NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics - Introduction (Macroeconomics)
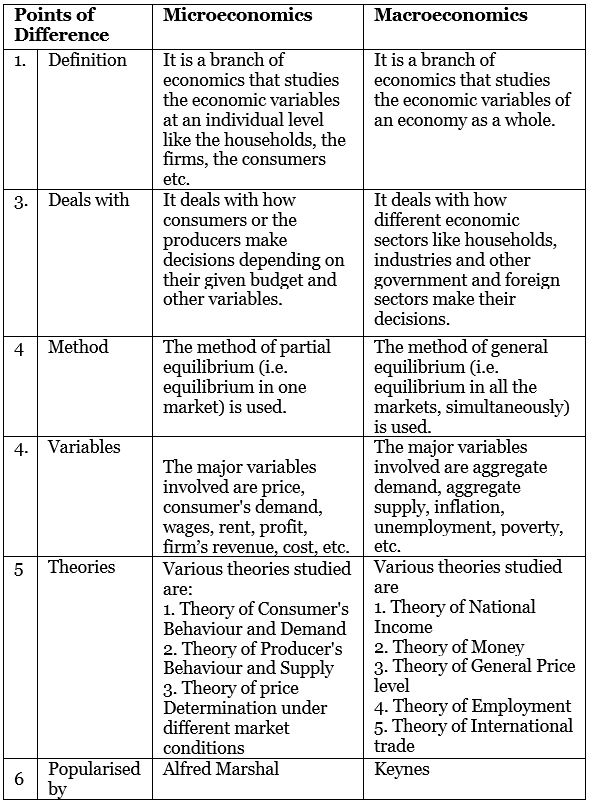
Q1: What is the difference between microeconomics and macroeconomics?
Ans:
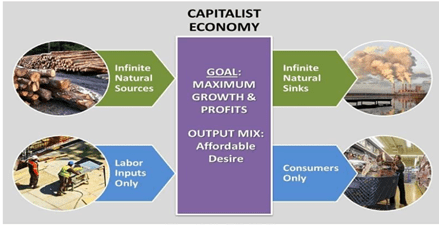
Q2: What are the important features of a capitalist economy?
Ans: The capitalist economy is an economic system where the means of production are privately owned. These means of production are driven by the motive of profit-making. This economic structure is also known as free market economy or laissez-faire.
The following are the features of a capitalist economy:
- Role of the government: The government provides the basic framework for the smooth functioning of an economy. It provides the basic framework and is responsible for the maintenance of law and order, justice, growth and stability, defence, etc.
- Profit motive: The economic agents are driven by the prime motive of profit maximization.
- Central problems: The central problems of an economy are solved by the market forces of demand and supply, i.e., the law of demand and supply operates here. The producers will supply only those goods and services that are demanded by the economy.
- Role of the private sector: The role of private individuals is more dominant. The main role of undertaking production and organising factors of production are played by private individuals and capitalists.
- Laissez-faire: This economy is also called `laissez faire’. It has minimum interference or restriction from the government.
Q3: Describe the four major sectors in an economy according to the macroeconomic point of view.
Ans: The four major sectors of an economy according to the macroeconomic point of view are:
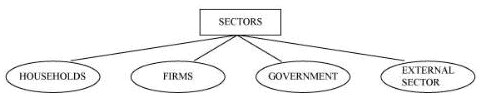
(i) Households: Households buy goods and services for consumption and also supply factors of production like land, labour, capital, and entrepreneurs. Households provide the market for the output of the firms.
(ii) Firms: Firms are economic units that carry out the production. They employ and organise factors of production and undertake production processes for the motive of profit-making.
(iii) Government: A state/government provides law and order, maintains growth and stability and provides administrative services. The main motive of a government is to undertake developmental projects such as dams, roads, and heavy industries that usually have long gestation periods. The government invests in the education, and health sector and provides these services at a nominal price. The motive of a government is to serve and not to make profits.
(iv) External sector: This sector is engaged in the export and import (external trade) of goods and services. If domestically produced goods and services are sold to the rest of the world, then it is called export. If the goods and services are purchased from the rest of the world, then it is called import.
Q4: Describe the Great Depression of 1929.
Ans: The Great Depression was a significant economic crisis that began in 1929 in the United States, following the stock market crash. It eventually affected many countries worldwide. Key points include:
- The crisis was primarily caused by a decline in demand due to underconsumption and overinvestment.
- As demand fell, finished goods accumulated, leading to lower prices and reduced profits.
- This resulted in a severe drop in employment, with the unemployment rate in the USA soaring from 3% to 25%.
- Consequently, income levels plummeted, further decreasing demand and production.
The Great Depression had profound implications for economics:
- It challenged the classical economic theories that relied on market forces.
- This crisis led to the rise of the Keynesian approach, which focused on the role of government intervention.
- It provided evidence for macroeconomics to emerge as a distinct field of study.
The cause-and-effect relationship of the Great Depression can be summarised as follows:
- Low demand → Overinvestment → Low employment → Low output → Low income → Low demand.
|
173 videos|487 docs|159 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics - Introduction (Macroeconomics)
| 1. What is the importance of studying macroeconomics? |  |
| 2. What are the key differences between microeconomics and macroeconomics? |  |
| 3. How does government intervention impact macroeconomic variables? |  |
| 4. What are the main goals of macroeconomic policy? |  |
| 5. How does international trade affect macroeconomics? |  |






















