would affect the whole society.
- A person under the 'veil of ignorance' is unaware of her/his possible position and status in the society therefore s/he would rationally decide from the point of view of the worst-off.
- It would be sensible in this situation for everyone to ensure that all resources are available equally to all persons.
- In this way Rawls, with his idea of 'veil of ignorance', is able to prove that fair and just distribution can be defended on rational grounds with the help of this idea.
Q5: What are generally considered to be the basic minimum requirements of people for living a healthy and productive life? What is the responsibility of governments in trying to ensure this minimum to all?
Ans: Basic minimum requirements for a healthy and productive life include:
- Housing
- Access to clean water
- A basic amount of nourishment
- Education
- A minimum wage
The government has a crucial role in ensuring these essentials are available to everyone, regardless of their class, caste, race, or gender, and at a cost they can afford. There are differing views on how to achieve this:
- Supporters of the free market believe that private agencies should provide goods and services, with the government focusing on empowering people to purchase them. However, this often benefits the wealthy.
- The government must regulate private agencies to prevent them from making essential goods and services unaffordable for the less privileged.
Q6: Which of the following arguments could be used to justify state action to provide basic minimum conditions of life to all citizens?
(a) Providing free services to the poor and needy can be justified as an act of charity.
(b) Providing all citizens with a basic minimum standard of living is one way of ensuring equality of opportunity.
(c) Some people are naturally lazy and we should be kind to them.
(d) Ensuring basic facilities and a minimum standard of living to all is a recognition of our shared humanity and a human right.
Ans:
(a) Providing free services to the poor and needy as an act of charity is unjustified basis of state action to provide basic minimum conditions of life to all citizens. Services to the poor and needy are their rights and the government should not give these to them as charity.
(b) Providing all citizens with a basic minimum standard of living to ensure equality of opportunity is justified basis of state action to provide basic minimum conditions of life to all citizens. This is because it is the responsibility of the government to provide opportunities for citizens.
(c) Being kind to people who are lazy is not rational thinking as laziness is not a physical handicap. Therefore, it is an unjustified basis for state action to provide basic minimum conditions of life to all citizens.
(d) Ensuring basic facilities and a minimum standard of living to all as a recognition of our shared humanity and human rights is a justified basis of state action to provide basic minimum conditions of life to all citizens.
|
142 videos|779 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Political Science - Social Justice
| 1. What is the importance of social justice in society? |  |
| 2. How can individuals contribute to social justice movements? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of social justice issues? |  |
| 4. How does social justice relate to education? |  |
| 5. What role do governments play in promoting social justice? |  |






















