NCERT Summary: Heat | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Hot and Cold |

|
| Measuring Temperature |

|
| Clinical Thermometer |

|
| Laboratory Thermometers |

|
| Transfer of Heat |

|
| Kinds of Clothes We Wear in Summer and Winter |

|
Introduction
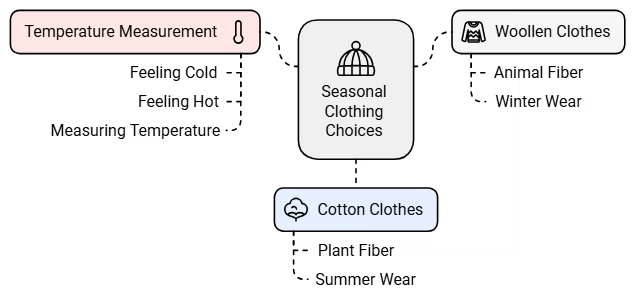
- We all know that woollen clothes come from animal fiber, and cotton clothes come from plant fiber.
- We wear woollen clothes in winter because they keep us warm, while in summer, we prefer light-colored cotton clothes because they help us stay cool.
- But have you ever wondered why certain clothes are better for certain seasons?
- In winter, you might feel cold inside your house, but stepping into the sunlight makes you feel warm.
- In summer, it can feel hot even when you're indoors.
- In this chapter, we'll explore how we can tell if something is hot or cold and how we measure temperature.

Hot and Cold
Have you ever experienced cold inside the house and warmth in the sun, during winter? Also, feeling hot inside as well as outside the house in the summer season?
To protect ourselves from the chilling cold, we wear clothes made of wool. These woolen clothes are obtained from wool-yielding animals such as sheep, goats, yack, etc. Wearing light-colored clothes during summer will give us a feeling of coolness.
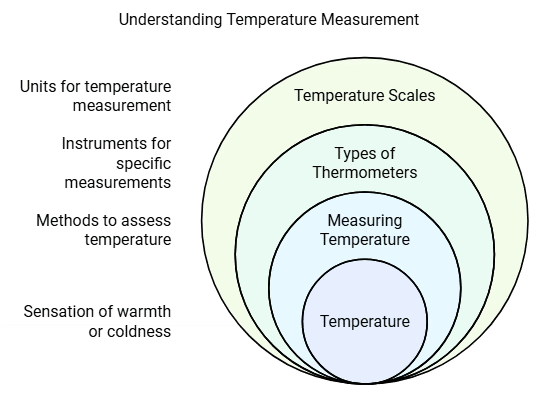
Temperature
- Temperature is a measure the sensation of warmth or coldness of an object, felt from contact with it.
- This sensation of touch gives an approximate or relative measure of the temperature.
- A thermometer is used to measure the temperature of an object - it is used to find how cold or hot the object is.
Measuring Temperature
- There are different types of thermometers that measure the temperatures of different things like air, our bodies, food and many other things.
- There are clinical thermometers, laboratory thermometers and digital thermometers.
- Temperature is measured in different scales, including Fahrenheit (F) and Celsius (or centigrade C).
- The units of the Fahrenheit and Celsius scales are called degrees and are denoted by °.
- He fixed the 0° of the scale at the freezing of water, and the 100° at the boiling of water.
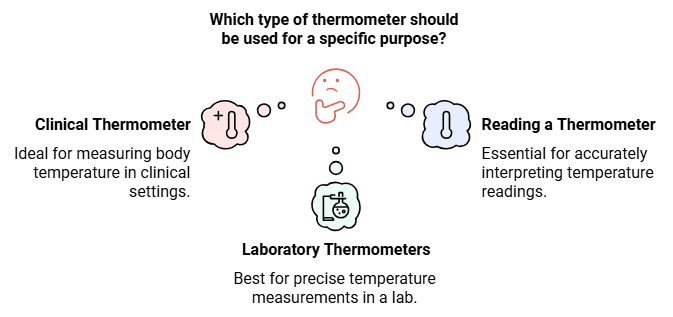
Clinical Thermometer

- These thermometers are used to measure the temperature of the human body, at home, clinics and hospitals.
- It has a kink that prevents the mercury from falling down rapidly so that the temperature can be noted conveniently.
- There are temperature scales on either side of the mercury thread, one in Celsius scale and the other in Fahrenheit scale.
- A clinical thermometer indicates temperatures 35° c to 45° c or from to 94° F to 108° F.
- Since the Fahrenheit scale is more sensitive than the Celsius scale, body temperature is measured in degrees Fahrenheit only.
- A healthy person's average body temperature is between 98.6° F to 98.8° F.
Precautions:
- See that the mercury levels are below the kink and don't hold the thermometer near its bulb.
- While noting down the reading in the thermometer, place the mercury level along the eyesight.
Reading a Thermometer
- Galileo invented a rudimentary water thermometer in 1593. He called this device a "thermoscope".
- However, this form was ineffective as water freezes at low temperatures.
- In 1714, Gabriel Fahrenheit invented the mercury thermometer, the modern thermometer.
- The long narrow uniform glass tube is called the stem of a thermometer.
- The small tube is called the bulb, which contains mercury.
- Mercury is toxic, and it is very difficult to dispose it when the thermometer breaks.
- So, nowadays digital thermometers are used to measure the temperature, as they do not contain mercury.
Laboratory Thermometers

- These thermometers are used to measure the temperature in school and other laboratories for scientific research.
- They are also used in the industry as they can measure temperatures higher than what clinical thermometers can record.
- The stem and the bulb are longer when compared to that of a clinical thermometer.
- A laboratory thermometer has only the Celsius scale ranging from -10° C to 110° C.
Precautions:
- Do not tilt the thermometer. Place it upright.
- Note the reading only when the bulb has been surrounded by the substance from all sides.
Relation between Celsius and Fahrenheit
The Celsius and Fahrenheit scales are related as: 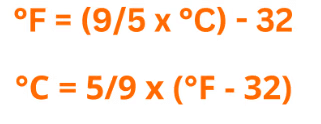 Where °C in temperature in Celsius and °F is temperature in Fahrenheit
Where °C in temperature in Celsius and °F is temperature in Fahrenheit
Transfer of Heat
- When an object is at a different temperature compared to its surroundings, heat transfer occurs until both the object and its surroundings reach the same temperature.
- Heat transfers occurs from hotter objects to colder objects.
- Also, heat from a hotter object is transferred to the particles of the surrounding air that are comparatively cooler.
- For example, when milk is boiled and the flame is off, the milk slowly transfers heat and becomes cooler.
There are three modes of heat exchange:
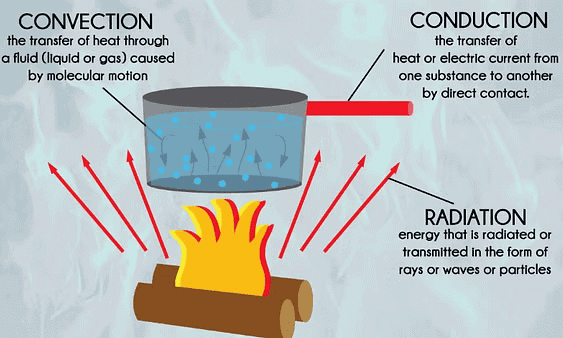
1. Conduction
- Conduction is the transfer of heat from the hotter part to the colder part of an object without the movement of its particles.
- Also, in conduction, heat gets transferred between substances that are in direct contact with each other.
- The better the conductor the more rapidly does the heat transfer take place.
- For example: when you pop corn in a cooker on a flame, heat is transferred from the flame to the corn by conduction.
 Conduction of heat by different materials
Conduction of heat by different materials
Conductors: Materials that allow the flow of heat are called conductors.
Examples: copper, steel, silver and iron.
Insulators: Materials that do not allow the flow of heat are called insulators.
Examples: wood, paper, rubber, cork, glass, Bakelite and ceramic.
2. Convection
- Convection is the transfer of heat by the movement of particles of a medium from one place to another. It takes place only in liquids and gases.
- Examples of convection are wind currents, the lower floor of a building is cooler than the upper floor, and water is warmer at the surface of a swimming pool or lake.
- Due to convection, the atmosphere at the seashore is always pleasant.
 Convection of heat in water
Convection of heat in water
Sea Breeze: A cool wind that blows from the sea towards the land during the day as the land heats up faster than the water.
Land Breeze: A cool wind that blows from the land towards the sea at night as the land cools down faster than the water.
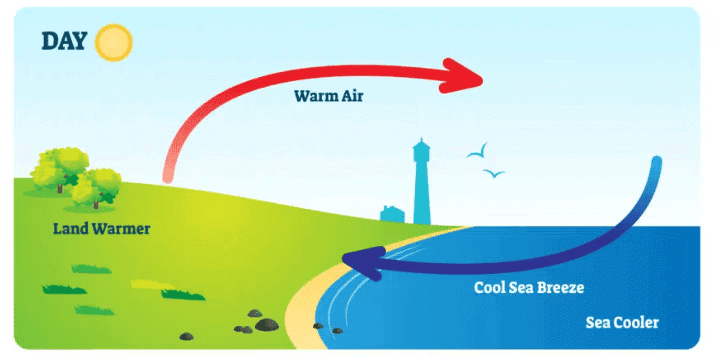 Sea Breeze
Sea Breeze
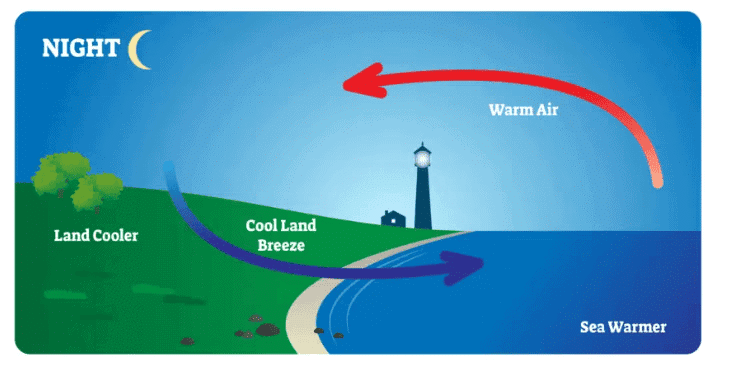 Land Breeze
Land Breeze
3. Radiation
Radiation is a way that heat can move from one place to another. It doesn’t need anything (like air, water, or solid objects) to carry it.
How Does It Work?
- Imagine the Sun. The Sun’s heat reaches us on Earth, even though there’s nothing (no air or water) between the Sun and Earth in space. This is because the heat travels by radiation.
- When you stand in front of a heater, you feel warm because of radiation. The heat travels through the air straight to your body.
Examples of Radiation:
- The Sun: We feel warm on a sunny day because the Sun radiates heat to us.
- Room Heater: When you sit near a heater, the warmth you feel is due to radiation.
- Cooling Hot Things: When you take a hot pan off the stove, it cools down by radiating heat into the air around it.
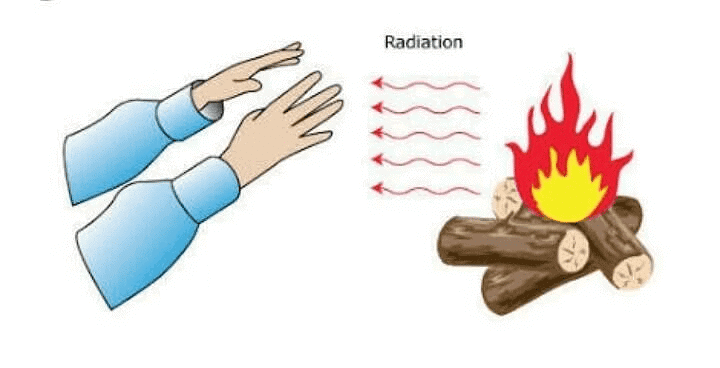 RadiationFun Fact: Your own body also gives off heat through radiation and can absorb heat from things around you.
RadiationFun Fact: Your own body also gives off heat through radiation and can absorb heat from things around you.
Radiation is just one of the ways heat can move. It’s special because it can happen even in space, where there’s no air!
Kinds of Clothes We Wear in Summer and Winter
Depending upon the season, we need to choose the clothes we wear.
Summer Clothes
 Summer Clothes
Summer Clothes
- In warm weather, it's better to wear white or light-colored clothes because they reflect heat and help keep your body cool.
- During the summer, clothes made of cotton are more comfortable as they allow the body heat to escape.
- Wearing loose clothes in hot weather helps to stay cool by allowing air to circulate beneath the fabric.
- Loose clothes are more suitable for summer compared to tight-fitting ones.
- Therefore, summer clothing should be breathable, light-colored, and loose-fitting rather than dark and tight.
Woolen Clothes Keep Us Warm in Winter
 Woolen Clothes
Woolen Clothes
- In cold weather, it's important to wear warm and thick and Dark clothes as it absorbs more heat and, therefore, we feel comfortable.
- A wool base layer helps maintain body temperature comfortably in cool or warm conditions.
- Wool clothing is good for cold weather because it keeps the body warm and shielded from cold winds.
- Wool is a great insulator and doesn't conduct heat well, allowing it to absorb moisture without feeling wet.
- The air trapped between wool fibers blocks heat from escaping the body and prevents cold air from reaching the skin.
- Woollen garments retain their shape well due to the crimp in the fibers, creating tiny air pockets that provide insulation.
- Sweaters, mufflers, cardigans, and other woolen clothes offer protection from winter.
|
90 videos|490 docs|209 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Summary: Heat - Science & Technology for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the difference between hot and cold temperatures? |  |
| 2. How does a clinical thermometer work? |  |
| 3. What are the key features of laboratory thermometers? |  |
| 4. What are the different methods of heat transfer? |  |
| 5. What types of clothes are appropriate for summer and winter? |  |















