NCERT Solutions for Class 6 History - Traders Kings and Pilgrims
Traders Kings And Pilgrims - Excercise
Let’s Recall
Ques 1. Match the following:
Muvendar | Mahayana Buddhism |
Lords of the dakshinapatha | Buddhacharita |
Ashvaghosha | Satavahana rulers |
Bodhisattvas | Chinese pilgrim |
Chinese pilgrim | Cholas, Cherasand Pandyas |
Ans:
Muvendar | Cholas, Cherasand Pandyas |
Lords of the dakshinapatha | Satavahana rulers |
Ashvaghosha | Buddhacharita |
Bodhisattvas | Mahayana Buddhism |
Chinese pilgrim | Chinese pilgrim |
Ques 2. Why did kings want to control the Silk Route?
Ans: The kings wanted to control the silk route because they believed that they would benefit from taxes, tributes and gifts that were brought by the traders travelling along the route.
Ques 3. What kinds of evidence do historians use to find out about trade and trade routes?
Ans: To find about trade and trade routes, historians use evidence present in the literature of the period like sangam poems and Sangam literature. Also, historians use objects like pottery, bowls and plates, found from several archaeological sites as evidence.
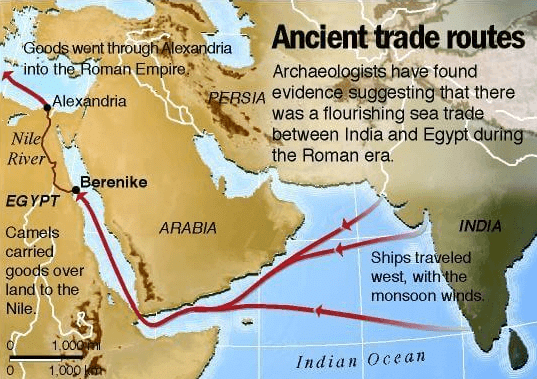
Fig: Trade and Trade Routes
South India was famous for gold, spices, especially pepper, and precious stones which were carried by ships, across the sea, and by land in caravans to Rome. Many Roman gold coins have been found in south India which proved the trade relations between ancient India and Rome.
Ques 4. What were the main features of Bhakti?
Ans: The main features of Bhakti were:
- It emphasised devotion and individual worship of a god or goddess, rather than the performance of elaborate sacrifices.
- According to system of belief, if a devotee worships the chosen deity with a pure heart, the deity will appear in the form in which he or she may desire.
- The deities were special, these images of the deity were often placed within special homes, places that we describe as temples.
Let’s Discuss
Ques 5. Discuss the reasons why the Chinese pilgrims came to India.
Ans: The Chinese pilgrims such as Fa Xian, Xuan Zang, I-Qing came to India to visit places associated with the life and teachings of the Buddha as well as famous monasteries.
Some like Xuan Zang spent time studying in Nalanda the most famous Buddhist monastery of the period.

Fig: Xuan Zang
Ques 6. Why do you think ordinary people were attracted to Bhakti?
Ans:
Ordinary people were attracted to Bhakti because anybody, whether rich or poor, belonging to the so-called ‘high’ or ‘low’ castes, man or woman, could follow the path of Bhakti.
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 6 History - Traders Kings and Pilgrims
| 1. Who were the traders, kings, and pilgrims mentioned in the chapter? |  |
| 2. What was the significance of the Silk Route in ancient times? |  |
| 3. What were the challenges faced by the traders and pilgrims during their journeys? |  |
| 4. How did the trade and commerce impact the society and economy in ancient times? |  |
| 5. What was the role of religion in the journeys of the pilgrims? |  |























