NCERT Summary: From Hunting-Gathering to Growing Food (Class 6) | History for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Human life has evolved over millions of years. In early stages, men were hunters and food gatherers.
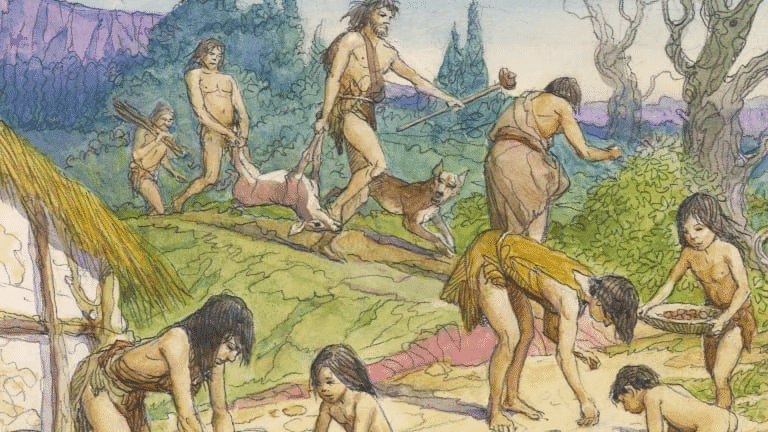 Hunters and food gatherers
Hunters and food gatherers
They hunted wild animals, fishes and gathered fruits, nuts and seeds.
The Earliest People: Why were they on the move?
- If they stayed in one place, resources like plants and animals would finish.
- Plants bear different fruits in different seasons. So, man too had to move in search of these, as per seasons.
- People had to move wherever water was available.
How do we know about these People?
- Archaeologists have found out several tools used by hunter-gatherers.
- Tools were made of stone, wood, etc.
- Tools were used to cut meat, chop fruits, etc.
- Wood was used to make huts and firewood.
Choosing a Place to Live In
- Early man lived near sources of water.
- They lived in places where stones were found and people made tools.
- The place was called factory site.
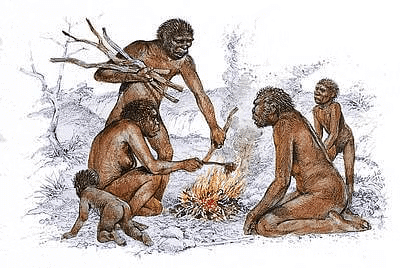 Early Man Life
Early Man Life
- The factory sites were found near discarded blocks of stone. These were known as habitation-cum-factory sites.
Rock Paintings and What they tell Us
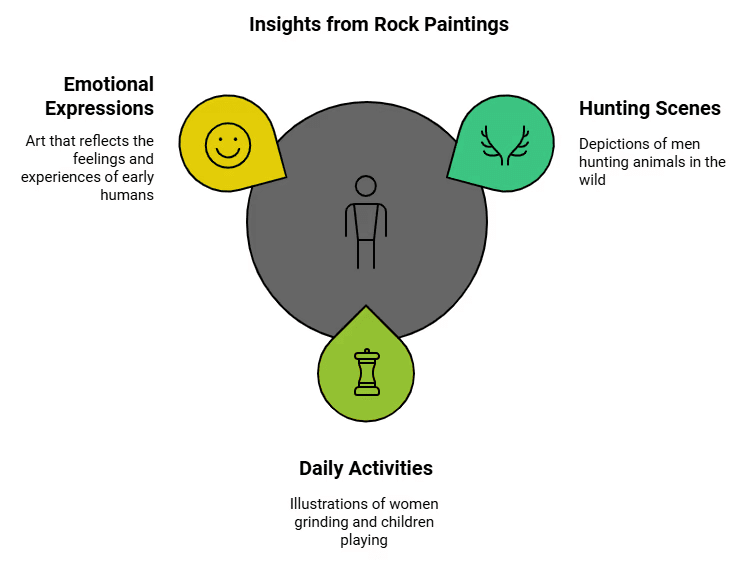
- Man early caves had paintings on the walls.
- These were found in M.P. and Southern U.P.
- Early man’s painted and what they felt in these paintings.
- They depicted men hunting, women grinding, children jumping, etc.
Sites
Sites are places where old objects like tools, pots, or buildings made and used by people in the past are found. These remains may be on the ground, underground, or underwater.
Finding out about the Fire
- Accidentally one of the biggest discoveries made by man was the fire.
- Over a period of time, man learnt several uses of fire.
- It was used in winters to keep warm and use it in the art of cooking food.
Names and dates
The Palaeolithic Age (Old Stone Age) lasted from about 2 million to 12,000 years ago.
- The name comes from Greek: palaeo (old) and lithos (stone).
- It is divided into Lower, Middle, and Upper Palaeolithic.
- This period covers 99% of human history.
The Mesolithic Age (Middle Stone Age) lasted from about 12,000 to 10,000 years ago.
- People used small stone tools called microliths.
- These were attached to handles of wood or bone to make tools like saws and sickles.
- Older tools were still used.
The Neolithic Age (New Stone Age) began around 10,000 years ago.
A Changing Environment
- The new stone age started a new era in history.
- After leading a nomadic life for many years, man around 10,000 years began to lead a settled life.
The Beginning of Farming and Herding
- As climate of the world changed man observed several things - areas where edible plants were found, how seeds broke off stalks, fell on the ground and how new plants sprouted from them.
- Man started cultivating crops.
- The first crops to be grown were cereal and barley.
- This is how by use of sickle men became food producers or farmers.
- Agriculture changed the life of man. They started leading a settled life.
Men as Herders:
- Humans even began to tame or domesticate animals like dog, horse, pig, goat, donkey, sheep, etc.
- The first animal to be tamed was dog.
- Animals provided milk, meat and even carried burden on their back.
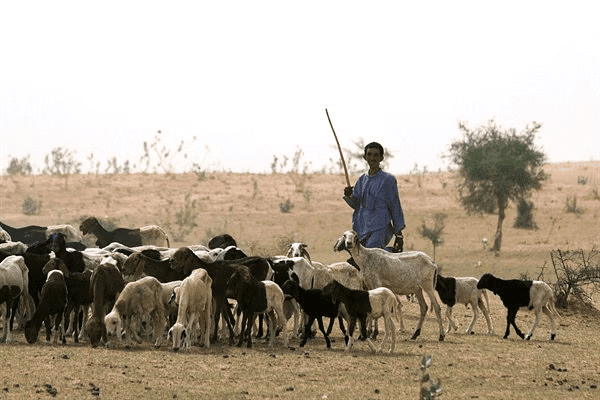 Men as herders
Men as herders
How do we know about Farmers and Herders:
- Archaeologists have found many traces of life of early farmers.
- Traces of farmers and herders were available through traces of pottery, pit houses, tools, paintings and daily life.
- Traces were found in Mehrgarh, Burzahom at North-Eastern parts of India etc.
Domestication is the process in which people grow plants and look after animals.
People choose plants and animals that are healthy and useful.
i) For plants: big grains, strong stalks, and no diseases.
ii) For animals: gentle and easy to manage.Over time, domesticated plants and animals became different from wild ones.
Example: Wild animals have bigger teeth and horns than domesticated ones.Domestication started about 12,000 years ago.
Most food we eat today comes from domesticated plants and animals.
Early domesticated plants: wheat and barley.
Early domesticated animals: sheep and goats.
A New Way of Life
People had to stay in the same place for a long time looking after the plants, watering, weeding, driving away animals and birds – till the grain ripened. Then they start thinking of storing the grain for food and seeds. They began making large clay pots, or wove baskets, or dug pits into the ground.
Storing animals
Animals that are reared can be used as a ‘store’ of food.
Towards a settled life
Archaeologists have found traces of huts or houses at some sites which shows that people have a stable life. 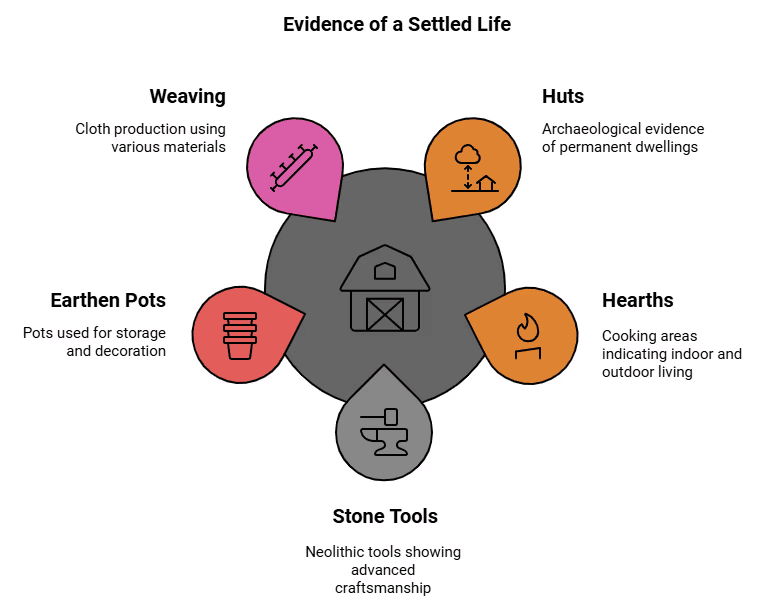
- They have also found cooking hearths both inside and outside the huts, which suggests that, depending on the weather, people used to cook food either indoors or outdoors.
- Stone tools have been found from many sites. Many of these are different from the earlier Palaeolithic tools and that is why they are called Neolithic. These include tools that were polished to give a fine cutting edge, and mortars and pestles. Mortars and pestles are used for grinding grain even today. Apart from these tools, some of the tools were also made of bone.
- Many kinds of earthen pots have also been found. These were used for decoration and for storing things.
- People also began weaving cloth, using different kinds of materials. For example: cotton.
The Chalcolithic Age:
- It was around 6,000 years back that man started using copper.
- Tools of copper were better than that of stone.
- It was also called the Copper Stone Age.
- It marked an important transition from use of stones to metals.
A closer look – Living and Dying in Mehrgarh
The North-West Mehrgarh:
- The earliest known civilization of the Indian subcontinent was in Mehrgarh (now Pakistan).
- It was here that man first tamed animals and reared them around 7,000 BC.
- Charred grains and bones of animals were found here.
- Glazed faience beads were made.
The North-East:
- Evidence of early settlements were found in Manipur, Tripura, Garo Hills.
- One important Neolithic site in Assam was Daojali Hading. Traces of polished stone tools, ceramics and kitchen items were found here.
|
216 videos|855 docs|219 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Summary: From Hunting-Gathering to Growing Food (Class 6) - History for UPSC CSE
| 1. Why were the earliest people on the move? |  |
| 2. How do we know about the earliest people? |  |
| 3. What factors did early humans consider when choosing a place to live? |  |
| 4. What do rock paintings tell us about early human life? |  |
| 5. How did the environment change and affect early human lifestyles? |  |






















